Each person comes into this world with his own purpose. This is what he should strive for. Only in this case does a person’s life gain meaning.
All dreams are meaningless, all plans will be covered with cobwebs, goals will not be achieved if they are not secured with actions. Is it possible to get to the right place with just a map, but without moving? Can the strictest and fairest law stop a criminal who has only heard of it? Is knowledge alone enough to become successful? Only action can lead to a person’s goal, only action will prevent crime, and it also affects our whole life. And what motivates a person to act is called “motivation”.
What is motivation
Psychology views motivation from the perspective of a need for something. Need, the feeling of discomfort associated with it, depends entirely on the situation - environment, mood. The state of “yesterday I wanted to, but today I don’t really want to” hardly motivates action.
Motivation is the thought of how good it would be if. In fact, it's a dream, but not every dream motivates you to get off the couch. This is the dream that makes her achieve it. Turns a person into a scientist who has created a hypothesis of his own satisfaction if certain conditions are achieved.
Any real scientist begins to think through a plan of action, conduct experiments, and move towards the goal step by step.
The starting point in motivation becomes internal discomfort, the discrepancy between the real and the desired. Motivation is what forces two factors to be correlated:
- I can or I can’t (opportunities);
- I want or don’t want (intentions).
A person’s capabilities depend on abilities, equipment and knowledge – competencies. This is how motivation can stimulate the internal development of abilities, learning, to lead to a goal. However, the absence of one of the elements will lead to the fact that volitional effort will not be formed, and lack of will will lead to disappointment and stress.
How motivation works: moving towards a goal
The main motivators that push a person to action are the desire to achieve something and the fear of losing something. The first includes all activities aimed at various achievements (purchase, search, victory), and the second includes the desire to avoid losses (time, finances, opportunities).
All others are derivatives of these 2 factors. A person commits all his actions because of one of these incentives.
For one person, going to the gym with a lot of people is a positive aspect, because there is an opportunity for communication, but for another, it is a negative aspect, because a large crowd of people makes him feel uncomfortable.
Main characteristics
Motivation consists of two parts:
- a person’s internal psychological attitude towards action or inaction;
- the ability to effectively correlate opportunities and abilities to achieve a goal.
It comes to a person in the form of specific experiences that are associated with positive emotions from achieving an object or realizing an idea. But the motive is realized only when it coincides with the ideals and cultural values of a person and society at a given moment in time.
The motif has several characteristics:
- gives energy for activity;
- directs actions to achieve goals;
- causes selectivity of attention;
- prepares for typical reaction scenarios.
The motive also necessarily includes the activity itself to achieve the goal. Motivation is not only how much a person wants to achieve a goal, but how much effort he is willing to put into it.
The struggle of motives
As already mentioned, a person is simultaneously driven by many different motives. And not all of them are equivalent and equally directed. Here's a classic example. A person sets an alarm clock at night, intending to get up early the next morning - for example, to go for a morning run. But the morning comes, the alarm clock rings, and this person no longer wants to get up. He finds himself in a situation where he needs to make a specific decision, and it depends on what motives prevail in him at the moment. Here we come across what is called willpower.
This example is not particularly critical, but there are situations in life when a person has to make very difficult choices. Any of the options for action is motivated in a certain way, and this brings discomfort and even real torment. So, in some cases we are faced with a choice - to save ourselves from trouble or to save our loved ones at the cost of our own lives. Such internal conflicts can lead to the development of depression or neurosis.
What should you do if you need to make such a choice? Experts advise not to give in to emotions and carefully consider all options if possible. There must be a rational approach here; you need to weigh all the pros and cons, the benefits and deprivations that the choice you make will bring. And above all, one should be guided by socially significant motives. After all, it often happens that we achieve our goal by “walking over our heads,” as a result of which friends, close people, and relatives turn away from us, as a result, we lose more than we gain.
A person is not aware of all his motives, but control of his motivational sphere is available to us. It is necessary to create a hierarchy of needs and motivations for yourself and focus on the most significant and important of them. Such a hierarchy will be associated primarily with social values.
The “pyramid of needs” compiled by the American psychologist Abraham Maslow is widely known. This system distributes needs into “lower” ones, which make humans related to other animals, and “higher” ones, which are unique to humans. It is curious that the lower needs are associated with the individual survival of the organism, while the higher ones pursue social goals. The highest needs are the need to understand one’s connection with the entire universe, and not just with one’s small group or human society in general.
Having certain needs, a person acquires the motivations associated with them. And they motivate him to do certain things. It happens that an activity seems “higher”, but in reality a person is guided by “lower” motives. So, a musician can create fashionable but primitive music just to feed himself (and generally make money). It happens that “for bread” people create real masterpieces. In other cases, setting “lower” goals is only an intermediate step, while in reality the person is motivated by higher considerations. Thus, the father of the family can take care of his health in order to have the strength to provide for his wife and children.
Types of motivation
A person goes towards something or leaves something.
In the first case, it is a positive motivation – movement “towards a goal”, in the second – a negative one – “from dissatisfaction (fear/poverty/poor self-esteem). But usually positive and negative motives are combined: if I quit smoking, I will become healthier, I will be able to play sports and earn more. “I’ll quit” in the context of a smoker is a negative attitude, but the ultimate goal is positive. Motivation makes you become better! External motivation is a call to action that can bring money, approval, or promotion. Doing something interesting for satisfaction and self-realization is internal motivation. External - can be determined by a motive from within - a view of the situation, the internal state of a person. As a result, external and internal motivation have blurred boundaries. Motive is what affects a person’s consciousness and depends on his picture of the world. Therefore, the need for movement necessarily includes characteristics of internal and external motives: by taking action, a person changes the world around him and his attitude towards it.
Basic stages of the motivation process
Any motivation goes through the following stages:
- A person has a certain need. When he begins to feel a lack of what he wants, a material, psychological or physiological need arises.
- Next, the person tries to find an opportunity to satisfy the need that has arisen.
- To do this, he comes up with a plan, a movement to satisfy the need. A person determines the direction of movement and realizes what means he will need for this.
- Then people move on to active actions: they implement their plans.
- Reward for work done and subsequent elimination of the need.
Extrinsic versus intrinsic motivation: which is stronger?
One side of motivation supports the other. Praise, gratitude or feedback from a client evokes a sense of professionalism and competence, which increases internal motivation. Then, for the sake of approval from outside, you want to increase your skills, efficiency, and develop as a person. Falling in love with work and being inspired by the activity appears.
The relationship between internal and external is shown in the types of motivation that express the desire for success, popularity, recognition of significance, overcoming and self-overcoming (improvement), and vocation. These types are presented in the form of a ladder of human self-development. They show how a focus on external success creates people who are satisfied with their work.
Factors that determine the level of motivation
The power of motivation consists of the factors that make it up:
- internal motive - the need for action, development, change forms the reason for movement. The goal or desired object (result of action) - must be so significant as to influence the picture of the world, capture consciousness and attention.
- The possibilities of satisfying a need are sometimes much smaller than the circumstances that have to be overcome. Therefore, a sober assessment of strengths and weaknesses is important.
- Ability to plan – a plan does not have to be on paper, but only in your head. To perform an action, you need to have knowledge and instructions for completing it. Lack of knowledge may be the reason for low levels of motivation.
- Self-control and implementation of the plan depends on what you have to sacrifice to achieve the goal. Insufficient reward can disappoint - that’s why motivation always consists of internal and external factors.
The vector of effort, the direction - it is important that a person is attracted to the external aspects of the process or result. It is the internal motive - the need for action, development, change that forms the reason for movement.
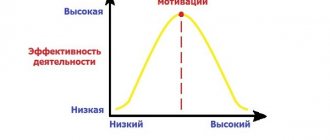
Diagnostics
Through multiple experiments, it was found that there is an optimal level of motivation. And diagnostics of this area makes it possible to determine how much the real level corresponds to the optimal level .
To carry out diagnostics, special techniques are used:
- thematic Apperception Test (TAT),
- Heckhausen motivation test,
- technique of color metaphors,
- repertory grid technique,
- Need for Achievement Questionnaire (Yu. Orlov).
In addition the interview method , when data is collected through personal contact between a specialist and the subject.
Methods (ways) of motivation
The methods of motivation depend on the object of effort. The term motivation is used to force a person to act in a certain way. To be more precise, motivation increases the effectiveness of a person’s activities in any field. Methods of exposure depend on the area of application.
Staff motivation
Personnel motivation refers to measures taken to increase labor efficiency. Depending on the goals and principles of management, the organization uses:
- financial incentives;
- organizational and administrative (fines, regulations, coercion, negative incentives);
- socio-psychological (addressed to internal motivation - involvement in something).
The choice of a motivational method in management depends on the manager’s skill and ability to find an individual approach to subordinates.
Student motivation
Teachers must take into account age-related characteristics of attention, thinking and memory in order to organize the cognitive activity of children of different ages. The most commonly used are classic
- verbal – a vivid, emotional story;
- visual and practical aids - cards with tasks, laboratory exercises that open up a desire to experiment in children;
- reproductive and search - methods of problem situations aimed at developing creative potential;
- independent work - preparing abstracts from a group or student, conducting observations that connect theory with practice.
How to increase motivation if you don't want to do anything
Think about what motivated you to change. It happens that you need to do things that you don’t want to do at all. In this case, ask yourself: why do you need to do this, remember the reason for which you need to overcome yourself.
Five minute rule. If you just can’t bring yourself to work for at least half an hour, devote just 5 minutes to this activity. Just start moving. As a rule, it is the hardest thing for us to start, but in the process we accept and continue to do the right thing with pleasure.
Fill yourself with energy. Think about what can make you cheerful right now, what will charge you with strength and positivity. Create a ritual for yourself before an important task, and then over time your brain will wait to complete the task.
Divide the task into simple and specific steps. This method will help overcome procrastination and trick our brains from fear of taking on such a huge task.
Think about what is stopping you from working. Maybe you're tired or want a snack. Find and eliminate the cause of fatigue and burnout. If necessary, take a weekend off.
Analyze your fears. This seems absurd. But in fact, our brain is designed in such a way that it tries to protect us from perceived dangers. And maybe a career and an athletic body don’t seem like something scary to you, but for the subconscious, such changes in life seem dangerous, since they require drastic changes, daily training and mental activity.
Find yourself a like-minded person, a mentor. It's always easier to do great things with someone who has similar interests and goals. You can motivate each other and prevent depression. In addition, when we see another person doing something that will lead him to his goal, we unconsciously do not want to lag behind and do the same
Start your day right. Plan everything in the evening. Make it a habit to start your day with your most challenging task. In the book “Get Out of Your Comfort Zone,” this principle is presented as “eat the frog.”
Read books and watch motivational films. And even if this is an external external motivation, you will still be inspired, which means you are determined to conquer new heights
Create the right environment. Set up your workplace in a comfortable environment. Prepare your sports uniform in the evening. Create an environment where you cannot put off an important task.
Record your progress. Don't forget to consider all your past successes and opportunities. Write them down and remember them. This will help you track how effectively you are moving forward. In addition, this method will not give you the opportunity to belittle your achievements. If you see how much you've done, it won't be difficult to motivate yourself to go further.
Reward yourself. Always make time and opportunities to celebrate your successes. If you complete the required task or step that brings you closer to your goal, reward yourself. This could be a trip to a cafe, a necessary purchase, or a trip to your favorite place. However, remember that rewards should not prevent you from achieving your goal and roll back your efforts. That is, if you have lost 1 kg, you do not need to reward yourself with cake.
How to become millionaires from scratch
Scope of application of the concept
Motivation is a broad concept, but in general it reflects the reasons for human behavior. In various scientific fields, a person is an object of research in various directions. Therefore, different types of motivation are considered. In psychology, it is a carrier of consciousness; in economics, it is a subject of economic activity with needs; and in management, it is an employee whose activities are subordinated to the company’s goals. Teachers motivate by increasing the activity of cognitive activity in schoolchildren and students. The term is used in marketing when a person with needs, motives and judgments makes a decision to purchase a product.
In psychology
Psychology seeks answers to two questions:
- How does human behavior differ from that of animals?
- How can behavior be regulated to solve the problems of training, education, and activity management?
Therefore, in the broad sense of the word, motivation includes:
- psychological and physiological characteristics of a person;
- environmental factors influencing behavior.
In the narrow sense of the word, these are psychological changes that shape, direct and support human behavior. These are reasons that explain why a person did what he did in a particular situation. Why? For what purpose? For what?
Psychology of motivation studies three aspects:
- biological and physiological mechanisms associated with the satisfaction of basic needs;
- behavioral or non-psychological stimuli from the internal and external environment - conditioned reflexes;
- psychological – psychological factors are considered (unconscious, internal and external stimuli, social factors, humanistic – human consciousness).
There are various branches of psychology that have studied aspects of behavior.
In management
In management, motivation is the process of stimulating one or more people to activities that are aimed at achieving the goals of the enterprise. It's a way to get work done efficiently.
Intangible
I have already mentioned more than once in my article that it is not only money that motivates well. Although you can’t go anywhere without them. It's a pity.
I myself could not use any other types of work motivation, but give out a lot of non-material motivation to my colleagues, if that alone were enough.
Therefore, we work comprehensively. Types of non-material motivation of personnel can be the following:
- Promotion. Both in the horizontal and vertical career ladder;
- Motivational speeches or meetings. They performed especially well during a crisis, when the morale of employees was falling;
- Motivational boards (easy to do if a CRM like Bitrix24 or Megaplan is implemented);
- Competitions and competitions;
- Cultural events within the company;
- Congratulations on significant dates for the employee;
- Public recognition of employee achievements;
- Peer ratings;
- Participation in meetings with management;
- Help with family matters.
Examples:
- I really like Zappos. It has a special department that helps employees solve ordinary, household, routine matters. For example, if you have a toothache, they can make an appointment with the dentist. Or take your mother to the hospital;
- At Google, department employees have a free lunch once a week, to which they can invite their loved ones;
- Also on Google for the best job in the client department, place a photo of a person with the caption “Best Employee of the Month”;
- At Lego, after 25 years of hard service, each employee is given a small gold bar shaped like a Lego piece;
- My favorite again is Zappos (in my opinion they have the coolest corporate culture). Once a month, your colleagues transfer the virtual dollars they have been given to the employee they like. All virtual money can be exchanged for very real ones.
By the way. If you decide to use CRM, then I recommend Megaplan, and especially for you - the “Megastart” promo code. It gives a 10% discount + another 14 days free -> megaplan.ru. Or test the most popular CRM in Russia – Bitrix 24.
This paragraph can be divided into two types: social and psychological. In order not to bother you, I deliberately combined all this into one.
I bet you didn’t even notice the difference in the examples given. If we summarize all this and call it in one phrase, we get “Make your colleagues HAPPY.”
Why do you need motivation?
Who needs it? Motivation is an instruction for behavior. When a person wants something, the brain independently finds clues to achieve success. A guy seeks a girl's attention, a child finds gifts from Santa Claus, a woman loses weight after giving birth. They are motivated because they know exactly what they want. The search for motivation is carried out by those who are not sure of the goal. A person who gets paid to work for survival will crawl to work. His ego will scream that it is better to sleep, but to sleep he will want to eat, and food is bought with money. And again we need to work!
Motivation is a struggle against one’s own habits and foundations. Therefore, trainers and motivators warn - get ready to change your life completely. Trying on someone else’s experience is being motivated by someone else’s success. This reveals the line between how external and internal motivation works - the difference between an imposed goal and determination.
Theory of motivation: features of the content direction
The emphasis in this direction of motivation for a person is on the analysis of human needs and methods of their systematization. The influence of internal emotional-volitional impulses on the formation of personality behavioral characteristics is studied. These principles of the theory of motivation were adhered to by Maslow, Herzberg, McClelland, and Alderfer.
- Maslow's theory. The most important thing in this theory of motivation for any person is that needs are formed into groups, between which a strict hierarchy is observed. This theory of human motivation can be illustrated using a pyramid, at the base of which are basic physiological needs, and the top of the pyramid is the achievement of self-actualization.
- Alderfer's ERG theory. According to this theory of human motivation, all needs can be classified into one of 3 groups (existence, connections and growth). The difference between this theory of human motivation from Maslow's theory is that Maslow recognized only a unidirectional movement from lower to higher needs;
- McClelland's theory. If you study this theory of motivation, you can see that throughout life a person can acquire the needs of achievement, participation and dominance, and one of them has a strong influence on his character and behavior;
- Herzberg's theory. This theory examines the influence of material and intangible factors on the development of personality and its activities. This theory of human motivation is widely used by managers of firms and enterprises to optimize the work of employees;
Practical advice
Motivation is needed by those who want to force a person to fulfill demands and obey. Therefore, they manage children, subordinates, consumers - buyers of goods and services. Even the desire to have a slim body is an imposed motive. To avoid needing motivation, you need:
- determine the type of activity you like;
- identify the goal that can be achieved in this activity;
- to have, as a result of achieving the goal, satisfaction of the financial and internal goals - gratitude, self-esteem, recognition of mastery.
That's when there will be no need for motivation. The purpose of the activity motivates itself.
Self-motivation methods to achieve results
When accepted methods of motivation do not work, methods that facilitate the search for internal resources to carry out activities will come to the rescue:
- Small steps method. The big task looks daunting. The use of a step-by-step method will help reduce the unpleasant psychological effect. Large tasks need to be broken down into small ones, and these into even smaller actions that can be completed in 5–10 minutes. Trying to get the job done right away is demotivating, but it’s easy to get motivated to complete a small task. In psychology, this approach is called “baby steps” - after all, in order to learn to run, a child must first take the first hesitant step.
- Negative reinforcement method. It is suitable when you need to overcome a bad habit or addiction. You need to come up with a punishment for yourself (for example, put 10 rubles in the piggy bank) and every time you failed to restrain yourself, “pay” for your mistake. The disadvantage of this method is that it cannot be used for large purposes.
- Authority method. Every person has an idol - a person whose opinion is significant. This technique is based on the desire to gain the approval of the idol. You need to imagine that he is monitoring the progress of the work. You can even write a report for it or record a video.
The main way to achieve a goal is a clear understanding of why a person needs it. It is useless to impose motivation. When performing an activity that one does not like or that irritates one, a person will dream of only one thing - to get rid of this responsibility. Motivation should be based on personal desire - then it will be effective.