- Main factors of personality formation in psychology
- 3 phases of personality formation in psychology
- Stage-by-stage formation of personality in psychology
- Theories of personality formation in psychology
- Personality formation in domestic and foreign psychology
- Formation of personal maturity in psychology
Personality formation in psychology has been considered and studied for many years. Both domestic and foreign psychologists put forward their theories. In general, they all imply that a person goes through certain stages in the process of growing up and life.
To achieve true growth and become a mature person, you need to know about the characteristics of each stage. This knowledge will help to correct certain abilities, which is important in the modern world.
Main factors of personality formation in psychology
During the formation of personality, an individual acquires qualities that were formed in people in the process of historical development. But you need to understand that the likelihood of a person developing a particular quality depends on a number of factors.
Personality formation factors:
- Education in childhood and self-education in adulthood.
In psychology, the key role in the formation of personality is usually assigned to the family, since it is this social institution that is entrusted with the main educational function.
As a rule, harmoniously developed individuals emerge from full-fledged and prosperous families. Whereas problems unresolved in childhood complicate the further process of development of the individual. We all initially enter society and act within its framework, adhering to the principles that we borrowed from our mother and father.
Children adopt styles, patterns of behavior, roles, strategies, types of thinking, expression of emotions from those adults who occupy an important place in their lives. From the parents, the child unconsciously inherits values and ideals, positive and negative qualities. So, the latter may include anxiety or suspiciousness.
Over time, the instructions once heard from parents are perceived as an inner voice. Moral qualities are gradually formed: conscience, honor, morality, but you need to understand that this does not always happen. Each person uses the knowledge acquired in childhood and develops his own ideas about behavior that is acceptable from a social point of view.
- Genetics.
There are no two people on Earth with an absolutely identical set of genes. Some component of individuality is determined genetically, so newborns are able to express basic emotions, since their temperament has already been determined.
When it comes to genetics, the role of family in shaping personality is just as important as in the process of education. After all, some mental illnesses are transmitted between relatives. Whereas the reference groups of relatives, friends, colleagues and other people from the close environment exert a social influence on the individual.
- Life experience.
Any event is reflected in a person’s inner world; the most serious marks are left by significant incidents. Often, individual experiences influence the future course of life. The fact is that in the process of formation and development of personality in psychology, the development of willpower, character, abilities, and the search for motivation occur.
- Mentality and culture.
The mentality or “character of a people” largely depends on the environment and climate in which a group of people usually lives. Thus, southerners are more active, temperamental, and prone to expressing emotions than residents of northern regions.
Culture, moral values, and socially accepted rules are instilled from birth and lead to the formation of personality. The behavior of representatives of some cultures is more cheeky; such people do not hide their natural feelings, while others have to restrain themselves and strictly follow the established rules of behavior.
All of these factors influence a person every time he comes into contact with an unusual sociocultural environment. In fact, personality formation represents changes as a result of entering a new social community. Individuality can manifest itself differently in a particular environment - it all depends on how successfully the individual overcomes the three phases of development.
Environment
Determining exactly what is the main factor for personality development is problematic. But the environment and social environment in which a child grows up shapes his habits and views. Changing attitudes that have been instilled since childhood is the most difficult thing to do.
A person is predominantly surrounded by people of the same social status, religion, and mentality. We choose this natural soft segregation on our own, because it is easier to communicate and develop with “our own kind.” Read about relationships in this section. The environment can change under the influence of external circumstances - personal development will also turn in the other direction. It is human nature to adapt to their environment; only a few strive to stand out from it. A few of these units form their own environment and become people capable of changing the world.
The influence of the social environment on development can be seen in the biography of any historically famous person: Mikhail Lomonosov, Adolf Hitler, Steve Jobs and others. But this influence also needs to be considered in conjunction with other circumstances.
Stage-by-stage formation of personality in psychology
It is customary to distinguish the following stages of personality formation in psychology:
- The desire to communicate or, on the contrary, to withdraw from people, which begins in the first year of life. Here the basis is contacts with adults, built on emotions.
- Gaining independence and confidence manifests itself in a child by the age of three through objective activities that allow him to get to know the things around the baby.
- Active exploration of the world, thanks to the child’s natural curiosity. At this stage, which lasts up to 13 years, communication and work skills develop. They train through role-playing games during their studies.
- Puberty, the choice of life values, and profession should be completed by the age of 20. Intimate communication and educational and professional activities play a key role here.
- Implementation of plans, realization of one's own capabilities, enjoying the results of work, raising children - lasts up to 60 years.
- The final stage is considered to be deepening into creativity, analysis and rethinking of life and actions.
It turns out that personality and its formation are not considered in psychology as a static structure. On the contrary, it is believed that an individual goes through a number of stages of development throughout his life.
Culture and art
The role of art in the formation of personality is also important and is the basis for the formation of a person as an individual. Understanding the world around us, studying history, immersing ourselves in art - all this helps to develop beyond the basic needs for food and socialization. Art is not the determining factor; the role of society in creating individuality is much more important. But it helps:
- think more broadly and critically;
- protect your “I” from mass views;
- find harmony between yourself and the world around you;
- express yourself;
- understand your inner world;
- destroy stereotypes, attitudes, social constructs.
Without immersion in culture and art, it is unlikely that you will be able to expand the boundaries of your own consciousness, go beyond the narrow boundaries of upbringing, and step over the pressure of society.
Theories of personality formation in psychology
Different areas of psychology consider the process of personality formation in their own way. There are psychodynamic, humanistic theories, trait theory, social learning theory, etc.
A number of theories have become the result of experiments, while others remain untested in practice. It must be understood that some teachings do not consider human life from birth to death, since it is believed that personality formation occurs in the early years or before reaching adulthood.
The theory of the American psychologist Erik Erikson is considered to be the most holistic, including a number of positions on this issue. He argued that personality is formed according to the epigenetic principle, that is, throughout a person’s life, he goes through eight stages of development. Moreover, such stages are determined genetically and are not influenced by social factors or even the individual himself.
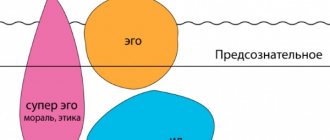
In psychoanalysis, the formation of personality is considered to be the adaptation to life in society of the natural, biological essence of a person. Namely: it is important for an individual to learn to satisfy his needs in a form that will not be rejected by society, and to develop protective mechanisms of the psyche.
A woman's behavior in relationships according to her sun sign
The article talks about what a woman’s behavior in a relationship can be according to her sun sign
Read >
The humanistic theories of A. Maslow and K. Rogers contradict the position of psychoanalysis and call the basis for personality formation the emergence of a person’s skills of self-expression and self-improvement. Humanistic theories are based on the idea of self-actualization, which is considered the key need of the individual. Human development occurs not through instinctive needs, but through higher spiritual and social values.
The formation of personality in psychology is considered as a person’s search for his “I”, the disclosure of internal potential. As a result, we can talk about an active, creative, spontaneous, honest individual, capable of being responsible, free from thought patterns, wise, ready to accept himself and others with all their shortcomings.
Among the components of personality, it is customary to distinguish the following properties:
- abilities, that is, individual qualities on which the possibility of achieving success in any activity depends;
- temperament or innate characteristics of higher nervous activity that determine human reactions in society;
- character is a set of cultivated qualities on the basis of which behavior towards oneself and others is established;
- the will or ability to achieve a goal;
- emotions, that is, emotional disturbances, experiences;
- motives, namely incentives that encourage a person to act;
- attitudes or beliefs, position on a certain issue.
Similar articles
Gemini man in marriage: rebellious duplicity or double supply of love Anastasia Grokhotova
•January 29, 3:41
The influence of elemental energies on a person’s personality: Fire, Earth, Air, Water Natalya Rascheskova •January 29, 3:41
Sagittarius child: personality formation Anastasia Grokhotova •January 29, 3:41
Scorpio child: development of a harmonious personality Anastasia Grokhotova •January 29, 3:41
Houses in horary astrology: meaning in various areas Elena Tarim •January 29, 3:41
Genetics and biology
The process of personality formation begins in the womb. It is not worth assuming that if you read Plato to an unborn child, he will grow up to be a thinker. At the stage of biological formation, genetic factors are laid down. Those diseases and pathologies that are transmitted to the baby from parents.
Genetic and biological factors influencing the formation of personality:
- Biochemical features: mental illness, material metabolism.
- Hereditary diseases.
- The lifestyle that the parents led while carrying the child: even the stress of the mother can affect the biochemical and physical development of the fetus.
- Anatomical features.
Genetics and biology are the base from which it all begins. Depending on the environment, upbringing and a number of other factors, a person will behave differently in different conditions. The personality of a disabled person who grows up in the center of a large city will be different from that of a person with the same condition who was born in a village in a newly developing country.
Personality formation in domestic and foreign psychology
From the point of view of considering activity and personality formation in psychology, the theory of E. Erikson is interesting. It is believed that a person goes through eight stages, in each of which there is a conflict between the opposing forces of his personality. A successful outcome entails the development or formation of new traits. In the opposite situation, neurosis and maladjustment are observed.
Personality formation in psychology according to E. Erikson involves stages where the following contradictions arise:
- trust and distrust in the world around us - lasts from birth to one year;
- independence and shame, doubts – up to 3 years;
- initiative and guilt – in the period from 4 to 5 years;
- hard work and feelings of inferiority – 6–11 years;
- awareness of belonging to a certain gender and lack of understanding of its characteristic behavior - from 12 to 18 years;
- the desire for intimate relationships and a feeling of isolation from others - the stage of early adulthood;
- vital activity and focus on one’s problems, needs, interests - observed during middle adulthood;
- a feeling of fullness of life and despair - late adulthood.
A man's behavior in relationships according to his solar zodiac sign
From the article you will learn what a man’s behavior in a relationship can be according to his sun sign
Read >
Russian psychologist V.I. Slobodchikov considered the formation of personality from the point of view of the development of subjectivity in relation to a person’s own behavior and assumed the presence of the following stages:
- Revival (up to a year).
During this period, the child gets acquainted with his body, becomes aware of it, which manifests itself as motor, sensory actions, and communication.
- Animation (from 11 months to 6.5 years).
A person’s self-determination in the world begins - the baby learns to walk, use objects, and gradually masters cultural skills and abilities. By the age of three, he understands his desires and capabilities, so the wording “I myself” appears in his speech.
- Personalization (from 5.5 years to 13–18 years).
Now a person begins to consider himself a real or potential creator of his own life. Communicating with peers and elders, he builds his identity and gradually realizes that he himself is responsible for his future.
- Individualization (from 17–21 years old to 31–42 years old).
There is an appropriation and individualization of values existing in society based on one’s own worldview and position. An individual struggles with group restrictions, other people’s assessments, moves away from stereotypes, other people’s opinions, and pressure. At this stage, he learns to accept or refuse what the world gives him.
- Universalization (from 39–45 years old and onwards).
Here the personality goes beyond individuality to the level of existentiality. Now a person perceives himself as a component of all humanity in the context of world history.
Personality formation is directly related to age-related changes. But the indicated periods give a large time dispersion, and the older the person, the wider the dispersion of personal development - popularly this is usually characterized as “precocious” or, on the contrary, “stuck in development.” Although in fact, there is no stuckness, there are simply differences between physical and personal growth.
Also, personality development is often regarded as a change in a person’s individual psychological space, which includes:
- body;
- surrounding significant objects;
- habits;
- relationships, connections;
- values.
You need to understand that the listed components do not appear immediately, but in the process of physical maturation - all elements cannot be found in a child. In order for a person to develop favorably, the components listed above must remain intact.
Upbringing
The basis for the formation of the entire personality is education in childhood. Later, a person begins to engage in self-education and self-development, but it all begins from childhood. Parents and other older relatives are involved in upbringing. Comrades, especially older ones, complete the picture of education. Kindergarten teachers, school teachers, and instructors in sections and clubs make their contribution.
Personality is a puzzle made up of various pieces. Even the most detailed psychoanalysis will not be able to determine in the future what circumstance influenced this or that character trait of an adult member of society. Education in childhood provides a pattern of behavior, an impetus for further self-development (or degradation, depending on the environment and other factors). The way parents influence the formation of personality largely determines future character, aspirations, psychological trauma, and other circumstances.
Children who strive to be like their elders in everything can copy from adults to form their “I”:
- manner of behavior;
- gender roles;
- type of thinking;
- different qualities of parents.
This copying in the future turns into installations. The positive ones are worth keeping. Negative ones can be dealt with independently or with the participation of a psychologist.
How do they affect a person?
Genes
The following characteristics are inherited:
- physical characteristics of a person - facial features, physique, eye, hair and skin color;
- physiological data - blood type, time of maturation of the body, metabolic characteristics, blood pressure level;
- features of the central nervous system - the structure of the cerebral cortex, vision, hearing, smell, etc.;
- predisposition to hereditary diseases - schizophrenia, blood diseases, diabetes and others.
Also, heredity determines the inclinations of a person - that is, his predisposition to one or another activity - ability to mathematics, music, drawing, certain sports, etc.
Society, environment or group
Man is a social being. The society with which he interacts influences his life, interests, and goals.
However, a person himself can also influence the society in which he lives. At the same time, the impact of the group on the individual cannot be called unequivocally negative or positive, since both options occur.
Positive impact of a group on a person:
- Interpersonal relationships in a group instill in a person norms of social behavior and also form life values. For example, by watching classmates, a student learns to remain quiet in class, and participation in a sports club instills a preference for a healthy lifestyle.
- develop better in a group . A child who attended preschool institutions finds a common language with peers faster than one who was raised in the family circle during preschool age.
- By communicating in a group of people, a person receives an assessment of his actions, which ultimately allows him to form an objective opinion about himself. For example, the admiration of members of a football team for their ability to handle the ball evokes positive emotions in a person, contributing to greater motivation in training.
However, society can also have a negative impact on a person:
- In society, the ideas of gifted creative individuals may be rejected .
The most famous example is the persecution and execution of Giordano Bruno for dissent. - A person can agree with the opinion of the group, having opposing views, and consciously go into internal conflict . Often such influence is exerted, for example, when committing group crimes.
There are also the following phenomena of group influence on a person, which can also be positive and negative:
- Social facilitation - in the presence of a group of people, an individual will be better able to perform tasks that are familiar to him.
- Social loafing is a subjective decrease in personal responsibility and, as a result, an individual exerts less effort to achieve a goal when a group is working on a single task.
- Deindividuation is a weakening of self-awareness in conditions where it is not customary for a group to focus on the individual.
At the same time, there may be a fear of public evaluation of one’s actions. - Group polarization is a phenomenon in which in a group of like-minded people there is a strengthening of pre-existing tendencies, expressed in a much more categorical form than in individual individuals.
- Groupthink is a phenomenon in which achieving consensus and group cohesion become more important when solving any problems by a group of people, to the detriment of the adequacy of the method of solving the problem.
- Minority influence. Disproportional influence of one charismatic group member over the majority of group members.
Social development of personality
Every day a person is forced to be in society, thus maintaining social connections. Every day there is communication with different people under different circumstances, which affects the individual. The social component of life is reflected in mental development, the formation of spiritual values and, most importantly, a person’s intelligence.
Consciousness and self-awareness must be determined in a person. As an individual, you must have the ability to think and make decisions independently. If this is reflected in a person, then he will be considered a person.
Society can define the personality of a person who is able to comprehend and apply existing social experience.
On the other hand, it is necessary to contribute to the development of this system, namely in the sphere of spirituality and material values. This requires personal growth and a constant desire for self-development and self-improvement.
Since ancient times, there have been debates between philosophers and scientists on the issues and features of personality formation. However, it is worth recognizing that this process has not yet been sufficiently understood and studied.
The formation of a person can be described as a process that cannot be predicted in advance. It is spontaneous and uncontrollable. There are opinions that it is impossible to change a person’s personality because this process is determined by fate and innate characteristics. But there are also opposing opinions.
Development of a child's personality
Let’s figure out at what age the process of developing a child’s personality occurs. If we take into account some factors, it becomes clear that a child is not capable of being an individual before the age of 2. Usually, this happens after the baby learns to speak, share opinions with others, and think about his own actions.
More often, psychologists note that the age of three is a significant point when a child develops self-awareness. But by the age of 4-5, he is fully aware of himself as a person who has some characteristics and values. It is important for parents to understand the process of developing a child’s personality, as it is related to the approach to parenting.
The requests that can be made of him depend on how deeply the child understands himself as a person. To properly raise a child, you need to have an understanding of the characteristic signs of psychology at various stages of development. Children under one year old do not know how to control their emotions, so it is pointless to explain to them that crying on the street is shameful and ugly. They are still entirely focused on immediate needs. At this stage, it is important for parents to understand that this is normal child behavior and they do not need to be punished for it.
Another situation: the baby is one year and 3 months old. His parents consider him an adult, because he can walk and speak some words, go to the potty. In general, he is already a little adapted to controlling emotions. After all, after a serious conversation, he will stop screaming, he knows how to be affectionate if he needs attention. But the baby uses the ability to control himself during such a period selectively when it turns out to be important for him personally. And here again mom and dad consider him spoiled.
And this behavior is natural at this time. Having initial abilities for self-control, the baby does not yet have the required motivation to limit himself. He doesn’t understand where the positive is and where the negative is. A certain moral maturity appears after 2 years, and sometimes by 3 years. It is associated with serious developments in social experience and better mastery of speech.
It turns out that, in accordance with current ideas about the development of personality, the upbringing of babies up to one year is based only on the organization of suitable conditions for comprehensive development. After a year, the child needs to be introduced to some of the norms of society, but do not immediately demand compliance with them. After 2 years of age, it is worth appealing to moral standards more persistently, but after 3 years, you can demand compliance with the rules. If at 3.5-4 years old a child constantly offends his peers and spoils toys, then this is evidence of gaps in upbringing or psychological problems.