You often hear people complaining about bad memory or complaining about being absent-minded. And, accordingly, they are looking for an opportunity to improve the memorization process, develop their attention and observation skills. But I have never heard anyone say that they don’t know how to think and would like to learn how to think. This is very strange, because thinking abilities are important in any activity. Maybe this happens because thinking is such a valuable gift that it is a shame to admit its lack?
What is thinking
Human thinking is the main achievement of millions of years of evolution. The world as we see it now is the result of the mental activity of the most outstanding representatives of Homo Sapiens.
In the broadest sense of the word, thinking is the process of processing information by the mind on the basis of a person’s existing knowledge and accumulated experience. As a result of this process, the initial information is analyzed, systematized, classified and acquires a new quality.
Why do you need to develop your thinking? The better it is developed in a person, the more effectively he interacts with the environment, other people, and in general, the more successful he is in life.
Thinking begins to form in early childhood and goes through several stages in its development. Scientists have found that the development of thinking of an individual person repeats the development of thinking of all humanity.
First, we learn to interact with specific objects, highlight their main properties and characteristics, and then we begin to operate with abstract images and concepts in our minds.
Intensive development of thinking occurs until about 20 years of age, then it slows down and can completely disappear if it is not consciously dealt with.
Teenage imagination
Imagination is a person’s ability to spontaneously arise or deliberately construct images, ideas and ideas in the mind. [1]
A developed imagination can influence the entire cognitive activity of a teenager, the emotional-volitional sphere and the personality itself. Some children find it easier to solve problems by imagining complex mathematical symbols rather than writing the solution on paper. And for others, a rich imagination, combined with theoretical thinking, helps them develop creatively - write poetry, draw, model. For a constrained, shy child, images in his mind help him to be more self-confident - first he will “play out” the situation in his imagination in order to act decisively in the future.
A child at the age of 12 already knows how to control his imagination. He clearly sees the difference between the fictional and real world. The imagination of a teenager is less productive than the imagination of an adult, but much richer than the fantasies of a younger child.
Despite all the “bonuses” that imagination gives, the development of imagination in a 13-15 year old teenager should be treated with increased attention. When a child is immersed in the world of experiences and deliberately leaves the real world for his fantasies, his mental activity decreases.
Types of thinking and ways to develop them
In psychology, there are several classifications of types of thinking. The most frequently used classification is based on the nature of mental processes occurring in the brain. This is where we will focus our attention. According to it, the following types of thinking are distinguished.
Visual-figurative
This type of thinking is closely related to the visual perception of objects and occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain. In the process of visual-figurative thinking, a person interacts with images of specific objects that are in short-term and operative memory.
For example, a child sees a picture of a ball flying towards the window and can figuratively imagine the development of the situation.
The older a person gets, the less often he resorts to visual-figurative thinking. Therefore, over time it begins to limp. If you've ever done a renovation, you know how difficult it can be to imagine a room with new wallpaper on the walls and furniture standing differently.
Fortunately, it can be developed at any age. The methods of development in an adult and a child are the same, so you can do this together with your child. Here are some simple tips:
- Every day before going to bed, remember your entire day in bright colors. Who did you meet today? What were these people wearing? What was the design of the buildings you entered? The more details you remember, the better.
- Perform unusual manipulations with images in your mind. For example, imagine that a bear and an elephant switched ears. Or that the whale grew legs. Don't limit your imagination. The more ridiculous a picture you can imagine in your mind, the more it will give impetus to the development of thinking.
- Several times a day, focus on some objects and try to find as many words as possible to describe them.
Visually effective
This type of thinking first begins to form in children at the age of approximately 1.5 years. It is associated with the manipulation of specific objects. A person solves practical problems directly in the current situation, performing certain actions. Visual-effective thinking is also called manual intelligence.
For example, a child builds a tower from cubes, sculpts from plasticine, or assembles a construction set. Or an adult rearranges furniture, lays parquet flooring, sews a button on trousers.
The left hemisphere of the brain is responsible for this type of thinking. You can develop it in the following ways:
- play chess;
- collect puzzles;
- make crafts from scrap materials;
- sculpt from clay or plasticine;
- fold origami figures from paper;
- build something from a constructor.
Abstract-logical
It is also often called verbal-logical or theoretical. The highest degree of mental activity available only to humans. With its help, we can “unstick” the thought process from specific objects and operate only with abstract concepts.
This type of thinking begins to develop at the age of 5–7 years. By the age of 16, as a rule, a child can already use it like an adult. Namely, analyze information coming from outside, highlight the properties of objects and phenomena without direct contact with them, classify and systematize data, isolate the main and secondary, etc.
The child learns to count using material objects at hand: fingers, cars, apples, cubes. If at this stage you try to explain to him what numbers are, he will not understand. Then, already at school, he will be able to make calculations without manipulation, resorting to the help of only abstract concepts.
Abstract-logical thinking operates in three main categories:
- A concept is the simplest unit of mental activity. With its help, we name an object and transfer it to the abstract plane, assigning it to a category already known to us. This is done on the basis of its essential features. Example: we see an airplane, identify the main features (two wings, a tail) and call it an airplane based on its similarity to similar objects already familiar to us.
- Judgment is the establishment of a relationship between several concepts and the formation of new concepts on the basis of this. An example of a proposition: “A plane, a car and a train are modes of transport.”
- Inference is the formation of new judgments from existing ones. “A plane is a mode of transport. Transport transports people and goods. The plane transports people and cargo.”
The development of abstract logical thinking should be given special attention to both children and adults. In the course of his life, a person most often uses it, with rare exceptions. Success in all areas of life depends on how well it is developed.
Here are some simple tips for its development:
- read words and sentences backwards;
- come up with contradictory phrases: bitter sugar, hot ice, solid liquid;
- compose fairy tales and stories with all kinds of plots;
- try to create visual images of abstract concepts in your head: inspiration, harmony, spirituality, hypothesis, etc.
Creative
This type of thinking allows us to process the most ordinary information in unusual ways, while obtaining qualitatively new results. It lies at the heart of all great inventions and works of art. Without it, we would not be able to move beyond existing algorithms and patterns.
If your creative thinking is poorly developed or not developed at all, then you do not know how to be flexible and respond to emerging changes. By upgrading it, you will not only become more efficient, but also begin to live a more interesting and rich life. So I advise you to start right now. Here's what will help you with this:
- Learn something new every day.
- Do ordinary things in unusual ways.
- Travel more.
- Include improvisation in the most ordinary life situations.
Is it possible to develop the thinking of an adult?
Perhaps another equally important reason for the reluctance to develop thinking is the belief that it is impossible for an adult to do this. And the only way to become even a little smarter is to accumulate knowledge.
But this point of view is wrong. It is not only possible, but also necessary to develop the thinking of an adult, but knowledge alone will not get you far. Information, regardless of its volume, is only a building material for thinking. Bricks alone are not enough for a mason to build a beautiful castle; he also needs skills, abilities, knowledge of techniques and craftsmanship as an alloy of all this combined.
One can, of course, recall the statement of the developers of intelligence tests that intelligence does not change with age. But thinking is not exactly intelligence. Thinking is an activity, and any activity requires the development and formation of skills. The process of developing thinking skills not only enriches a person with new ways and techniques of thinking, but also develops and complicates the brain itself.
Our brain is a very flexible and sensitive instrument that is designed to be constantly active. The effectiveness and quality of our thinking depend on it. Indeed, in the process of brain work, new connections are formed between neurons, neural networks become more complex, and therefore, thinking abilities develop.
So, the answer to the question “is it necessary to develop thinking” is obvious. It remains to figure out how to do this.
Mental operations
To give you an idea of what a multifaceted and complex process our thinking is, I will list some of its capabilities. Even the most powerful computer next to it will seem like a child's toy.
- Comparison – highlighting the similarities and differences of several objects. “The shape of an apple is similar to a peach, and the color of a pear.”
- Analysis is the division of objects into their component parts. “A chair consists of legs, a seat and a back.”
- Synthesis is the joining together of disparate elements. “Stick, stick, cucumber - so the little man came out.”
- Induction is the derivation of inference from the particular to the general. Distribution of knowledge about one object to a group of similar ones. “This dog chews a bone, so dogs can chew bones.”
- Deduction is the opposite of induction. Endowing an object with specific properties based on its membership in a group. “Ants can lift objects heavier than their own weight. So this particular ant can lift more than its own weight.”
- Combination – searching for solutions to a problem based on a combination of different methods. Underlies combinatorial thinking. Used, for example, when playing chess.
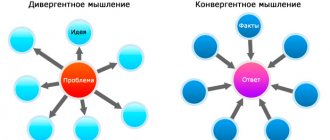
- Divergence is the search for multiple solutions to one problem. We use divergent thinking during brainstorming.
- Convergence is the search for the only correct solution based on learned algorithms. It is used when solving problems in which there can be only one correct answer and it can be obtained only in one way.
This is not all the capabilities of our brain. If you want to learn more, I advise you to read special books on thinking development. We will look at some of them towards the end of the article.
Logic problems for cool down
Problem 14
You are given three letters. One will have to be swallowed immediately. In each letter you will find a couple of sentences. Two sentences in one letter are true, in the other they are false, and in the third they are half true and false. See what offers are there:
First letter:
- Don't eat this letter.
- Be sure to eat the second letter.
Second letter:
- You shouldn't eat the first letter.
- Chew the third letter.
Third letter:
- This letter is not worth eating.
- Hurry up and eat the first letter.
Share your opinion on which letter to eat?
Answer
Third letter.
Problem 15
You find yourself in a room with four doors and a tiny window. Three of the doors are false, that is, there is brickwork immediately behind them. And one door with access to the street. You have been given a key that opens all four doors, but you have no idea which door will lead to the street. You can only try once. When one door is opened, the remaining locks are locked mechanically and irrevocably. In addition, the room is dark and slightly illuminated by the light of a single candle.
What measures will you take to find the only door that leads to the street?
Answer
It is worth opening the window and placing the candle one by one on the doors: to the cracks or to the keyhole. At the same time, look carefully at the candle flame. An oscillating flame will indicate exit.
Did these logic problems seem easy to you or not so easy?
Universal recommendations for developing thinking
Let's move on from theory to practice. Follow our guidelines to sharpen your mind and make it razor sharp.
Read more
Nothing contributes to the development of mental activity more than reading. Just be careful - not all literature is equally useful. Pulp novels, second-rate detective stories, memoirs of pop stars only clog the brain.
I advise you to read classical literature, encyclopedias, books on philosophy and psychology. The process of reading itself activates various parts of the brain, and the information that we draw from books expands our conceptual apparatus.
Use your left hand
We all know that the left hand is connected to the right hemisphere, and the right hand to the left. Most of us are right-handed, so our right hemisphere is much less developed. But it is precisely this that is responsible for creative and imaginative thinking. To bridge the gap between the two halves of the brain, you need to start using your left hand as often as possible (for left-handers, the right).
Here are some ideas of what you can do with your left hand without compromising the result:
- brush your teeth;
- open the door with a key;
- eat with a spoon;
- type a message on your phone;
- paint.
At first it will be unusual and the actions will take longer. But then you will get used to it and feel the effect. Thinking will become more flexible, livelier and brighter.
Keep a diary
The habit of recording your thoughts on paper is very useful for the development of thinking. You learn to think analytically, systematize information, highlight the main thing, cut off the unnecessary. Abstract reasoning on abstract topics is of particular value: about the processes taking place in the world, about your attitude towards them, about general philosophical concepts.
Using these records, you can then track the evolution of your thinking. Your first written down thoughts will seem childish and naive to you. As you move through the pages of your diary, your thoughts will develop with you and become slimmer and deeper.
Communicate with those who are smarter
The environment greatly influences a person. It’s not for nothing that they say: “Whoever you mess with, that’s how you’ll gain.” Often people avoid communicating with those who are better than them in some way, for fear of lowering their self-esteem. But if you really want to achieve results, you will have to go through this stress.
Surround yourself with people who are passionate, versatile, and who love to think and reason. The difference in thinking abilities will spur you to develop.
But communication with slackers and whiners, on the contrary, will have to be reduced. Otherwise, you won’t even notice how they will drag you into their swamp called the “comfort zone.” And there is nothing there except the prospect of being firmly attached to the sofa.
Play mind games
Today, collective intellectual games are at the peak of popularity. In every major city you can find a club for fans of “What? Where? When?”, “Brain Ring” and all kinds of quizzes. Join them and you will kill two birds with one stone.
Firstly, such games are great for developing logic. Most of the questions there are written in such a way that anyone can come up with the answer, regardless of their level of knowledge. You will train your mind in a fun and playful way, and bright emotions and excitement will make the training several times more effective.
Secondly, you will meet interesting, enthusiastic, thoughtful people. This is exactly what we talked about a little earlier. A useful and fun pastime can later develop into a strong friendship.
Solve crosswords and puzzles
Buy a crossword puzzle magazine and try to carry it with you everywhere. Guess them as soon as the opportunity arises. For example, in line at a bank or in a hospital. This is much more useful than wasting time fiddling with your phone.
Don't look for easy ways
Sometimes it’s useful to give your brain a jolt by creating artificial stressful situations. In such conditions, development occurs faster and more intensely. Try to arrive in an unfamiliar area and navigate there only using a map, without asking random passers-by for directions.
The same can be done if you are going to another city or country. Even a banal trip to the shopping center can be used for good. Do not ask consultants for help in finding the product you are interested in, try to navigate yourself.
Train your memory
Memory and thinking are interconnected processes. It is memory that determines how quickly you think and how often you make mistakes. Therefore, be sure to pay special attention to this cognitive function.
As a workout, you can learn poetry, memorize shopping and to-do lists. You can go further and enroll in memory development courses. This way you will achieve the desired effect faster and will not give up classes after two days.
How to identify poor development
The level of development of people of the same age may differ. Some people tend to analyze and think deeply, while others think superficially.
Signs of underdevelopment in an adult:
- Difficulties in completing tasks at work when colleagues cope without difficulty;
- It is difficult to formulate thoughts, construct speech correctly, frequent use of filler words;
- Mistakes are often made when writing words and sentences;
- Tension and migraines during decision making;
- Inability to logically distribute your tasks. It's hard to plan a route for the day;
- It is difficult to understand the meaning of what is read or said.
It's hard for a girl to think
The student is underdeveloped if:
- He doesn't read well;
- He cannot retell the meaning of what he read or heard;
- His speech is unrelated in meaning, he cannot formulate a thought;
- He has a bad memory;
- He can’t count, doesn’t know simple things: colors, names of objects.
Note! The child may have speech defects that are not related to mental development. Only a speech therapist can identify speech abnormalities, give recommendations and determine treatment methods.
Well-developed thinking is necessary for both a programmer and a private entrepreneur. A schoolchild and student will not be able to succeed in their studies without the ability to reason, draw conclusions and absorb information. Regardless of age, position and social status, your brain needs to be regularly trained and fully developed.
Exercises
Now let's play a little. I have selected interesting exercises for you to develop your thinking in a playful way.
Connecting the unconnected
A fun and exciting exercise for adults and children. Its essence is that you need to combine two completely unrelated concepts in one sentence. For example, a jellyfish and a computer. The more proposals you can come up with, the better.
This exercise is often used during castings for radio presenters. Representatives of this profession must be able to immediately jump from one topic to another and do it beautifully and naturally.
What options can you come up with with our example? At least this: “The computer screensaver had a picture of a jellyfish.” Or, for example: “Dima was sitting at the computer and dreaming of a sea full of jellyfish, crabs, and dolphins.” Now you try it. Once you understand this couple of concepts, take on the following:
- dog and microphone;
- tower and belt;
- bridge and button;
- lawnmower and flea;
- Moon and subbotnik.
Instructions
Imagine that aliens flew to Earth and decided to settle here. Their civilization is completely different from ours, so the most ordinary objects are a wonder to them. You need to write instructions for the most commonly used items to make life easier for guests.
For example, let's create instructions for a toothbrush.
- A toothbrush is a device for cleaning teeth.
- It should be used twice a day - morning and evening.
- Go into the bathroom, stand in front of the mirror, take the brush in your hand and wet it with tap water.
- Then squeeze some toothpaste onto it and bring it to your teeth.
- Make rotational movements to remove dirt from your teeth for three minutes.
- After that, wash it in running water and put it back in place.
As you can see, everything is simple. Now it's your turn to write the instructions. Here's a list of items to get you started: comb, fork, key, glasses, chair, soap.
Two events
Between two events that, at first glance, are in no way connected with each other, you need to stretch a logical chain of reasoning in order to get a coherent and coherent story. Let's take the following events:
- A dog whined pitifully in the yard.
- The ship's mast was struck by lightning and a fire started on deck.
Here’s what I got: “A dog whined pitifully in the yard. Jack realized that he could no longer endure this dull, monotonous life, and decided to go on an adventure. His uncle was a sea captain, and at night the boy secretly sneaked onto his ship moored in the port. In the morning he woke up from strong rocking and realized that the ship had already sailed and was caught in a strong storm. The mast of the ship was struck by lightning and a fire started on deck.”
I have prepared a few more pairs of events for you - practice!
- The phone rang in the boss's office. The car crashed into a pole at full speed.
- The rocket took off from the ground and soared into the sky. The boy put his hand in his pocket and found a note there.
- The man got out of the subway and went straight to the bookstore. A family of rhinos in Africa has given birth to a baby.
Logic chains
The best exercise for developing logic. Suitable for everyone - children, teenagers, students and adults. His goal is to learn to establish logical connections between objects and phenomena.
You will be presented with two different concepts. Your task is to identify what can connect them. An example is an apple and a dog.
- Both objects belong to living nature.
- Both contain water.
- Representatives of both species have been in space.
- Both can cause injury to a person, etc.
Other options: syringe and pie, skirt and deer, chicken and bench, milk and bulldozer, cloud and crocodile.
It's the other way around
For this exercise you will need a newspaper, magazine or, at worst, an online news portal. Take a catchy headline and swap the nouns in it. It was: “The Russian national team players returned home on bicycles.” It became: “Bicycles returned home on the Russian national team players.” Delirium is delirium.
Your task is to come up with a story that fits the title and makes it more or less meaningful. For example: “The Russian national team players decided to buy back the royal bicycles taken out of the country during the revolution and return them to their homeland.”
The essence of verbal-logical (abstract) thinking
Any thinking can be precise (when we understand exactly what we are thinking about) and abstract (generalized). In other words, a person examines the picture not in detail, but in general terms. He can guess, assume, summarize information and draw appropriate conclusions.
The main characteristics of a person who thinks abstractly:
- easily evaluates and compares phenomena and objects that are completely different in characteristics and purpose;
- classifies and divides knowledge;
- continuously analyzes what is happening;
- distinguishes particular events from the whole;
- extracts what is significant and cuts out unimportant details and events;
- classifies objects and phenomena according to certain criteria;
- finds common ground between the general and the particular.
It is worth noting that age does not in any way affect the ability to think. You can train both the thinking of a child and an adult. The effectiveness of such training also does not depend on age. There are simple and effective training methods.
Useful literature
Remember the first point of our recommendations for developing thinking? The one that talked about reading. It's time to bring it to life. I’m sharing with you three of my favorite books on thinking development:
- “Lateral thinking. Textbook” Edward de Bono. The book by a world-famous psychologist is dedicated to the development of creative, out-of-the-box thinking. The author is confident that this type of thinking is the future. Considering that in schools and institutes creative thinking is not taught at all, a person who has developed it to a high level will have a serious competitive advantage. In the book you will find many different exercises that will teach you to think outside the box and in an original way.
- “Brain Accelerators” Richard Nisbett. This book will teach you how to apply methods and techniques from various sciences in order to think more effectively and efficiently. You will learn why logical and mathematical laws do not apply to all situations and how to avoid common mistakes in drawing conclusions. The book is serious and may seem difficult to some, but this is its main value.
- "Thinking. System research” Andrey Kurpatov. Perhaps the most voluminous, deep and unexpected book dedicated to thinking. After reading it, you will know everything about thinking. There are no exercises or tasks in it, but there is a lot of information to comprehend.
Human cognitive development
The entire human mental system requires constant development, starting from birth, and even certain genetic data, without development, can lead to degradation and loss. It was in this vein that the concept of cognitive thinking appeared, which literally means aimed at comprehensive development. Thus, by taking action to develop your thinking in different types and areas, you support cognitive development.
The concept of the human cognitive system is characterized by some basic properties, such as efficiency, algorithmicity, digestibility, adaptability and expressiveness. These are the components for constantly developing your thinking and obtaining positive results. According to research, each person, provided there is no damage, is born with approximately similar inclinations for cognitive development and his further success in this matter depends only on classes and exercises.
Online trainers and applications for developing thinking
In the age of high technology, it would be a sin not to take advantage of the achievements of scientific progress. There are a lot of cool services that will turn thinking training into an exciting game.
Vikium
Vikium is a service with online simulators for the development of various brain functions: thinking, memory, attention, emotional intelligence. He will select an individual training program for you based on testing. The exercise machines are suitable for all ages and easy to use.
BrainApps
On the BrainApps platform you will find 52 simulators for the development of cognitive functions of the brain. All simulators are made in the form of games, so you won't be bored. By training 20 minutes a day, by the end of the first month you will improve your initial performance by 15%.
Da Vinci's riddles
Everyone knows that the greatest artist of all times knew a lot about riddles. Therefore, this interesting application was named after him. It contains the best logic puzzles. They are divided into several categories: art, mathematics, history, logic, technology. Initially, one riddle is open in each category, but as you solve them, new ones open up.
Quiz “What? Where? When?"
The application is based on the legendary TV game. You can feel like a real expert and compete with other participants. There is also the opportunity to play tournaments with friends and come up with your own questions. The application trains abstract logical thinking and develops intuition.
In my mind
A domestic application based on the book of the famous teacher S. A. Rachinsky “1,001 tasks for mental calculation.” In the 19th century, students in rural schools easily solved these mathematical problems in their heads. Will you succeed?
Teenage attention
Attention is a person’s ability to concentrate his cognitive processes on a specific object in order to study it comprehensively. [1]
One of the main features of a child’s development at 10-12 years old is that, unlike younger schoolchildren, he can control his attention. The level of concentration of a teenager on any type of activity is sometimes selective. A simple example: a child is very attentive and focused when he is doing his favorite hobby or playing with friends, but in school during class he may be constantly distracted because he finds the activity boring.
It is inattention that often “slows down” the mental development of a child 13-15 years old and older, and also becomes the cause of poor discipline and performance at school. But according to many psychologists, this problem is rather social in nature, it is not determined by any disturbances in the development of cognitive processes - the child is always more attentive to those objects that are interesting to him. The task of parents is to help the teenager develop the ability to concentrate. An equally important function is assumed by teachers at school - the presentation of educational material should be interesting and appropriate to the age group of children.
Developing attention in a teenager is extremely important. This teaches him [2]:
- be focused on a specific activity for a long time;
- select from the list of tasks the most significant for yourself;
- perform tasks consisting of many operations;
- quickly “switch” to performing other tasks if external circumstances require it.
How analytical thinking is useful
Well-developed analytical thinking allows you to timely and effectively cope with even the most complex task and find several possible options for solving it.
A person with predominant analytical thinking makes thoughtful and informed decisions, knows how to plan and make forecasts of his activities.
Employees endowed with such qualities are highly valued in companies. In any professional field, the ability to quickly find a decent way out of a difficult situation will be an advantage. By the way, this ability is useful in everyday life.
Causes of problems with the development of cognitive processes in adolescents
All cognitive processes - thinking, memory, attention, imagination - are inextricably linked with each other. A child will have a good memory if he is attentive and can concentrate on what is important. He learns to think with a rich abstract imagination and the ability to remember theoretical information.
What factors can negatively affect the development of cognitive processes in a teenager?
- Physical and mental stress.
- Increased excitability of the nervous system.
- Impressionability.
- A serious hobby that occupies all his time and thoughts.
- Insufficient training of cognitive processes.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad habits.