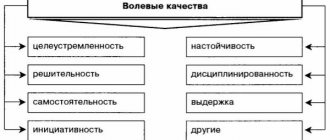
Personality is a person with a characteristic set of mental properties that determine actions and behavior that are significant for society, distinguishing him from others. Interconnected socialization and personality education transform a person-individual into a full-fledged, independent person of value to society, with individuality. Personal development is the main problem and subject of research in pedagogy, sociology, psychology, and psychiatry.
We recommend: “Problems of social education.”
Socialization concept
Socialization is the entry of an individual into the social environment through his familiarization with social norms and social values of the existing system. A socialized person is the basis of a full-fledged society, actively performing the functions assigned to him by society and the state.
Socialization is influenced by groups of factors:
- macro factors - planet, country, society, space;
- mesofactors – ethnicity, mass media, region, settlement;
- microfactors - family, society, educational influence.
Socialization of personality in psychology is the systematic entry of an individual into the existing social environment, familiarization with a complex of social relationships, and acquisition of individuality. The process is two-way: on the one hand, the assimilation of social experience and psychological attitudes, and on the other, its active reproduction. The first is the impact of the surrounding space, the environment on a person, the second is the impact of a person on the environment.
Factors
Factors that determine human socialization can be divided into 2 groups: social and socio-psychological.
The first group reflects the socio-cultural aspect of socialization and reflects the characteristics of personality development depending on the culture in which it develops, the historical factor and the ethnic characteristics of the person’s environment.
This group contains:
- Macro factors. They reflect the development of the individual in relation to his residence in large social communities (at the level of the state and national culture).
- Microfactors. They reflect the development of the individual in relation to his development and upbringing in small social communities (school, university, work team).
- Mesofactors. They reflect the socialization of the individual through his residence in medium-sized communities (regions, settlements).
Individual-personal factors highlight the role of personality traits in the process of socialization. It is necessary to take into account the subjective assimilation of influences from society and individuals who perceive the same phenomena differently. All people derive completely different experiences from objectively similar situations, so this factor must be taken into account when studying socialization.
Stages of socialization
The time stages of an individual’s inclusion in society are identified:
- primary – adaptation, from the moment of birth to the end of adolescence. The child adapts, adjusts, and assimilates the social experience accumulated by the parents;
- stage of individualization - begins with adolescence. She is characterized by the desire to stand out and express herself. The result of the stage during its normal course is the formation of stable properties, attitudes, and relationship values;
- integration – characterized by the desire to find one’s place in society. Integration is considered successful if the individual is accepted by society or the collective;
- labor stage – social maturity of a person, period of labor activity. A person assimilates accumulated experience and is able to reproduce it;
- post-work – old age. The main direction is the transfer of accumulated social experience to the next generation.
Socialization as a factor in the development of a student’s personality
In many ways, of course, socialization is important at school age, and there are a number of specific reasons for this.
Firstly, when a child just comes to school, the process of secondary socialization begins. Everything is new for him there: teachers who may have completely different thoughts and behave differently than usual parents, and a new team with whom he will also have to build competent communication.
This is new to the child, and this can be quite a difficult period for him, but it is necessary for future development. A person needs to learn to live in society outside the family and be able to communicate with a variety of people.
The teenage period, when the child is in middle and high school, is also important. During puberty, not only the body changes, but also the way of thinking. Parents, their opinions and way of life usually fade into the background, and the vacated place is taken by friends. It will be the children of the followers who will have the hardest time in this situation; they may be crushed by more authoritative individuals.
And, of course, do not forget about the “pendulum effect”. As a sign of protest, which is an inextricable companion of adolescence, the child will want something opposite than what he has in his family, and this can lead to disastrous consequences. Therefore, it is important for parents to keep their finger on the pulse and control their child.
Concept of education
Upbringing is a microfactor influencing socialization . A socialized individual conforms to norms, values, resists the negative effects of the environment, trends that inhibit or deviate the development of individuality.
There is no generally accepted definition of the term. This is due to the polysemy of the concept. It is considered as a socially oriented activity, process, impact on an individual.
Education is the directed influence on human activity of organized institutions of society, the environment, and one’s own activity. It is aimed at the formation of the necessary stable personality traits and individual qualities.
In psychological science, education is an activity that transfers social, historically accumulated experience to the next generation. It is a purposeful action on consciousness, then on behavior through the formation of life-significant attitudes, ideals, and value orientations that provide conditions for further development and preparation of the individual for life in society and work. The goal is the expected planned changes obtained under the influence of prepared actions. Results – the degree of assimilation of planned features, norms, rules. The norms that parents seek from the child become internal ideals, principles of worldview.
Important
Lack of education leads to deviations in mental development and disruption of the formation of social roles required for life in human society.
Stages of the process of personality socialization according to Erikson
Erik Erikson is a renowned developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst. According to him, there are the following stages of the socialization process:
| 1 | Infancy (from birth to one and a half years). At the earliest stage of socialization, the formation of basic trust in the world occurs. The main role in this is played by the child’s mother, and the dynamics of the development of trust depend on her. If there is too little communication with the mother, the child’s psychological development will slow down. |
| 2 | Early childhood (from 1.5 to 4 years). The child’s independence and autonomy are being formed. The child begins to walk, can already clean up his toys, etc. Parents gradually teach their child to be neat and tidy. |
| 3 | Childhood (from 4 to 6 years). During the game, the child develops a sense of enterprise and initiative, he develops his creativity, memory, logical thinking, and gains ideas about the interaction of people with each other. He is actively expanding the scope of his knowledge about the world. If you deprive a child of the opportunity to develop and socialize through play, this will be reflected in passivity, lack of initiative and lack of self-confidence in the future. |
| 4 | Junior school age (from 6 to 11 years). At this stage, socialization no longer occurs only with the participation of parents. The school introduces the child to the norms of behavior, and in communicating with classmates he receives the social experience he needs. Success or failure in studies can affect the further development of the individual. If, for example, a child is unable to study, and instead of help he receives reproaches from teachers and parents, this can lead to uncertainty, loss of interest in studies and even a feeling of inferiority. |
| 5 | Adolescence (from 11 to 20 years). At this stage, the individual is very concerned about how he appears to the people around him. This is partly due to puberty. A teenager faces the need to self-determinate and find his professional calling. |
| 6 | Youth (from 21 to 25 years old). A person is looking for a life partner, actively interacting with other people, especially within his social group. Feelings of closeness and unity with other people appear, and often the individual begins to identify himself with a social group. At the same time, due to an identity crisis, a person often feels lonely and isolated. |
| 7 | Maturity (from 25 to 55-60 years). A person invests himself in what he loves and develops a sense of identity. Interaction with other people, especially children, is of great importance. |
| 6 | Old age (from 55-60 years to death). This stage is characterized by rethinking one’s life and reflecting on the past years. A person understands that life is coming to an end. In this regard, he can distance himself from what is happening around him. |
Of course, this topic is much broader and interesting, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to talk about everything in one article. However, what has been said is already quite enough to get an idea of socialization, as well as draw certain conclusions about your development and the development of your children.
We hope you found this article helpful. We wish you success!
We also recommend reading:
- Storytelling
- Formation of self-esteem in children
- The role of art in children's development
- Social groups: signs, types, functions
- Personality criteria
- Social setting
- Eric Berne "People Who Play Games" - summary
- Formation of self-awareness
- Psychosocial development theory
- Piaget's theory of cognitive development
- “I-concept”: characteristics, features, meaning
Key words:1Self-knowledge
Education is an action aimed at the individual
Education is an indicator of development or a directed psychological, pedagogical process of the formation of important personal qualities. It depends on one’s own efforts, inclinations, inclinations, and performance, manifested in different types of activities. This explains its different effect on people living and brought up in the same conditions.
Modern methods of personality education
It performs the following functions:
- organizes influences, factors;
- creates conditions for accelerated entry of a person into society;
- helps to overcome and reduce the negative consequences of spontaneous socialization, impart a positive personal orientation and motivation.
Forms of manifestations
Socialization in psychology is a process during which a person perceives and masters social experience depending on his subjective characteristics.
Socialization can manifest itself in the following ways:
- the personality easily adapts to social conditions;
- the individual acquires values, attitudes and norms of behavior in society;
- the personality reproduces socially approved patterns of behavior in society;
- human activity is aimed at moral behavior, the development of humanistic values;
- in life a person constantly develops his personal qualities;
- the individual identifies himself with social roles;
- In the process of development, a person becomes intellectually mature and acquires the ability to analyze;
- the individual is responsible for his actions to the collective;
- the individual develops self-awareness and learns to reflect.
Types of education
There are mental, physical, and labor education. According to another classification - moral, physical, labor, aesthetic. Legal, gender, economic, and environmental are often added.
What qualities to cultivate? The basis can be considered the content proposed by the Russian teacher Karakovsky, who identified universal human values: Man, Family, Knowledge, Work, Culture, Earth, Fatherland, Peace. Acceptance of values gives rise to positive traits, moral qualities, correct needs, and actions.
Personal education is divided into models that depend on the development of society at various historical stages, the ratio of social groups, and socio-political orientation. It is enough to recall the foundations of a totalitarian and democratic society, which differ in value systems and require the formation of different personality traits.
Education takes place in two ways:
- By communicating, explaining socially significant goals, principles, values, and norms of behavior. The method eliminates the possibility of searching and making mistakes. It is based on the processing of a person’s existing motivations for understanding his relationship to reality.
- With the help of special conditions created to form cognitive interest and stimulate active socially useful activities.
The first method is traditional, the second is modern. Both of them are effective when used together and complement each other.
Goals and functions
The main goal of socialization is a person’s assimilation of norms and rules that allow him to successfully integrate into society and interact with other people, and maintain productive contact.
Functions:
- normative and regulatory;
- personal-transformational;
- value-orientation;
- information and communication;
- creative;
- function of reproduction or procreation;
- compensatory.
If at least one of the functions has not been fulfilled, socialization cannot be considered successful, because the situation may skew towards desocialization or resocialization.
Principles of harmonious development
The formation of a harmonious personality is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- formation of the consciousness of a citizen, a patriot;
- familiarization with universal human values;
- development of creativity, ability to create;
- formation of an adequate self-concept, the ability of self-realization.
Principles to be followed:
- respectful, trusting relationships between teachers and students;
- conformity with nature (taking into account age, gender, and other natural characteristics);
- cultural conformity (reliance on the cultural traditions of the people);
- humanization, aestheticization of the environment of an educational institution.
Theories
| Theory | Scientist | Idea |
| Personality development theory | Charles Cooley George Herbert Mead | “Mirror reflection” or perception of oneself through ideas about the value judgments of others |
| Psychoanalytic theories | Sigmund Freud Eric Ericson | Personality develops in stages, approaching puberty. Each stage is associated with overcoming crisis conditions. |
| Developmental theory of cognition | Jean Piaget | Personality develops gradually, during the passage of stages. At each stage, a new cognitive skill develops. |
| Moral theory | Lawrence Kohlberg | Moral development occurs through stages, each of which involves the acquisition of new cognitive abilities and the skill of understanding the feelings of others. |
According to Freud
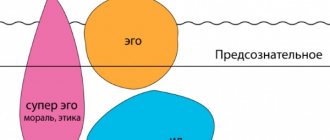
S. Freud's personality theory assumes that a person has three personal states (Id, Ego, super-Ego).
The id, “It,” is the energy that motivates a person to receive pleasure.
The ego, the “I,” acts as a controller, which, guided by reality, allows a person to regulate the Id. The superego, the “I,” is the parent within a person.
That part of the mind that evaluates behavior and strives to bring it to the standard set by the parents.
Freud also identifies 4 stages of sexual development :
- oral;
- anal;
- phallic;
- genital
At each stage, a conflict arises between the prohibitions established by the parents. And then the conflict arises with the Superego, which plays the role of a parent. Socialization occurs at the junction of these contradictions.
The connection between education and socialization
Both socialization and education are aimed at mastering moral standards. But there are differences. The first is aimed at the development of spiritual qualities, the spiritual health of society, the second is the development of personal qualities. One cannot exist without the other. If society does not strive for spiritual healing, socialization becomes a standard adaptation. A society striving for sustainable formation and development of personality ensures harmony of freedoms, rights, and responsibilities of all citizens. If the social system is maintained by coercive methods, the society cannot be called healthy.
The role of the team in the education of the individual
Socialization is influenced by upbringing and other factors. It is impossible to form a personality from scratch only through the educational influence of school; before entering an educational institution, the child is already influenced by the family and microenvironment.
Unlike socialization, which always takes place spontaneously, education is a directed process; it is considered as a mechanism, a means of controlling normal entry into social life. Its main function is to regulate the influence of the social environment and create conditions for successful development.
Socialization is a continuous process; a person interacts with its factors throughout his life. Education is discrete. It is systematic, but carried out by special organizations limited in time and space.
Management methods
Socialization in psychology is a process that plays a decisive role in personality development from an early age. Socialization management methods are most often used in education; comparison of the features of the socialization process and the possibilities of education allows us to determine the specific functions of educational activities in managing the positive socialization of the child.
Compensation for the shortcomings of primary socialization
It is known that primary socialization plays an important role in the child’s acquisition of first communication skills and his understanding of behavioral norms. The prevalence of child abuse leads to the fact that entire groups of minors become victims of unfavorable socialization conditions.
The decline of the family institution itself, experienced by adults, also has an adverse effect on the socialization of children. Therefore, education must fulfill the task of compensating for the attention that the child did not receive in the family.
It can be performed by the teacher using the following positions:
- accepting the child as he is;
- understanding the reasons for a child’s isolation;
- creating a situation of success for the child;
- inclusion of the child in activity situations where he can feel significant.
Prevention or correction of children's complexes
Children often lack self-confidence due to a feeling of failure in their activities. The child feels discomfort due to the disdainful attitude and hostility on the part of his peers, begins to consider his appearance ugly and find fault with himself.
These processes lead to the formation of complexes and learned helplessness in the child, which subsequently interferes with the realization of the personality and its socialization. Therefore, it is important to create a favorable environment for the child’s development and convince him of his own usefulness and usefulness.
Expanding children's social experience
The formation of healthy socialization can be helped by the use of a set of activities, participation in which allows the individual to broaden his horizons and acquire the experience of humane relations in interpersonal interaction.
Such events include:
- excursions to museums, art galleries;
- communication with institutions of additional education and culture;
- socially oriented activities (improvement of the architectural and spatial environment, performance of concerts in front of the population);
- meetings with representatives of different professions.
The process of personal socialization is an important phenomenon that begins to manifest itself from childhood. Psychology distinguishes forms, types and stages of socialization, knowledge of which, along with correct diagnosis, can help to promptly identify problems in interaction with society and correct them in a timely manner using methods for managing the socialization process.
Author: Anna Fleyman
Family: the emergence of personality
The family is the main agent of primary socialization , the child’s first environment, which determines the entire subsequent process of entering society.
With the help of the family, children fit into society. Parents shape the child's qualities from the early stages. The absence and lack of attention of parents contributes to the appearance in children of many psychological, social deviations and complexes that greatly disrupt normal activities in the future.
Parents create the basis of personal qualities, social status affects the status of the child, profession determines the educational and cultural level. The family lays the foundation for moral, family, and gender values.
Family can be a negative influence. Alcoholism, conflicts, divorces, social exclusion, and cruel treatment leave a serious imprint on the development of a child’s qualities that are important for society and his worldview.
The family is at the center of problems related to the physical, psychological, and social health of children. Social development also depends on other agents, the qualities of the individual, and innate traits. Therefore, children raised in a dysfunctional family do not necessarily grow up to be criminals, but can become highly moral people and full-fledged individuals.
Concept and factors of personal self-development
Self-development is constant hard work on yourself, self-improvement and the development of personal qualities. Like socialization, this process continues throughout life.
Stages of self-development
- Self-knowledge, as well as analysis of one’s own personality and activities in its most diverse manifestations.
The most important and fundamental thing for a person is to understand who she is, what her strengths are, what her weaknesses are. What should she strive for and what is missing? Without self-analysis, no development will be possible; a person simply will not understand what to do and why.
- Formation of an ideal image.
Roughly speaking, setting specific goals. A person decides what he wants to be, and then moves on to the next stage.
- Creating a self-development plan.
At this stage, a clear plan is created: a person not only understands what he wants, but also knows how to achieve it.
- Implementation of a self-development plan.
Everything here is clear from the name: a person creates a clear plan and strictly follows it in order to achieve his goal.
- Summarizing
After the goal is achieved, the person analyzes the entire process again from the very beginning.
Basic forms of self-development
- Self-affirmation. It makes it possible to express yourself fully as an individual, with the help of confirmation in one form or another.
- Self improvement. The desire to become even better in accordance with a previously created ideal image.
- Self-actualization. The desire to identify a certain potential in oneself and use it in life, as well as to use one’s capabilities to the maximum to achieve this goal.
Self-development factors
- Internal.
These include a person’s personal qualities, worldview, preferences, as well as personal interests and goals.
- External.
External factors include everything that surrounds a person: family, education system, government agencies, etc., as well as their influence on him and his development.
- Social.
Social factors include a person’s environment, its characteristics and how it affects him. Self-identification also plays an important role here, or more precisely, whether a person feels belonging to a particular social group or not.
- Hereditary.
These include any factors that are inherited and can somehow influence his life. For example, this includes a predisposition to psychiatric illnesses.
School is a social institution
The school provides children with a systematic education and provides a comprehensive educational process. Educational and educational institutions are the concentration of culture, political and moral values. The school is designed to support socialization, which begins in the family, and correct it if necessary, which is quite difficult to do. The work of an institution depends on the personal and professional qualities of teachers, educators, the microclimate of the team, forms, methods, the modernity of the educational institution, and many other factors.
Human socialization and personality education are inextricably linked processes, complementary and at the same time opposite. Without them, the full development of a person as a full-fledged member of society, who is a formed personality, is impossible.
Man as object and subject
A person acts as an object of socialization , since he is exposed to the influence of society. An individual absorbs social attitudes and values in the process of interaction with significant people.
Society, in turn, strives to turn people into “standard” and “normal” representatives of society and is actively working on this.
However, a person can also be considered as a subject of socialization . After all, the individual is not just a passive observer. During the adaptation process, he performs certain tasks, showing activity and subjectivity:
- natural-cultural tasks;
- socio-cultural tasks;
- socio-psychological tasks.