Causes of forest fire
There are several reasons why a fire occurs in a forest:
- lightning striking a dry tree;
- unextinguished fire;
- a cigarette butt thrown on dry grass;
- clearing the area of dead wood;
- abandoned matches and flammable objects;
- natural gas or oil leak.
Natural causes of forest fires are less common; careless handling of fire is more common. It is necessary to know the basic actions in case of a forest fire and preventive measures.
Signs of a forest fire
For every person living near a forest area, it is important to know the signs of a fire in the forest. Actions in a wildfire area will depend on the classification of the fire.
Forest fire classification:
- grassroots;
- grassroots sustainable;
- underground;
- riding
Ground fire is more common; dry grass and litter burn. The spread of fire is up to 3 meters per minute, the height of the fire is up to 1.5 meters. The fire jumps from one place to another, the root system of the trees is not disturbed. Such a fire can be extinguished quickly and occurs in the spring, when the soil is still moist.
A ground fire that occurs during a drought causes irreparable damage to trees, the soil and roots burn out, and some trees fall out of the ground. The soil burns to a depth of 15 cm. In the presence of dry dead wood, it spreads quickly and can develop into raised wood. Fires are difficult to extinguish because they occur in hard-to-reach places. The main actions in case of a forest fire will be carried out with the help of aviation.
An underground fire occurs in a peat layer up to 50 cm deep. It appears independently or as a consequence of a ground fire. In this case, the forest cannot be saved, because the soil burns deeply. The smoke and substances released during combustion are dangerous to humans. Externally it may appear as a slight smoldering, but inside the peat burns out. An animal that falls into a burning peat pit will not survive.
A crown fire spreads up to 100 meters per minute. Mounted fire is found in coniferous forests and closely planted trees. Fire on the crown of trees spreads faster than on the bottom. Such a fire is dependent on wind and rain.
If you smell burning for a long time and see the anxiety of your pets, then perhaps a fire has broken out in the forest somewhere nearby.
Actions of the population in the event of a natural fire
The culprit of forest fires is most often humans. Most fires occur as a result of agricultural fires, burning garbage, in picnic areas, picking mushrooms and berries, during hunting, from a thrown burning match, or an unextinguished cigarette. A fire in the forest that is not completely extinguished causes major subsequent disasters.
The Civil Defense Department of the city of Vladimir reminds that during a fire danger period, being in the forest is prohibited:
— make fires, use barbecues and other cooking equipment;
- smoke, throw away burning matches, cigarette butts, shake out burning ash from smoking pipes;
— shoot weapons, use pyrotechnic products;
- leave cleaning material oiled or soaked in gasoline, kerosene or other flammable substances in the forest;
— fill the tanks of operating internal combustion engines with fuel, take out equipment for work with a faulty engine power supply system, and also smoke or use open fire near vehicles being refueled;
- burn grass and stubble in the fields.
Persons guilty of violating fire safety rules, depending on the nature of the violations and their consequences, bear disciplinary, administrative or criminal liability.
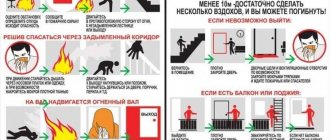
What to do if you find yourself in a forest fire area? First of all, go to a safe place. Your main task is to save your own life and maintain your health. If the fire is grassroots or local, you can try to extinguish the flame yourself: knock it down by covering it with branches of deciduous trees, pouring water, throwing wet soil, trampling it with your feet. When extinguishing a fire, act carefully, do not go far from roads and clearings, do not lose sight of other participants in the extinguishing, maintain visual and audio contact with them.
If you do not have the ability to localize and extinguish the fire on your own:
— if possible, contact rescuers by mobile phone;
- immediately warn everyone nearby to leave the danger zone;
— organize people to go out onto a road or clearing, a wide clearing, to the bank of a river or reservoir, or into a field. Immediately agree that you are walking in a group and do not disperse to each side. Do not run uphill from fire: fire always moves uphill faster than a person. Avoid depressions in the soil, especially narrow hollows. Do not climb trees, this will not help you escape from the fire;
— leave the danger zone quickly, being perpendicular to the direction of fire movement;
- if it is impossible to escape from a fire, enter a body of water if it is nearby, or cover yourself with wet clothes;
- once you find yourself in an open space or clearing, breathe, bending down to the ground, there the air is less smoky;
— cover your mouth and nose with a cotton-gauze bandage or cloth;
- after leaving the fire zone, report the location, size and nature of the fire to the fire service or forestry department.
Residents of populated areas located in an area exposed to the danger of wildfires must, if possible, monitor the fire situation in the vicinity of the populated area, prevent themselves and restrain others from actions that contribute to the occurrence of a natural fire. Listen carefully to information on television and radio channels about the fire situation.
Having heard a signal (received information) about the danger of a natural fire, you MUST:
- listen carefully to information about the emergency situation and instructions on the procedure to act.
— navigate the area, determine dangerous directions and the approximate distance of the fire front;
- do not use your phone unnecessarily so that it is free to communicate with you.
— if possible, check with local authorities about the gathering place for evacuation, if it has not been determined in advance, and prepare for it;
— prepare documents, clothes, necessary things, a supply of food for several days, medicines, respiratory protection. If there is smoke, immediately put on personal respiratory protection; in their absence, be sure to use cotton-gauze bandages, improvised fabric products moistened with water, etc. etc.;
— place documents and valuables in a safe, accessible place. If possible, protect existing explosive and fire hazardous substances and materials (fuel containers, gas cylinders, etc.) from fire;
- move pets to a safe place, if this has not been done in advance; if it is impossible to drive away, do not leave pets on a leash or in enclosed spaces.
If there is an immediate danger of a natural fire, you MUST:
- before leaving the house, turn off the electricity and gas supply, extinguish the fire in the stoves, close the windows and doors;
— take prepared documents, wearable things and food, go along a predetermined (shortest) safe route to the designated collection point for evacuation, and along the way provide assistance to the disabled, children and the elderly;
— at the collection point, report your arrival, listen carefully to firefighters and rescuers, and act on their instructions;
— do not refuse the offered help and evacuation!
If it was not possible to leave the danger zone, in case of loss of orientation, impossibility of exiting to the designated point, it is necessary to go outside the populated area in the direction opposite to the approach of the fire and smoke front, then moving in the direction of the wind, moving away from the edge of the fire perpendicular to it, along clearings , roads, banks of streams, clearings, move away from the fire and, if possible, contact rescuers, carefully monitor the surrounding area and situation and remain in place until help arrives.
If you are leaving a dangerous zone in personal transport, move only along roads in a safe direction; if the car breaks down or gets stuck, leave it, find a safe place for yourself and your fellow travelers and call for help.
In any situation, do not lose your composure, do not panic and remember: the uniform number for firefighters and rescuers is “01” (from a landline), “101” (from a mobile phone).
The single number for calling emergency services is “112”
Actions in case of forest fire
Actions in case of a forest fire should be as follows:
- do not panic;
- determine which way the wind is blowing;
- find out fire spread and speed;
- it is necessary to walk along the spread of the fire;
- You cannot run in the direction of the fire’s advance, you may end up in a closed ring;
- bend down to the ground if you feel short of air;
- breathe through a wet rag;
- if you see a body of water nearby, then take a dip in it and cover yourself with wet clothes;
- warn others about the danger, help get out of the fire zone;
- Call the Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations at 112.
When putting out a fire, remember your own safety, stay close to the road or body of water.
Types of crown fires
There are two types of crown fires:
- Runaway, which spreads much faster than grassroots. This type of crown fire is the most dangerous, since the fire engulfs the crowns and quickly moves from one tree to another, changing its direction. The main negative factor is the wind. Spreading at a speed of 250-300 m/min, the fire covers large areas in a short period of time and descends, creating conditions for the development of a ground fire.
- Stable. It moves simultaneously with the lower edge, therefore it is considered more predictable. The fire does not spread through the crowns on its own; it evenly covers the entire height of the tree, burning out the ground cover as well. Despite its predictability, a persistent fire is considered a general disaster, after which only charred trunks and large branches remain.
Roof fires are divided according to the speed of fire spread:
- weak – up to 3 m/s;
- medium – up to 100 m/s;
- strong – over 100 m/s.
By burn area:
- 0.1-2 Ha – normal fire;
- up to 20 hectares – small fire;
- 20-200 Ha – medium scale;
- up to 2000 Ha – large;
- over 2000 hectares – a disaster.
The average burnout time for an area of 500 hectares during a medium-speed crown fire is 10-15 days.
Rules for extinguishing a small fire
Actions during a forest fire will depend on the size of the fire. To prevent fire, remember the rules of behavior in the forest during the fire season. Forbidden:
- light an open fire;
- throw away cigarette butts and unextinguished matches;
- use flammable items;
- leave bottles and glass; under certain conditions, glass can act as a lens;
- use flammable liquid, throw away oily rags or bottles after using fuel;
- burn dry grass in the forest, fields, and populated areas.
The actions of the population in case of a small-area forest fire must be deliberate. It is necessary to start extinguishing quickly. The fire can be trampled or covered with earth. In case of a high fire, use branches of deciduous trees to knock down the fire or a non-flammable liquid, water from the nearest body of water. Make sure the fire is extinguished and will not re-ignite after you leave.
Safety measures and rules of behavior in the forest:
- Light a fire only in designated areas.
- If there are no such places, then prepare the site for its cultivation yourself, clearing it of grass, leaves and branches down to the ground.
- The fire must be completely extinguished before leaving the site. Leave the resting place only after making sure that not a single log or branch is smoldering anymore.
- In the event of a dangerous fire, extinguish the fire with water or, by covering it with earth, you can knock out the fire with branches of deciduous trees.
What to do when a fire approaches a populated area
Human actions in a forest fire zone that is approaching a populated area consist of mass evacuation of residents. You should exit without getting into the path of the fire. First of all, those who need help are taken out; it is advisable to take documents and valuables with them.
You need to walk along roads or along rivers. Use wet rags and damp clothing to protect your respiratory system in case of heavy smoke caused by a forest fire. A person’s actions must be aimed at saving his own life and the lives of those around him. You can try to save some things by hiding them in stone buildings, in a cellar or hole in the ground. If there is nowhere to evacuate, then it is necessary to wait out the disaster in large open areas or in stone buildings with a high impermeability threshold.
Security measures
A memo on what to do in the event of a forest fire describes the rules of conduct for people caught in the fire zone until rescuers arrive.
In case of heavy smoke
The rules require protecting the respiratory system from exposure to harmful combustion products. To do this, you need to wear a respirator, a damp cotton-gauze bandage, and if they are missing, breathe through a cloth soaked in water. If there is a child nearby, take care of yourself first, and then protect his breathing.
Important! The greatest amount of oxygen accumulates near the surface of the earth. Therefore, when moving, it is recommended to bend down as low as possible.
While in the forest
If a wave of fire is approaching you, you should throw away everything unnecessary. When you have an emergency supply, it is better to take it with you. You must try to overcome the fire zone in the direction against the wind, covering your head and face with wet clothes.
Instructions for rescue from a forest fire.
If this is not possible, try to find a swamp, an island, a sandbank, a cave, a rock and hide there. Find shelter away from falling trees.
If you manage to find a pond, lie down in it, but make sure that there are no thickets of reeds nearby.
If you have a sleeping bag, wrap yourself entirely in it and lower yourself onto the shallows. When the fire is already close, you need to periodically turn over, if possible wetting your clothes and face mask.
What is forbidden to do
The rules of conduct in case of a fire in the forest clearly state that people are not allowed to take part in localizing a fire:
- wearing clothes made of synthetic fabric or high heels;
- who have taken alcohol or drugs based on it in the last 24 hours;
- those with poor health, children or old age.
Actions to take when fire approaches the house
Actions in the event of a forest fire that is approaching the house should be aimed at evacuating people and calling the fire department. Persons who cannot provide assistance in extinguishing the fire are required to be evacuated; these are children and the elderly. Remove animals from the house and, if possible, take them to a safe place. Close the house, fill all containers with water, both inside and outside the house. Tell your friends that you are staying in the house.
Remove synthetic clothing and replace it with thick cotton clothing. Prepare a face scarf and gloves to protect your hands. There should be wet blankets or pieces of fabric in the house; they can be used for small fires.
Close all doors inside the house tightly to prevent the spread of fire. Remove unnecessary items from the window sills, move the furniture to the center of the room, place valuables in the basement and close it. Monitor the area to detect the first signs of fire or smoke.
Call the fire department in a timely manner. This can be done from a landline phone 01, or using cellular communication 112, even with a negative balance.
Ground fires
A few words about ground fire. It does not spread as quickly as the mounted one. In the thicket of the forest between the tree trunks there is no strong wind. Therefore, the fire spreads from tree to tree until the previous one reaches maximum fire activity, so that the flames, high temperatures and thermal energy do not set fire to the neighboring one. Therefore, we can say that ground fires are ordinary forest fires that cover the moss and grass cover of the earth, as well as low-height vegetation. This is the first stage of a forest disaster, which gradually turns into the upper stage.
So, the main distinguishing characteristic of a ground fire is its spread through the lower layer of vegetation. Like the horseman, it is divided into two types: fluent and stable. In the first case, it is rapid spread over dry fallen leaves. This happens in the spring, when the greenery has not yet emerged from under the soil.
The second type manifests itself in the summer during the dry season. Moss, lichens, fallen leaves, dried by the sun, burn quickly. Such a fire lingers in one place for a long time, spreading throughout the entire perimeter. In this case, the soil layer burns deeply. Fallen nuts and seeds remain under the fire, so they will not germinate next year. This also applies to trees, the trunks of which, together with the bark, burn through the core.
Ground fire
By the way, dead wood combustion types are a resistant variety. In fact, the fire is fueled by forest debris, of which there is always a lot. If we talk about the speed of spread of the grassroots type, then here, as in the case of the top type, there are three positions:
- Weak – up to 1 m/s.
- Average – 1-3 m/s.
- Strong – more than 3 m/s.
What happens during a ground fire? Basically, grass, moss and other vegetation of small height burn. Therefore, such fires can be extinguished effectively even with brooms and branches. The main thing is to meet them halfway, knocking out the flames with these simple devices.
An effective option is to dig a trench along the front. Sometimes it will be enough to remove the turf or remove dead wood.
This method is often used; it is used only in calm conditions. They dig a trench and create a fire zone between it and the fire. This is essentially a controlled fire option. An effective way to extinguish a fire at any stage.
What is the danger of ground fires
The biggest danger is the transition to the riding stage. This should not be allowed under any circumstances. Although this often happens if there is a strong wind.
The second danger is the death of all life on earth. This applies to both plants and animals. If the fire cannot be extinguished in time, then the ecosystem in the zone will not soon come to its senses. Vacant areas covered with black ash remain empty for a long time.
Ground fire burns everything deep in the ground
The third danger is thick smoke and toxic substances from burning vegetation. They spread over large areas, which reduces people's well-being. Statistics show that people often die from poisoning from the combustion products of forests.