Let us pay attention to one of the already traditionally used cleaning methods. Let's consider ultraviolet water disinfection: the pros and cons, all stages of its implementation, the equipment used, and so on. Maximum useful information so that you can form a correct impression of how effective the method is and understand whether it will suit you.
Let us immediately note that this technology is being introduced at the initial stage of complex action on the liquid and therefore can precede chlorination. It has become widespread and remains relevant also because it is reagent-free. This is an important point that allows you to exclude by-products from entering the work stream and does not change the physical, mechanical or organoleptic properties of H2O.
What does UV water disinfection mean?
This is its treatment (for the purpose of cleaning) with electromagnetic radiation, the length of which is 10-400 nm. It can be near, medium or far; Usually the second option, 200-270 nm, is relevant, since relatively narrow spectral limits are needed for efficiency.
Technology Basics
In most cases, installations are equipped with low mercury pressure lamps, since they produce a wave of 260 nm, which provides the maximum bactericidal effect on the liquid. At the same time, softening is carried out, which is also important.
The desired result is achieved due to the ability of UV to pass through cell walls and quickly get to DNA and RNA, that is, to the information center that controls the development and functioning of microorganisms. The rays ensure the absorption of nucleic acids, which is why the latter stop dividing. Thanks to this, bacteria lose their reproductive ability, and since they are dangerous only when they get inside us and actively multiply, the threat is eliminated.
Ultraviolet water treatment technology
The process is quite simple and understandable - it can be represented as the following diagram:
- flow is passed through the system;
- passing through the filter, it washes the quartz cover, which protects the lamp from contact with liquid;
- the latter evaporates mercury (or other metal), as a result of which rays with the required wavelength are formed;
- H2O receives the required amount of UV, which sterilizes microorganisms.
Conditions for using the method
The method will be effective in practice only if a number of requirements are met:
- The correct dosage depends on the intensity and duration of UV production, which are calculated based on the number of microorganisms and their resistance; if it is insufficient, bacteria will not lose their ability to reproduce; if it is excessive, the working environment will be oversaturated with iron.
- Acceptable proportion and composition of impurities - if they are more than normal, they are coarsely dispersed or change color, this seriously worsens the results, and often even makes the process useless. Large particles clog the filter, turning into a kind of shield for bacteria, but the deterioration of organoleptics is a minus in itself.
- The absence of E. coli - it has maximum resistance to rays, which means that if it is contained in a liquid, it will make it difficult to neutralize other microorganisms and, most definitely, will make H2O dangerous for use in everyday life.
Design of a water disinfection installation
The design of all installations for ultraviolet water purification is the same. This design consists of several lamps (usually four), located in quartz cases. They are washed with water, and under the influence of ultraviolet light the liquid is cleared of bacteria.
To select a cleaning installation, consider the following criteria:
- Performance:
since such devices constantly act on the liquid, their power is calculated depending on the amount of water processed. Accordingly, the performance of the device is selected depending on the volume of water that needs to be disinfected. If there is a need to increase the power of the device, a storage tank is connected to it. - Throughput:
this indicator depends on the chemical and physical properties of the liquid. In other words, the tougher and dirtier it is, the more powerful the equipment should be. - Power:
in the case of a UV water treatment plant, this characteristic shows what radiation dose will be applied to the water. This indicator cannot be calculated independently, since it depends on the species diversity of microorganisms and their resistance to radiation, and this indicator can only be calculated in the laboratory.
Advantages and disadvantages
When deciding whether to install a device for ultraviolet water purification at home, it is worth considering the pros and cons of such designs (Figure 3).
Since UV radiation is natural, it does not change the structure of water and does not have a negative effect on it, therefore this method is considered one of the most popular and popular.
The advantages of this type of cleaning include:
- Versatility:
ultraviolet radiation destroys most pathogenic microorganisms living in water. - Speed:
under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, microbes die within a few seconds of exposure, but this indicator directly depends on the power of the installation. - Environmental friendliness:
water purification with UV radiation does not involve the use of chemicals, so the liquid becomes completely suitable for human use and does not require additional filtration.
But this method also has disadvantages. Firstly, there may be microorganisms in the water that are resistant to such radiation. They are rare, but if they are found in water, ultraviolet cleaning will have to be supplemented with other means.
Secondly, heavily polluted water must first be purified from large particles of debris and other impurities, since UV rays do not eliminate them.
Figure 3. Drawings and operation diagram of a classic installation
In addition, do not forget that water becomes clean only at the moment of contact with the installation and microbes can reappear in it. But this problem is not significant if you are confident in the quality and tightness of the cleaning system.
Areas in which UV sterilizers are used
All kinds of systems and installations for water treatment with ultraviolet radiation have found wide application in a variety of areas, and the main ones are:
MBFT-75 Membrane for 75GPD
SF-mix Clack up to 0.8 m3/h
SF-mix Runxin up to 0.8 m3/h
- Food grade – make the liquid suitable for preparing drinks and dishes.
- Catering - help ensure the proper level of hygiene of staff and premises.
- Wellness – protect the reduced immunity of hospital guests who come to recuperate and are especially vulnerable to viruses and diseases.
- Extraction and supply - they are involved in the purification of the flow obtained from wells and boreholes.
- Livestock and fisheries – contribute to the creation of suitable habitats in dolphinariums and aquariums.
- Mass bathing protects visitors to water parks and swimming pools from bacteria.
- Utility - become the key to the effective removal of microorganisms from drains so that residents of populated areas are not at risk of epidemics.
Hence the conclusion - the importance and relevance of such equipment is difficult to overestimate; it is used everywhere.
UV disinfectant
Design of a UV disinfectant
Water purification with ultraviolet light allows you to treat water better than chlorine. But a physical filter is more expensive than a chemical one. Ultraviolet rays will be effective only after preliminary filtering of water from dirt, impurities, helminth eggs, and microorganisms.
The liquid that is planned to be passed through this purification method must have up to 50 polymorphic bacteria per 0.1 liter of liquid. Otherwise, additional filters will be required. The result does not last long after water is disinfected with ultraviolet radiation. Before using it or using it for other purposes, the cleaning procedure must be repeated.
Ultraviolet sterilization requires preliminary calculations like other methods. It is necessary to know the volume of liquid that will be passed through the device, the operating time of the lamp, and the number of microbes per 1 ml. The result of the calculations will be the amount of electricity required for the procedure.
Operating principle of a UV disinfectant
Scheme of action of ultraviolet disinfection
An ultraviolet lamp for water purification acts on deoxyribonucleic (DNA) and ribonucleic (RNA) acids inside each microorganism in the water. The acid is destroyed and the ability to reproduce is lost. This happens due to the flow of medium-length waves. The range is between 200 nm and 240 nm. The strongest disinfection effect occurs at 254 nm. Ultraviolet light is created by geocharging lamps located in a quartz case. The basic principle of the device is neutralization, not destruction of microorganisms.
You can purchase this device here.
Design features of the UV disinfectant
Increasing the service life of an ultraviolet disinfectant requires lamp care. As the volume of liquid passed through increases, salt deposits on the device itself also grow. You can clean them in the same way as scale on a kettle: mechanically, or by running a weak solution of acetic/citric acid through the installation. Irradiation of a liquid is possible after removing particles from it that have shielding properties.
Advantages of ultraviolet water disinfection
The main advantages are as follows:
- The lamps used are powerful enough and are able to stably maintain a suitable wavelength to neutralize up to 99% of bacteria existing today.
- The method is completely safe for human health, even in the long term - proven back in the 20th century.
- The technology makes it possible to neutralize infectious agents and disease carriers, that is, the most dangerous bacteria.
- During exposure, the waves do not change the structure of the liquid, do not introduce foreign substances into it and do not provoke their formation; organoleptic properties are also preserved.
- It is not difficult to equip the cleaning system with switches, with which the equipment will be started automatically, and the required radiation dosage will be selected - also without human intervention.
- The process of functioning of the equipment is easily controlled, and changes in ultraviolet standards (either up or down from the recommended values) do not pose a threat to end consumers.
- A full task cycle lasts up to 10 seconds - during this time, waves from the lamps are able to pass through the entire volume of liquid; This method simply has no analogues in terms of speed.
- H2O that has undergone such preparation can be used immediately - it does not need to be stored, which eliminates the cost of arranging tanks or any other storage facilities from the budget.
A separate advantage is compatibility with other technologies. In practice, all of the listed advantages clearly dominate the disadvantages, which also exist and for the sake of objectivity need to be considered.
Water disinfection methods
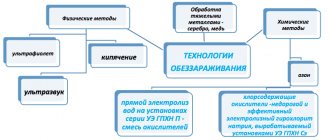
Before disinfecting water, when choosing a water disinfectant, you should understand that complete purification of water from all bacteria and minerals will make it unsuitable for human consumption. Therefore, when choosing a method for disinfecting water, you need to be careful. There are several ways to influence microorganisms harmful to humans:
- Chemical methods of water disinfection (reagent);
- Physical methods (reagent-free);
- Combined methods of influencing microorganisms.
The chemical method involves the use of various coagulant reagents added to water for disinfection. This method also includes: chlorination, ozonation, the use of silver, silicon, sodium hypochlorite and other substances that can at least stop the proliferation of bacteria, and at most completely get rid of them.
Physical, reagent-free exposure is carried out using UV water disinfection, electric pulse and other methods.
Combined methods include both chemical and physical effects alternately. These methods are considered the most effective in disinfecting and purifying various impurities contained in water.
Disadvantages of water disinfection with UV radiation
- Ultraviolet light neutralizes all microorganisms, except those that are resistant to it, for example, it cannot cope with E. coli; in the case of it, you will have to look for another method.
- To obtain results, the liquid must first be purified - mechanically remove large particles and other impurities from it, and after completing the full procedure cycle, chlorination must also be carried out.
- It is necessary to control the level of iron - make sure that it does not exceed the permissible norm, otherwise its fractions will be deposited on the quartz cover and reduce the efficiency of the process.
- There is no cumulative effect - the action is one-time, and if after it the H2O sits in the tank for some time, viruses or bacteria can re-enter in it.
Other technologies for water disinfection in a private home
Alternative methods are considered taking into account:
- efficiency;
- initial and operating costs;
- safety (convenience) of users.
The examples given highlight characteristic advantages and disadvantages that must be taken into account when choosing a disinfection system to equip a private home.
Electromagnetic processing
To effectively influence microorganisms, it is necessary to create a sufficiently strong alternating field in the working area. Aquashield professional PRO series converters have the appropriate technical parameters.
The independent review protocol confirms a reduction in tested bacterial populations by 99.99% compared to the original content. However, to obtain such a result, it is necessary to ensure circulation of the contaminated liquid in a closed circuit for 60 minutes. The technique is suitable for pipeline disinfection when the specified conditions are met or for the flow-through destruction of non-pathogenic bacteria with a limited concentration of microorganisms.
The main function of the electromagnetic converter is protection against scale. The Aquashield PRO device prevents the formation and fixation of calcium deposits at a distance of up to 2 km from the installation site of the coil.
The following facts will help you objectively evaluate the advantages of equipment in this series:
- the technique can be used at very high (up to 21 mEq/l) levels of hardness;
- the manufacturer produces models for installation on pipelines with a nominal diameter of up to 800 mm;
- the cost of the basic converter is 16,900 with delivery to any address in the Russian Federation;
- official warranty – 7 years.
Aquashield PRO can be used for preliminary disinfection and to prevent the fixation of salts on the quartz cover of the UV installation. At the same time, protection against scale is provided for all equipment connected to the water supply in the house.
Chlorination
This method of water disinfection is better suited for solving industrial problems. Aggressive chlorine activates corrosion. Boiling drinking water does not remove harmful chemical compounds, but increases the carcinogenic properties of the contaminated liquid.
Chlorination is used in everyday life to disinfect swimming pools. This procedure is complemented by mechanical filtration to restore the clarity of the liquid. When disinfecting and disinfecting water with chlorine, dosage is carefully controlled.
Ozonation
To generate gas, a special apparatus equipped with a high-voltage spark gap is used. Ozonation destroys microbes and fungi and activates the oxidation of impurities. In addition to disinfection, the technology is used to clarify water. As a rule, this treatment is combined with the subsequent passage of liquid through a layer of activated carbon granules.
The toxicity of ozone determines the mandatory application of safety regulations. The maximum permissible concentration in the atmosphere of residential premises has been established. To comply with sanitary rules, the working container is supplemented with a special device (destructor), which ensures gas decomposition.
conclusions
To make a reliable and safe UV installation with your own hands, you will have to buy high-quality components. The total costs are comparable to the purchase of a factory product, so there is no economic feasibility when choosing a homemade product.
Ultraviolet treatment is effective in maintaining the cleanliness of the bulb and timely replacement of lamps. Prevents calcium contaminants from attaching to an electromagnetic transducer or other anti-scale agent. At the final stage of drinking water preparation, a carbon filter is used to retain residual impurities and eliminate tastes and odors.
Source of bactericidal radiation
This is a device or element that produces waves in the range of 205-215 nm. Received the general name “germicidal lamp”, the most common type of which is a low-pressure mercury discharge lamp. Under the influence of electricity, it evaporates a mixture of metal and argon, and over 60% of this substance is converted into UV with a spectrum of 253.7 nm, that is, with maximum effectiveness against bacteria.
Other advantages that ensure widespread use include a long service life, from 5 to 8 thousand hours. The service life of analogues is approximately 10 times shorter. Another advantage is significant unit power, reaching 1000 W, due to which the number of sources in the system can be reduced to a minimum.
And finally, another plus is a flask made of uviol or other special glass, which blocks the output of waves up to 185 nm and thus prevents O3 from entering the liquid. We will consider the design features of such lamps below.
Comparison of the main methods of disinfection: chlorination, ozonation, UV irradiation of water
All methods by their nature are divided into 3 types: they can be chemical, physical or complex (combined). The first category includes those in which soluble reagents are added to H2O that inhibit or kill microorganisms.
At the same time, saturation of the flow from the source with the same Cl has its own characteristics:
- the dosage must be strictly controlled - if there is too little of the substance, it will not have an effect, and when too much, the liquid will become toxic;
- this technology is not environmentally friendly - it pollutes the environment;
- by-products of reactions pose a threat to the body - they contribute to the formation of cancer cells and disrupt the normal functioning of vital systems;
- When boiled, dioxin is released - a fairly strong poison.
SF-mix manual up to 0.8 m3/h
AMETHYST - 02 M up to 2 cubic meters/day.
Aeration unit AS-1054 VO-90
Adding O3 gives a faster effect, because the gas neutralizes bacteria in just a minute, but this method also has nuances that prevent it from becoming widely used:
- the equipment is expensive, and its operation involves high energy costs;
- the reagent is explosive, so it should be used with extreme caution;
- the liquid acquires an unpleasant odor, and it cannot be immediately supplied to the points of final consumption - it must be settled, waiting for all O3 compounds to disintegrate.
But ultraviolet water treatment, as the best example of physical technology, is free of these disadvantages. It is accessible, completely environmentally friendly, produced in a matter of seconds, has no side effects, and does not change the properties of the liquid in any way. If we compare it with other methods, it is cheaper, simpler, faster and safer to implement and that is why it dominates, being the priority option. Methods such as boiling lose even more, since their full cycle requires a significant investment of time. Combined ones involve the construction of complex equipment complexes, therefore they are suitable only for industrial production and objects similar in scale.
Disinfection technologies
Distilled water, completely purified from all foreign bacteria and minerals, is unsuitable for drinking and can be harmful to health. It contributes to the disruption of water-salt balance. There are several ways to make water safe and edible. They involve different expenditures of funds and have nuances in use. Conventionally divided into three types:
- chemical;
- physical;
- combined.
Chemical is possible using ozone, chlorine, antiseptics, silver. They are added to water and sometimes dissolved in it. They inhibit foreign bacteria, stopping their development, or neutralize them completely. One of the most common disinfectants is chlorine. Its main advantage is its low price and prolonged effect. To independently disinfect water using this method, you need knowledge of safety precautions and accurate calculations of the dosage of the active substance. An insufficient amount of the substance will kill part of the unwanted composition. The remaining bacteria receive favorable soil for reproduction. Excess chemical reagent will turn water into poison.
Negative effects of chlorination:
- promotes the growth of cancer cells;
- pollutes the environment;
- forms the poison dioxin when boiled;
- disrupts the normal functioning of the body.
The use of ozone attracts consumers. The gas can purify water from infections in a few seconds. But there are also disadvantages:
- high cost of a water treatment plant and its maintenance;
- unpleasant odor of ozone, although it does not affect water quality;
- high electricity consumption to create gas;
- explosion hazard;
- It takes time for the ozone to decompose and subsequently be transported.
Polymer reagents (antiseptics) compared to chlorine:
- safe for humans;
- preserve the fabric of the swimsuit and the integrity of the metal;
- last a long time.
Disinfection by the sorption method is possible using a carbon filter. These products are manufactured by:
- "Aquapro";
- "Aquaphor";
- "Athol."
Water purification using silver and silicon cannot be called complete. Filters simply stop the growth of bacteria. Silver, as a metal, tends to accumulate in the body. Then it is difficult to remove it from there and prevent poisoning.
The physical method allows you to purify water using sound, light or temperature influences. Boiling, which belongs to this category, is a simple and popular method. Comfortable temperature for microorganisms to live, below the boiling point. Therefore, after the procedure they become non-viable. The disadvantage of this method is that it is time-consuming. You have to sit and wait until the water cools down. Ultraviolet filters are also representatives of this category.
The combined system involves disinfecting liquids using several different barriers. Includes chemical and physical methods. At industrial and municipal enterprises, complexes are being built that make it possible to repeatedly increase the production of fluid purified from infections.
Equipment for UV water treatment
The modern choice of installations is quite rich: there are budget ones, with add-on capabilities that promise to be relevant for many years to come. And all of them (of fairly high quality) can also boast of versatility: they are used in different temperature conditions.
The most effective systems, naturally, have impressive dimensions, but it is convenient that for home use the power of equipment with a simplified design, without mechanical catches, is quite enough. She is able to cope with the task of collecting liquid from a pond or garden lake, which is subsequently used to irrigate vegetation.
How do units for ultraviolet irradiation of water work and what are the differences?
They all work according to the same scheme (already given above) - let’s briefly repeat it:
- liquid is passed through the system;
- when passing past the quartz filter cover, it is saturated with waves with a frequency of 260 nm, blocking the ability of microorganisms to reproduce;
- after which the flow is immediately distributed to the end points of consumption or, less commonly, sent to reservoirs.
The equipment differs from each other in the following parameters:
- Productivity – reduced to the speed of passage of the medium per hour; the higher it is, the better, which is understandable.
- The transmittance of waves of the required length - it directly depends on the properties of the taken H2O (it decreases in turbid or contaminated with large fractions).
- Power – expressed in the dose given at a time; as it increases, the number of source lamps required for the effective functioning of one system and a certain volume of liquid decreases.
What parts does the UV water disinfection unit consist of?
Each of them, regardless of characteristics, has the same set of basic structural components. Let's take a closer look at them.
Low pressure lamps
The generally accepted abbreviation is ND. The most popular option is mercury amalgam discharge models, in which the metal is in a bound state, along with argon, and evaporates under the influence of electricity. They are so popular because they produce a wave with a maximum effective length of 260 nm.
Quartz cases
They cover the sources (UVI) so that they do not come into contact with the liquid, and also maintain the set temperature. Must be partially transparent - with a bandwidth of 254 nm to prevent short wavelengths from reaching H2O.
Main table dispenser AquaPro 919H/RO (hot and cold water)
Main table dispenser AquaPro 929CH/RO (cooling/heating)
Floor dispenser AquaPro 311 (empty, without cooling)
electronic ballasts
These are starting devices, also responsible for regulating the lamps. The higher their quality, the greater the number of on/off cycles they provide, and the longer the system for ultraviolet disinfection of drinking water operates. For example, provided that the supply voltage is stable, it will last up to 16 thousand hours.
UV sensors
These are controllers that automatically check wave deflection and other changes that the human eye cannot detect. Their presence increases the final cost of the system, so budget installations are not equipped with them, but professional equipment simply needs them.
Remote Control
Needed to remotely set commands: connects to a PC, has a high security class, is protected from moisture and dust, and has an intuitive interface.
Disinfection chamber
It contains lamps for ultraviolet water disinfection and flow distributors that ensure normal distribution and compensation of the liquid. It must be spacious enough to accommodate these elements, as well as durable, sealed, have anti-corrosion properties, and do not emit harmful substances during operation. Typically made of duplex steel (for aggressive environments) or AISI 304 or 316 stainless steel.
Cover cleaning systems
Suspended particles stick to the casings, photochemical reactions occur on their surfaces - all this results in the appearance of contamination. To prevent them from reducing the efficiency of the equipment, they are removed - mechanically or using reagents. The first option is good because it does not require turning off the installation, but the second is more reliable and allows you to restore the optical performance of the protective housing.
How to choose the right installation for water disinfection with ultraviolet rays
There are many options, so in order not to make a mistake, you should proceed from what you personally need, which means making a purchase based on the following indicators:
- The concentration and type of microorganisms that need to be eliminated - it is important that they do not have resistance, like E. coli; plus, their quantity determines the dosage of the active substance, so it is worthwhile to conduct a contamination analysis first.
- The level of sterilization - for liquids subsequently used for food purposes, it should be 100%; for waste water, a more modest result will be sufficient.
- Ambient temperature - if it does not reach +16-20 0C, you need a model with low pressure lamps, but if it reaches 85 0C, you will need a version with medium category evaporators.
- Transparency is the number of waves with a length of 260 nm that the quartz cover can transmit and the liquid must receive.
Principle of operation
Almost all installations have a standard design based on a simple operating principle. There is a reservoir into which liquid flows. This tank has pipes. There are ultraviolet lamps in the center. When water enters this section, it is exposed to ultraviolet lamps and after that it moves on, passing through the outlet pipes.
UV sterilizers
What are UV sterilizers? This is a kind of chamber that is made of stainless steel. Inside this disinfection chamber there are ultraviolet lamps enclosed in quartz covers (they are responsible for ensuring that the UV lamp does not come into contact with water).
When water passes through this chamber, it is irradiated with ultraviolet light. It destroys absolutely all microorganisms that are present there.
Scheme of ultraviolet water disinfection
The ultraviolet water sterilizer has a cleaning system for the covers, because mineral deposits and organic deposits can accumulate on their inner surface during operation.
Manufacturers of such devices have made sure that these deposits can be cleaned without even removing the lamps. It's very convenient and safe. UV lamps can work on average for 1300-1500 hours, then the lamp should be replaced with a new one.
Irradiation with a UV lamp is absolutely safe when purifying water. This technology is considered one of the safest among reagent-free cleaning methods. Ultraviolet water disinfection is a very good alternative to chlorine cleaning.
When can you use a UV disinfectant?
Only in case of preliminary and correct preparation, otherwise the result will be either insufficiently effective or completely null. It is necessary to physically clean the flow of foreign objects, iron, hardness salts, large fractions, and E. coli. At the same time, it is important that the llama body remains uncontaminated, otherwise waves of vapors simply will not pass through it.
We will help you simplify your choice of system. Our catalog contains a wide variety of disinfection units, and during a consultation we will determine which one is best suited for your needs. Contact us, together we will make UV disinfection of drinking water as effective as possible, including from an economic and domestic point of view.
UV equipment for water disinfection
Modern installations for UV disinfection of drinking water consist of a disinfection chamber made of stainless steel. Less commonly, plastic is used for these purposes.
This vessel contains an ultraviolet lamp, protected from water getting into it with a special protective coating. During the time that the water flow is in such a filter under UV radiation, all dangerous microorganisms in the liquid are destroyed.
Such systems for UV water disinfection do not require constant human monitoring, since the provided control unit automatically turns on the lamp after water is supplied. Another advantage of modern filters is remote controls that allow you to control the operation of the system. The device is also capable of signaling any malfunctions that have occurred.
Let's talk separately about installations for sterilization of wastewater. They are large in size, and before entering the chamber there are often additional filters for preliminary mechanical purification of the incoming liquid.
Industrial devices for UV water disinfection are equipped with a large number of lamps - up to several dozen - since such systems must purify large volumes of liquid at a time.
It is necessary to regularly replace lamps and clean quartz protective covers. The fact is that various types of deposits accumulate on the covers, which reduce the effect of UV rays. We emphasize: such an installation does not require any other maintenance.
Read material on the topic: Sorptive water purification: why is it needed and where is it used