Water is a factor that directly affects the quality of human life. A person’s mood in the morning after washing his face depends on its color and smell, and the well-being and health of the body depends on its composition.
Water, being the basis of life, easily spreads infectious diseases. To prevent the transmission of pathogens through drinking water, disinfection and disinfection of the liquid are used. These processes eliminate fungi, bacteria, bad taste and color, ensuring safe drinking water.
Purification and disinfection of drinking water for supply to residential buildings is carried out at water treatment stations of centralized water supply. There are also methods and installations for local use - in the form of small water purification systems from a well or methods that allow you to purify water collected in a bottle.
Classification of water disinfection methods
To choose the right disinfection method, contaminated water is analyzed. The number and type of microorganisms and the degree of collateral contamination are examined. The volume of water that will be treated and the economic factor are also determined.
Water that has undergone purification is transparent and colorless, odorless and has no taste or aftertaste. To achieve this effect, the following groups of methods are used:
- physical;
- chemical;
- combined.
Each group has its own distinctive characteristics, but all methods, in one way or another, allow the removal of pathogenic microorganisms from water. You can obtain detailed information on equipment for water purification and disinfection in Tyumen.
The chemical method is working with reagents added to water. Physical disinfection is carried out using temperature or various radiations. Combined methods combine the work of these two groups.
The most effective ways
Infectious safety of water is an important and pressing problem, which is why many methods have been invented to rid water of microorganisms. Disinfection methods continue to improve. They become more effective and accessible. Nowadays, the following methods are considered the best:
- heat treatment using high temperatures;
- ozonation;
- ultrasonic treatment;
- reagent methods;
- ultraviolet irradiation of liquid;
- high-power electrical discharges.
Polymer antiseptics
Another popular chemical method is the use of polymer reagents. The most famous today is Biopag. Most often it is used in public swimming pools and water parks.
The advantages of this method of water purification and disinfection:
- Does not harm human or animal health.
- Does not impart a specific odor, taste or color to water.
- Quite easy to use.
- Does not have a corrosive effect on metal.
- Does not cause allergic reactions.
Disadvantages - may irritate the skin and mucous membranes.
Physical methods of water disinfection
Before them, the water must be purified to remove suspended matter and impurities. For this purpose, coagulation, sorption, flotation and filtration are used.
This type of method includes the use of:
- ultrasound;
- ultraviolet;
- high temperatures;
- electricity.
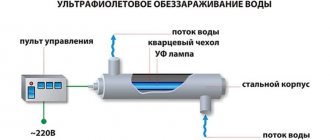
Ultraviolet disinfection
The disinfecting effect of ultraviolet radiation has been known for a very long time. Its work is similar to sunlight, which successfully destroys unadapted microorganisms outside the Earth's ozone layer. Ultraviolet radiation affects cells, creating cross-links in DNA, as a result of which the cell loses the ability to divide and dies (Fig. 2).
The installation consists of lamps placed in quartz cases. The lamps produce research that instantly destroys microorganisms, and the covers do not allow the lamps to cool down. The quality of disinfection when using this method depends on the transparency of the water: the cleaner the incoming liquid, the further the light spreads and the less the lamp becomes dirty. To do this, before disinfection, the water goes through other stages of purification, including mechanical filters. The reservoir through which the water flows is usually equipped with a stirrer. Mixing the layers of liquid allows the disinfection process to proceed more evenly.
Design of a UV disinfection installation
It is important to know that lamps and covers require regular maintenance: the structure must be disassembled and cleaned at least once a quarter.
Then the efficiency of the process will not deteriorate due to the appearance of scale and other contaminants. The lamps themselves must be replaced once a year.
Ultrasonic disinfection units
The operation of such installations is based on cavitation. Due to the intense vibrations to which water is subjected due to high-frequency sound, numerous voids are formed in the liquid, as if it “boils”. An instantaneous pressure drop leads to rupture of cell membranes and death of microorganisms.
Equipment for ultrasonic water treatment is effective, but requires high costs and proper operation. It is important that the staff knows how to handle the device - its effectiveness depends on the quality of the equipment settings.
Thermal disinfection
This method is extremely common among the population and is actively used in everyday life. Using high temperature, that is, boiling, water is purified from almost all possible pathogenic organisms. In addition to this, water hardness is reduced and the content of dissolved gases is reduced. The taste of the water remains the same. However, boiling has one drawback: the water is considered safe for about a day, after which bacteria and viruses can again settle in it.
Boiling water is a reliable and simple method of disinfection
Electric pulse disinfection
The technique is as follows: electrical discharges entering the water create a shock wave, microorganisms fall under the hydraulic shock and die. This method does not require preliminary purification and is effective even with increased turbidity. Not only vegetative, but also spore-forming bacteria die. The advantage is the long-term preservation of the effect (up to 4 months), but the disadvantage is the considerable cost and high energy consumption.
Ultrasound
The action here is based on cavitation. This is the name for the ability of a number of sound frequencies to form voids that create a large difference in pressure. This dissonance leads to rupture of the cell membranes of viruses and bacteria, which leads to the death of microorganisms. Efficiency depends on the intensity of sound vibrations.
This method is not widely used, primarily due to its high cost. Certain equipment and specially trained personnel are required. It is important to remember that ultrasound is dangerous for bacteria only at certain frequencies. Low waves, on the contrary, can cause an acceleration in the growth of the number of microorganisms in the water.
Chemical methods of water disinfection
They are based on chemical reactions that occur between a contaminant or microorganism and a reagent added to a liquid.
When using chemical disinfection, it is important to control the dose of the reagent.
It must be accurate. A lack of substance will not be able to fulfill its purpose. In addition, a small amount of the reagent will lead to increased activity of viruses and bacteria.
To improve the performance of the chemical, it is added in excess. In this case, harmful microorganisms die, and the effect lasts for a long time. The excess is calculated separately: if you add too much, the reagent will reach the consumer, and he will be poisoned.
Chlorination
Chlorine is widespread and used in water treatment in many countries around the world. It successfully copes with any volume of microbiological contaminants. Chlorination leads to the death of most pathogenic organisms and is cheap and accessible. In addition, the use of chlorine and its compounds makes it possible to extract metals and hydrogen sulfide from water. Chlorination is used in municipal drinking water systems. It is also used in swimming pools where large numbers of people gather.
However, this method has a number of disadvantages. Chlorine is extremely dangerous, causes cancer and cell mutations, and is toxic. If excess chlorine does not disappear in the pipeline but reaches the public, it can lead to serious health problems. The danger is especially strong during transition periods (autumn and spring), when, due to increased pollution of surface waters, the dose of the reagent during water treatment is increased. Boiling such water will not help avoid negative consequences, but on the contrary, chlorine will turn into dioxin, which is a powerful poison. In order to allow excess chlorine to evaporate, tap water is collected in large containers and left for a day in a well-ventilated area.
Ozonation
Ozone has a strong oxidizing effect. It penetrates the cell and destroys its walls, leading to the death of the bacterium. This substance is not only a strong antiseptic, but also discolors and deodorizes water and oxidizes metals. Ozone works quickly and gets rid of almost all microorganisms in water, surpassing chlorine in this characteristic.
Ozonation is considered the safest and most effective method, but it also has several disadvantages. Excess ozone leads to corrosion of metal parts of equipment and pipelines, equipment wears out and breaks down faster than usual. In addition, the latest research notes that ozonation causes the “awakening” of microorganisms that were in conditional hibernation.
Scheme of the ozonation process
The method is characterized by high installation costs and high energy consumption. To work with ozonizing equipment, highly qualified personnel are required, because the gas is toxic and explosive. In order to release water to the population, it is necessary to wait out the period of ozone decay, otherwise people may suffer.
Disinfection with polymer compounds
No harm to health, destruction of odors, tastes and colors, long duration of action - the listed advantages relate to disinfection using polymer reagents. This type of substance is also called polymer antiseptics. They do not cause corrosion or damage the fabric, do not cause allergies and are effective.
Oligodynamy
It is based on the ability of noble metals (such as gold, silver and copper) to disinfect water.
The fact that these metals have an antiseptic effect has been known for a long time. Copper and its alloys are often used in field conditions when it is necessary to individually disinfect a small volume of liquid.
For a more extensive effect of metals on microorganisms, ionizers are used. These are flow devices operating on the basis of galvanic couple and electrophoresis.
Disinfection with silver
This metal is considered to be one of the most ancient methods of water disinfection. In ancient times, it was widely believed that silver could cure any disease. It is now known that it has a negative effect on many microorganisms, but it is not known whether silver destroys protozoan bacteria.
This product gives a visible effect in water purification. However, it negatively affects the human body when accumulated in it. It’s not for nothing that silver has a high hazard class. Disinfection of water with silver ions is not considered a safe method, and therefore is practically not used in industry. Silver ionizers are used in isolated cases in everyday life for processing small volumes of water.
Compact household water ionizer (silverizer)
Iodination and bromination
Iodine is widely known and used in medicine since ancient times. Scientists have repeatedly tried to use its disinfecting effect in water treatment, but its use leads to an unpleasant odor. Bromine copes well with almost all known pathogenic microorganisms. But it has a significant drawback - high cost. Due to their disadvantages, these two substances are not used for treating wastewater and drinking water.
Physical methods
This will include non-chemical methods of influencing microorganisms in liquids. Their use is most often preceded by filtration and coagulation of water. This removes suspended particles, worm eggs, and a significant portion of the microbes in the liquid.
The most common methods:
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
- Impact of ultrasound.
- Boiling. An effective way to disinfect water in natural conditions.
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Combined methods of water disinfection
Integrated methods rely on a combination of physical and chemical methods to improve performance. An example is a combination of ultraviolet radiation and chlorination (sometimes chlorination is replaced by ozonation). UV lamps destroy microorganisms, and chlorine or ozone prevent their re-occurrence. In addition, oxidation and heavy metal treatment work well together. The oxidizing reagent disinfects, and metals prolong the bactericidal effect.
Combination of UV disinfection and ultrasound action
Cleaning methods
First of all, let us note the fact that complete purification of all elements contained in it (including bacteria) will make the liquid completely unsuitable for drinking and cooking. Therefore, you need to wisely choose a method of water disinfection and be confident in its high-quality implementation.
Disinfection should always be preceded by a chemical and biological examination of the liquid. Based on its results, one of the disinfection methods is chosen:
- Chemical, reagent.
- Combined.
- Reagent-free, physical.
Each of them is a method of water disinfection, but according to its own specific method. For example, chemical is exposure using coagulant reagents, physical methods are reagent-free exposure. There are also innovative ones that we will definitely examine throughout the material.
An interesting use of combined methods is the use of both physical and chemical cleansing alternately. It is considered today the most effective in disinfection - not only allows you to get rid of bacteria, but also helps prevent them from returning. The use of several methods of water disinfection also guarantees its purification from the maximum amount of pollutants.
How to disinfect water at home
There are five ways to quickly disinfect a small volume of water:
- boiling;
- adding potassium permanganate;
- use of disinfectant tablets;
- use of herbs and flowers;
- infusion with silicon.
Potassium permanganate is added to water in an amount of 1-2 g per bucket of water, after which the contaminants precipitate.
Special tablets for destroying microorganisms are used to neutralize water from a well, well or spring. They are the most modern method, accessible, inexpensive and effective. Many tablets, such as the Aquatabs brand, can be used to purify large volumes of liquid.
If water needs to be disinfected while hiking, you can use special herbs: St. John's wort, lingonberry, chamomile or celandine.
You can also use silicon: it is placed in water and left for a day.
Cleaning with plant materials
Some plants (or parts thereof) contain substances that inhibit the activity of pathogenic microflora:
- birch bark, oak, willow or willow bark. Mix 100-150 g of plant material with 10 liters of water and boil for 30-40 minutes or leave for 6 hours;
- young branches of pine, spruce or juniper. They can be prepared in a similar way;
- red rowan leaves. You need to add them to the water at the rate of 10-20 pieces for every 2-3 liters and leave for 2 hours.
Regulatory documentation in the field of drinking water safety
The state strictly controls water quality through regulations, rules and restrictions. The basis of legislative acts in the field of protection of water resources and control of the quality of water used are two documents: the Federal Law “On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population” and the Water Code.
The first law contains requirements for the quality of water supply sources from which water is supplied to residential buildings and for agricultural needs. The second document describes the standards for the use of water sources and instructions for ensuring their safety, and also defines penalties.
GOST standards
GOSTs describe the rules by which the quality of waste and drinking water must be monitored. They contain methods for conducting analyzes in the field, and also allow you to divide waters into groups. The most important GOSTs are presented in the table.
SNiPs
Building codes and regulations determine the requirements for the construction of water treatment facilities and for the installation of various types of pipelines and water supply systems. The information is contained in SNiPs under the following numbers: SNiP 2.04.01-85, SNiP 3.05.01-85, SNiP 3.05.04-85.
SanPiNy
Sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations contain hygienic requirements for the quality of various groups of water, composition, water intake structures and location of water intakes: SanPiN 2.1.4.559-96, SanPiN 4630-88, SanPiN 2.1.4.544-96, SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1 .1.984-00.
Thus, the effectiveness of tap water disinfection is monitored with established regularity and in accordance with many rules and regulations. And a large number of different methods for disinfecting fresh water allow you to choose the best option for any conditions. What makes properly purified and treated water safe for human consumption.
Disinfection of drinking water in field conditions
Boiling is the easiest way to purify water in the field. At temperatures above +85 ºC, all pathogenic microbes and parasites die within 5–30 minutes. Cover the container with a lid and reduce the heat to low (the liquid will evaporate less).
Boiling can be replaced by placing hot stones in a bowl of water. They are left to cool completely.
Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate powder) is the most reliable method of disinfection. It destroys bacteria and their metabolic products.
Throw a few crystals into 4 liters of water. The solution is made barely pink, the concentration of the drug should be 0.01–0.1%. The liquid is allowed to settle for 0.5–1 hour, and the upper 2/3 parts are used for drinking. The remainder is poured out.
In field conditions, disinfection is also carried out using “emergency” methods:
- iodine - 15 drops/1 l;
- hydrogen peroxide - 1-2 tbsp. l/1 l.
Leave water with iodine, potassium permanganate or peroxide for 30 minutes. Then it is passed through a homemade activated carbon filter. This will improve the taste.