Achievement motivation theory is one of the most famous works of American psychologist David Clarence McClelland, which is also commonly known as need satisfaction theory, needs theory and the three needs theory. McClelland developed this concept in the early 60s, influenced by the writings of Henry Murray.
Motivational theory explains how a person's needs change over time as their life experiences change. It also answers the question of how human behavior is influenced by the need to achieve success, power and “belonging.” McClelland argued that every person's motivation is determined by these three factors - regardless of age, gender, race or culture to which he belongs.
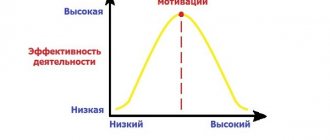
Motivation to achieve your goals
A pronounced need to achieve set goals is a trait of strong, principled, strong-willed individuals. Motivation to achieve success is the desire to achieve high results in the chosen field of activity.
A. Maslow represented the needs of people as a pyramid consisting of physiological needs, security, belonging, recognition, knowledge of the world, self-knowledge. When needs are not fulfilled, a person feels unhappy, trying to find out the reason. Reluctance to find out the reasons gives rise to apathy and depression.
Strong motivation
Determined by factors:
- The desire to achieve success.
- No fear of difficult tasks.
- The desire to perform the assigned task efficiently.
- Self improvement.
Let's imagine two equally capable schoolchildren. A student with a strong motivation for results studies daily independently or with tutors, trying to understand incomprehensible topics. Strives to get only good grades.
A child with weak motivation for results, when faced with difficulties, will prefer not to deal with them. The student will copy from a friend.
They rarely achieve success only if they have abilities and talents. There is a famous motivational quote for success by Goethe: “genius is 1% talent and 99% perspiration.”
Remembering ambitions
The word “ambition” evokes negative associations for many people. This is probably because it is often combined with the word “overpriced.” People with inflated ambitions pretend to do a lot without having sufficient grounds for it, and overestimate their personal qualities and capabilities. Conversely, a person with low ambitions does not need anything: he strives to satisfy only minimal needs.
But ambitions can also be healthy. And in this case, they are an excellent source of motivation. A person with healthy ambitions is constantly on the move, he strives to stand out with his knowledge and skills, sets goals and achieves them. And although psychologists claim that ambition begins in childhood, it can still be developed in oneself. Communication with ambitious people who always need more than others especially helps in this. The desire to keep up with them, to be no worse, is a good motivation in the desire to become successful.
Formula for successful results:
U = C*M*St;
Where U is success, S is ability, M is motive, St is situation (favorable or unfavorable environment for development). Using the formula, the further chance of achieving goals is determined.
Motivation to achieve success plays a major role; a person with a highly developed desire works harder, which is noticed by managers during interviews, coaches when recruiting a team, and teachers. The motivation for achieving success and avoiding failure are different - timely identification helps self-development.
McClelland's study of need
Achievement theory (or need for achievement) was primarily promoted by American psychologist David McClelland. He spent much of his life developing the idea that three key needs are acquired through learning or experience. They cannot be learned at some seminar, but you can still learn them if you practice for several months or a year. What are these three needs:
- Need for achievement. Selecting situations where success depends on performance
- The need to belong. Essentially, being close to someone. Such a person enjoys mutual friendship with others
- Need for strength. Those who have this need have a great need to control events and things or influence others
Main differences
There are two main types - motivation to achieve success and avoid failure.
Achieving success | Avoiding Failure |
| Clear focus on success | Success is unimportant |
| Correct assessment of opportunities | Inability to calculate strength |
| Setting realistic goals | Setting goals that are too easy or too difficult |
| Healthy self-esteem | High or low self-esteem |
| Understanding the importance of failure | Fear of failure |
| Joy to a new activity | Fear of unknown activities |
| Perseverance, maximum use of resources | Lack of persistence, taking only shortcuts |
| Optimistic view | Pessimistic view |
If you are motivated to avoid failures and have no desire to achieve success, you should think about it. Special Ehlers tests will help determine your level of aspiration.
Watch motivating films and videos, read motivating books
Motivational films will help create the right mood. For example, “The Pursuit of Happiness” (about a single father who wants his child to be happy), “The Social Network” (about the story of the creation of Facebook by classmates who made them millionaires), “Always Say Yes” (about about how a short word “yes” can change your whole life), “Rain Man”, “Knockin’ on Heaven’s Door”, “...And in my soul I’m dancing”, “Until I play the game”, etc.
Among the books one can highlight the books by Ray Bradbury “A Cure for Melancholy” and “Dandelion Wine”, Lance Armstrong’s “My Return to Life”, Greg Mortenson’s “Three Cups of Tea”, Jerry and Esther Hicks’ “Sarah”, etc.
However, everyone probably has their own book or film that they want to return to again and again, especially when their mental strength is running low. The main thing is not to forget that, in the words of the English poet Matthew Arnold, “the biggest bankrupt in this world is a man who has lost his enthusiasm for life.”
Level up
To level up you need:
- Think about the successful outcome of the business started;
- Don't compare yourself;
- Notice even small results of your own, keep a diary;
- Read biographies of successful individuals, notice similar difficulties;
- Limit your social circle, give preference to optimistic people;
- Study psychology, watch relevant films and videos.
- Participate in various trainings and webinars. Study the biography of a potential coach, read reviews.
The ability to plan is an important development factor
Classification and motivation possibilities
Why is motivation needed, how does it affect a person? Based on common characteristics, motivation can be divided into 4 large groups, which play a key role during the entire process.
The first is basic groups. The classification of motivation in this case will be as follows:
- material (desire for wealth, luxury, security);
- labor (the desire to earn a promotion at work, to receive positive sanctions in the form of a bonus or award);
- status (motivation to change position, change career, changes in personal life);
- spiritual (thoughts about achieving internal constancy, studying an important detail that has not yet been described).
They are responsible for the initial emergence of the desire to achieve the desired result. They are retained throughout the entire process, but can be changed or replaced. In some cases, they may serve as a reason to stop motivating. For example, when there is an easier and more affordable alternative that forces you to abandon a previously thought-up plan.
The second group is ways to achieve the goal:
- normative (suggestion, persuasion, information);
- coercive (insults, threats, intimidation, pressure);
- stimulating (providing real benefits and conditions, concluding written and oral agreements).
Influence the choice of means to be used during inducement. In frequent cases, they are combined and used in certain situations. For effective action, material goods are also used. The ability to persuade/pressure an interlocutor in many cases allows you to achieve a positive result, but any success must be consolidated.
The third group is the causes of occurrence. Classification:
- internal (appears during a mental or physical process, when a person solves a problem, forms motives);
- external (sources of influence from outside, such as wages or orders).
Strong motivation is only possible if there are internal and external sources. At the moment when you want to quit following the steps to achieve a goal, a person subconsciously begins to remember other reasons that in the future encourage him to work even harder.
The fourth group is focus on achieving results:
- positive (incentives, rewards, praise);
- negative (penalties, fines, public reprimand).
In reality, there are cases when a person strives to achieve one result, but in the end he gets something completely different. The mistake lies in choosing the direction of motivation. The general characteristics of motivation will tell you how to proceed.
Stimulation
Stimulation involves creating the most effective working conditions. Encouragement can be material or moral in nature. Natural incentives that encourage an employee to work are not enough for effective work. A special feature of employee incentives is their reliance on the standard level of labor. The employee is aware of the degree of responsibility, purpose, and penalties. The loss of material reward is expressed by partial payment of bonuses or complete deprivation.
Discipline is partly a method of coercion and restriction of personal freedom. The line between coercion and stimulation is conditional - an employee with developed responsibility is always disciplined. The employee performs assigned duties efficiently and conscientiously.
Incentive system
- Monetary incentives. Earning money is a common goal for workers.
- Social incentives include:
- Decent conditions. Organization of the workplace, absence of extraneous sounds, moderate lighting, effective distribution of labor and rest;
- The ability to replace monotonous activities with a creative process;
- Availability of free time. Rest promotes productive work;
- Good relationships within the team. The authority of the leader’s personality, the leader’s perception of the boss;
- Opportunity for career growth.
3. Psychological stimulation is focused on accepting the employee as a multifaceted personality. The perception of an employee as a mechanism that performs a set of actions gives rise to negative consequences - lack of desire to work, dismissal.
We think not about the difficulties that lie ahead of us, but about the benefits that we will ultimately receive
We describe in detail in our minds or on paper all the benefits that we will receive when we achieve our goal. They will inspire and motivate us. We answer ourselves the questions: how will our lives change - financial situation, lifestyle, what interesting people will we be able to meet, what new things will we be able to learn, where to go, how will our horizons expand, what opportunities will appear?
From photographs and drawings that correspond to what we want to achieve, we can create our own “dream collage” and hang it so that our gaze falls on it as often as possible, not letting us forget about the reward for our labors awaiting us. Such visualization of desires can be a good motivation. At the same time, we create an “anti-collage”, where we also colorfully depict what we don’t want, are afraid of and want to avoid - black and white photographs depicting boring, dull people, poverty, misery, etc.
Daily trainings for yourself and family
You can motivate yourself to complete tasks in a circle of close people, ask for advice and find out what other people think about you. Such methods of motivation help you look at yourself from the other side, see what is being done wrong, where a mistake is being made:
- Braggart. Where to find motivation, how to develop it? This complex will help you change your ideas about your own life. The exercise is aimed at developing the inner world and unlocking creative potential. A person needs to imagine himself as the head of a well-known company; the boss has professional employees at his disposal. For the first time, a manager must reproach his employees, show his advantage, and deprive employees of a well-deserved bonus. In the second case, the boss should treat his team favorably. Listen to their requests, ideas, reward the best employees of the company. Thus, a person clearly sees that much depends on himself. The result of actions directly depends on a person’s attitude towards the process itself. A clear understanding of goals and ways to achieve them is the key to success and self-realization.
- Analysis of justifications. How often does a person find a seemingly logical explanation for a situation, but at the same time say nothing about the mistakes made? The goal of this exercise is to understand that everything depends only on your own strengths, and not on imaginary problems. The exercise works as a motivation mechanism; it allows you to find the missing detail or missed action in time. Most of the reasons for failure are related to wrong thinking, choosing the wrong path. It is the person’s own fault that he failed to achieve what he wanted. But this is not a reason to give up all ideas and go into depression, this is just a starting point for new achievements. When an individual begins to look for external reasons for failure, then he blocks his true motives and desires. A search for other reasons may indicate that a person:
- does not know how to organize and control himself;
- does not know how to set priorities correctly;
- does not know how to systematically perform work.
To complete the exercise, you should take a blank piece of paper and write a sentence, for example: “I did not complete this task because...”. It is necessary to analyze the justification and answer the questions:
- Why was this particular justification chosen, is there an alternative to this?
- Does it depend on external and internal factors?
- What is preventing this situation from being corrected?
At this stage, you should consider what measures can be taken to achieve the goal. The main motivation tools: money, health, connections.
The Problem of Incentive Reduction
Lack of motivation is familiar to many people. Experts name 3 main reasons that are associated with the loss of desire to achieve goals. By carefully analyzing them, a person can rethink his own behavior and find new ways to solve pressing problems. How to get your motivation back:
- “Workout and proper nutrition from Monday.” Does a person believe himself when he says that he is going to go on a diet on Monday? Of course, it is much easier to postpone a difficult task until a later date than to start right now. In most cases, such ideas are not brought to life, and then disappear altogether. This is especially true for representatives of the fair sex. An excellent motivation for girls in such a situation: “I’ll start right now and finish the job much earlier.”
- “I want to be unique now and forever.” A person strives to get everything at once, dreams of possessing luxurious treasures, having a magnificent figure and a loving family. But is it really possible to achieve all this right away? In reality, you have to choose what is more important and useful at this stage. But this does not mean that there is no opportunity to achieve other goals.
- “I can’t do this because...” No matter what the answer is, people have heard this phrase millions of times. Instead of actually doing something significant, a person seeks to find a reason not to do it. And, as a rule, these very reasons are absurd and illogical.
How to develop motivation and fight your own laziness? Success doesn't just happen, it needs to be planned. Loss of motivation is a sign that an individual must reconsider his needs. A person must present a real picture of what he wants, set specific deadlines, see the goal and independently pave the way to it.
Modern Z Ouchi Theory
The concept of motivation differs in many cultures. Japanese experiments in the field of psychology and medicine prompted the brilliant American psychologist William Ouchi to create his own model Z. It is based on the principle of collectivism, when a person is presented not as a separate element, but as an important part of the entire mechanism. And if he refuses his work, then the whole device will immediately collapse.
To use Theory Z, you need to understand that most employees like to work in a team rather than handle a difficult task alone. In addition, employees are firmly confident that the employer will take care of them, and they, in turn, will do a high-quality job. Model Z will actively develop if the company meets the wishes of employees. The manager must give employees the opportunity to improve their skills and get promoted up the career ladder.
Mutual understanding and mutual commitment are the main principles of motivation, the key to a successful business and an excellent tool for stimulating employees. Employees interested in increased pay, receiving awards and badges, bonuses and changing positions will strengthen the company’s position and promote it to a leading position.
Applicable in this case are motivation methods that affect staff, students and the person himself. In all cases, it is necessary to focus on material incentives and compliance with moral standards. For example, students receive a scholarship for successful studies, and staff receive a scholarship for quality work completed on time. However, with self-motivation the situation is a little more complicated. It is always difficult to start, namely to find a reason for which all efforts will be made. Nevertheless, it is one’s own desire that can radically change not only life, but also the person himself.