In psychology, the concept of personality is one of the most important, since this science deals with the study of man as a subject of the social environment. It has long been established that each human body is individual from a physiological and psychological point of view. The concept of individuality allows each person to be considered unique. However, this concept itself comes into force only in the process of human interaction with other people.
By personality is meant an exclusively social being that is capable of coming into contact with other individuals. Personal characteristics tend to change depending on the situation, but this concept is an indivisible structure. In psychology and psychiatry, the subject of study is the individual, in contrast to other medical sciences, where actions are aimed at human physiology.
The psychological structure of a person determines the qualities that characterize a particular person to a greater extent. The totality of such properties and parameters represents a complete psychological picture of an individual. A lot of theories are being created that try to fully embrace the structure of personality. Some of them are immediately forgotten, but most continue to develop and improve. For psychology, the most characteristic is the basic model, which is based on the starting criteria that determine personality:
- Self-awareness. This is a person’s ability to be aware of his own “I” and its distinctive features. Self-awareness confirms that a person’s personality is unified and stable.
- Directionality. The concept implies the presence of any main or priority goals and objectives of the individual. This also includes the attitude towards oneself, loved ones, tastes, smells, work activities and other significant components.
- Temperament. An innate quality that is based on the predominance of the processes of excitation and inhibition of the nervous system.
- Character. Partially hereditary, but largely acquired personality trait that determines the characteristics of behavior or response in a given situation.
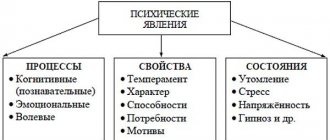
- Mental processes and states. This includes basic cognitive functions: sensation, perception, inference and others.
- Capabilities. This refers to a person’s innate predisposition to a particular activity.
- Experience of a psychological nature. Personality is capable of changing and adapting to changes in the surrounding world, as well as under the influence of experience. As you grow older, your values and sometimes even your tastes change.
The intellectual abilities of the brain play an important role in the formation of personality, and their development has a positive effect on the person as a whole. You can improve most brain functions using the BrainApps resource, which contains more than 100 games developed by professional psychologists.
Psychological structure of personality
Personal structure in psychology is characterized through certain psychological properties, without particularly affecting its relationship with society and the entire world around it.
Personality structure in psychology briefly. There are several components in personality psychology.
The first component of structure is directionality. The focus structure covers attitudes, needs, interests. One component of orientation determines human activity, that is, it plays a leading role, and all other components rely on it and adapt. For example, a person may have a need for something, but, in fact, he has no interest in a certain subject.
The second component of the structure is capabilities. They give a person the opportunity to realize himself in a certain activity, achieve success and new discoveries in it. It is the abilities that constitute a person’s orientation, which determines his main activity.
Character, as a manifestation of personality behavior, is the third component of the structure. Character is the property that is most easily observed, so a person is sometimes judged simply by her character, without taking into account abilities, motivation and other qualities. Character is a complex system that includes the emotional sphere, intellectual abilities, volitional qualities, and moral qualities that mainly determine actions.
Another component is the self-regulation system. Self-control of a person ensures proper planning of behavior and correction of actions.
Mental processes are also part of the personality structure; they reflect the level of mental activity, which is expressed in activity.
Focus and motivation
The result of an individual’s activity depends on motivation, which can be external and internal.
Extrinsic motivation may involve gaining approval from others. Intrinsic motivation lies in the interest of the individual himself to complete a specific task. Internal motivation has a much better effect on a person, because in this way he develops himself. The better motivated a person is, the more he believes in his own abilities and the more desire he has to work to achieve his goal. It is extremely important that a person understands why he is doing his work, only in this case he will do it efficiently. If work does not provide any benefits and does not bring you closer to the goal, then any person will quickly get bored with it
Social structure of personality
When defining personality in sociology, it should not be reduced exclusively to the subjective side; the main thing in the structure is social quality. Therefore, a person must determine objective and subjective social properties that form his functionality in activities that depend on the influence of society.
Personality structure in sociology briefly. It constitutes a system of properties of an individual, which are formed on the basis of his various activities, which are influenced by society and those social institutions in which the individual is included.
Personal structure in sociology has three approaches to designation.
Within the first approach, a person has the following substructures: activity - purposeful actions of a person in relation to some object or person; culture – social norms and rules that guide a person’s actions; memory is the totality of all knowledge acquired through life experience.
The second approach reveals the personal structure in the following components: value orientations, culture, social status and roles.
If we combine these approaches, then we can say that personality in sociology reflects certain character traits that it acquires in the process of interaction with society.
Types
There are several main personality types:
- Socialized - which are adapted to the conditions of social life.
- Desocialized - who deviate from the requirements of society. These include marginalized individuals. The problem of the individual in this case is non-acceptance by society.
- Mentally abnormal are persons who have some delays in mental development, psychopaths. Here the personality problem is that people try to avoid such persons.
A socialized normal entity has a number of features. She has autonomy, assertion of her own individuality. If critical situations arise, the socialized nature retains its strategy and does not change its life principles and positions. If extreme situations and psychological breakdowns arise, such a nature can prevent the consequences by reassessing values. The concept of such a personality involves maintaining an optimal mood in any situation.
If an individual is mentally balanced, then he builds friendly relationships with other people and is altruistic in relation to their needs. When constructing life plans, a normal nature proceeds from reality and has a sense of honor and justice. She is persistent in achieving her goals and can easily adjust her own behavior. The sources of success or failure for her are herself, and not external circumstances.
If difficult situations arise, a well-developed individual is able to take responsibility and take reasonable risks. So, the human essence is something that has a consciousness of its own isolation, which allows it to be free from the dictates of power and remain calm under any conditions. Such personality abilities make it strong and contribute to further development. The core is spirituality, which is represented by the highest manifestation of human essence, commitment to morality.
Personality structure according to Freud
The structure of personality in Freudian psychology has three components: Id, Ego and Super Ego.
The first component of the Id is the oldest, unconscious substance that carries human energy, responsible for instincts, desires and libido. This is a primitive aspect, operating on the principles of biological attraction and pleasure, when the tension of sustained desire is discharged, it is carried out through fantasies or reflex actions. It knows no boundaries, so its desires can become a problem in a person’s social life.
The Ego is the consciousness that controls the It. The ego satisfies the desires of the id, but only after analyzing the circumstances and conditions, so that these desires, when released, do not contradict the rules of society.
The super ego is the repository of a person’s moral and ethical principles, rules and taboos that guide his behavior. They are formed in childhood, approximately 3–5 years, when parents are most actively involved in raising the child. Certain rules are fixed in the ideological orientation of the child, and he supplements it with his own norms, which he acquires in life experience.
For harmonious development, all three components are important: Id, Ego and Super Ego must interact equally. If any of the substances is too active, then the balance will be disrupted, which can lead to psychological abnormalities.
Thanks to the interaction of the three components, protective mechanisms are developed. The main ones are: denial, projection, substitution, rationalization, formation of reactions.
Denial suppresses the internal impulses of the individual.
Projection is the attribution of one's own vices to others.
Substitution means replacing an inaccessible but desired object with another, more acceptable one.
With the help of rationalization, a person can give a reasonable explanation for his actions. Formation of a reaction is an action used by a person, thanks to which he takes an action opposite to his forbidden impulses.
Freud identified two complexes in the personality structure: Oedipus and Electra. According to them, children view their parents as sexual partners and are jealous of the other parent. Girls perceive their mother as a threat because she spends a lot of time with her dad, and boys are jealous of their mother before their father.
Directional forms
A person’s main life orientation is expressed in his goals for life, priorities, hobbies, worldview, and beliefs. Let's consider all forms of directionality:
Wish
This form implies not only the desired object, but also the methods of obtaining it. Also, the desires of the individual give rise to the formation of goals.
Pursuit
It is a desire with a deliberate choice and a plan to achieve what you want.
Interest
This is a focus on learning new information, a manifestation of a person’s cognitive needs.
Addiction
It is expressed in a person’s desire to engage in any particular activity. As a result, he improves his skills in his chosen field to achieve success.
Worldview
Includes views on life, as well as a person’s place in it.
Belief
A form of direction that encourages a person to act in accordance with his views on life.
Ideal
An ideal image for a person, which he strives to embody.
Installation
The attitude can be: positive, negative, neutral and consists of a person’s outlook on life and values.
Position
Includes the motives and desires of a person that guide him in life.
Target
The result that a person wants to achieve in his activities.
Personality structure according to Rubinstein
According to Rubinstein, personality has three components. The first component is directionality. The structure of orientation consists of needs, beliefs, interests, motives, behavior and worldview. A person’s orientation expresses his self-concept and social essence, orients a person’s activity and activity regardless of specific environmental conditions.
The second component consists of knowledge, ability and skills, the main means of activity that a person acquires in the process of cognitive and objective activity. Having knowledge helps a person to navigate well in the outside world; skills ensure the execution of certain activities. Skills help achieve results in new areas of subject activity; they can be transformed into abilities.
Individual - typological properties constitute the third component of personality; they manifest themselves in character, temperament and abilities, which ensure the originality of a person, the uniqueness of his personality and determine behavior.
The unity of all substructures ensures adequate functioning of a person in society and his mental health.
Also in a person, it is possible to determine certain levels of organization that implement it as a subject of life. Living standard - it includes life experience, moral standards, and worldview. The personal level consists of individual characterological features. The mental level consists of mental processes and their activity and specificity.
For Rubinstein, personality is formed through interaction with the world and society. The core of personality includes the motives of conscious actions, but also, a person has unconscious motives.
Personality structure according to Jung
Jung identifies three components: consciousness, the individual unconscious and the collective unconscious. In turn, consciousness has two substructures: the persona, which expresses the human “I” for others, and the self as it is – the ego.
In the structure of consciousness, the person is the most superficial level (conformity archetype). This component of the personality structure includes social roles and statuses through which a person is socialized in society. This is a kind of mask that a person puts on when interacting with people. With the help of persona, people attract attention to themselves and make an impression on others. Behind external signs, symbols of covering oneself with clothes, accessories, a person can hide his true thoughts, he hides behind external properties. Symbols of confirmation of social status are also important, for example, a car, expensive clothes, a house. Such signs can appear in the symbolic dreams of a person worried about his status, when he dreams, for example, that an object that he is afraid of losing in real life, he loses it in a dream. On the one hand, such dreams contribute to an increase in anxiety and fear, but on the other hand, they act in such a way that a person begins to think differently, he begins to take the thing lost in a dream more seriously in order to preserve it in life.
The ego is the core of personality in its structure and combines all the information known to a person, his thoughts and experiences, and is now aware of himself, all his actions and decisions. The ego provides a sense of coherence, the integrity of what is happening, the stability of mental activity and the continuity of the flow of feelings and thoughts. The ego is a product of the unconscious, but is the most conscious component because it acts from personal experience and based on acquired knowledge.
The individual unconscious is thoughts, experiences, beliefs, desires that were previously very relevant, but having experienced them, a person erases them from his consciousness. Thus, they faded into the background and remained, in principle, forgotten, but they cannot simply be repressed, therefore the unconscious is a repository for all experiences, unnecessary knowledge and transforms them into memories, which will sometimes come out. The individual unconscious has several component archetypes: shadow, anima and animus, self.
The shadow is the dark, bad double of the personality; it contains all the vicious desires, evil feelings and immoral ideas, which the personality considers very low and tries to look less at his shadow, so as not to face his vices openly. Although the shadow is a central element of the individual unconscious, Jung says that the shadow is not repressed, but is another human self. A person should not ignore the shadow, he should accept his dark side and be able to evaluate his good traits in accordance with those negative ones hiding in the shadow.
The archetypes representing the beginnings of women and men are the anima, which is represented in men, the animus - in women. The animus gives women masculine traits, for example, strong will, rationality, strong character, while the anima allows men to sometimes show weaknesses, lack of strength of character, and irrationality. This idea is based on the fact that the bodies of both sexes contain hormones of the opposite sexes. The presence of such archetypes makes it easier for men and women to find a common language and understand each other.
Chief among all individual unconscious archetypes is the self. This is the core of a person, around which all other components are gathered and the integrity of the personality is ensured.
Jung said that people confuse the meaning of ego and self and give more importance to the ego. But the self will not be able to take place until the harmony of all components of the personality is achieved. The self and ego can exist together, but the individual needs certain experiences to achieve a strong ego-self connection. Having achieved this, the personality becomes truly holistic, harmonious and realized. If a person’s process of integration of his personality is disrupted, this can lead to neuroses. And in this case, analytical psychotherapy is used, aimed at optimizing the activities of the conscious and unconscious. Basically the goal of psychotherapy is to work with the "extraction" of the unconscious emotional complex and work with it so that the person rethinks it and looks at things differently. When a person becomes aware of this unconscious complex, he is on the path to recovery.
Professional orientation
Each profession requires the possession of specific character traits that are necessary to achieve success in that field. In psychology, several personality types are defined:
Realistic type
They prefer physical labor and working with real objects. The following professions suit them most: builder, technician, mechanic.
Conventional type
The personality is attentive, focused and calm in nature. Such people are responsible and always complete their work on time. Preferred professions: librarian, merchandiser.
Intelligent type
These people love to think and learn new information. They love to do research work. The most suitable professions: teacher, writer.
Enterprising type
Such individuals have leadership qualities and are excellent at managing. The following professions are suitable: manager, businessman.
Social type
People with a well-developed sense of empathy who strive to help others. The following professions are suitable: doctor, social worker.
Artistic type
Such individuals do not like to work according to a schedule and put themselves into any kind of framework. They are unpredictable and creative. Best professions: artist, poet.
Personality structure according to Leontiev
The concept and structure of personality in A. N. Leontyev goes beyond the plane of relations to the world. Behind its definition, personality is another individual reality. This is not a mixture of biological features, it is a highly organized, social unity of features. A person becomes a personality in the process of life activity, certain actions, thanks to which he gains experience and socializes. Personality is experience itself.
Personality is not a complete person, as he is with all his biological and social factors. There are features that are not included in personality, but until it has manifested itself it is difficult to say in advance. Personality appears in the process of relations with society. When a personality arises, we can talk about its structure. The entire personality is a connected, integral unity, independent of the biological individual. An individual is a unity of biological, biochemical processes, organ systems, their functions; they do not play a role in the socialization and achievements of the individual.
Personality, as a non-biological unity, arises in the course of life and certain activities. Therefore, what emerges is the structure of the individual and a personal structure independent of him.
Personality has a hierarchical structure of factors formed by the historical course of events. It manifests itself through the differentiation of different types of activities and their restructuring, in the process secondary, higher connections arise.
The personality behind A. N. Leontiev is characterized as a wide variety of actual relationships of the subject that determine his life. This activity forms the foundation. But not all a person’s activities determine his life and build his personality. People do many different actions and deeds that have no direct relation to the development of the personal structure and may simply be external, not truly affecting the person and not contributing to its structure.
The second thing through which a personality is characterized is the level of development of connections between secondary actions, that is, the formation of motives and their hierarchy.
The third characteristic that denotes personality is the type of structure; it can be monovertex or polyvertex. Not every motive for a person is the goal of his life, is not his pinnacle, and cannot withstand the entire load of the pinnacle of personality. This structure is an inverted pyramid, where the top, together with the leading life goal, is at the bottom and bears all the load that is associated with achieving this goal. Depending on the main life goal set, it will depend on whether it can withstand the entire structure and the actions associated with it and the experience gained.
The basic motive of the individual must be defined in such a way as to support the entire structure. The motive sets the activity; based on this, the personality structure can be defined as a hierarchy of motives, a stable structure of the main motivational actions.
A.N. Leontiev identifies three more basic parameters in the personal structure: the breadth of a person’s relationships with the world, the level of their hierarchy and their joint structure. The psychologist also highlighted one interesting aspect of the theory, such as the rebirth of personality, and an analysis of what happens to it at this time. A person masters his behavior, new ways of resolving motivational conflicts that are associated with consciousness and volitional properties are formed. An ideal motive that is independent and lies outside the vectors of the external field, which is capable of subordinating actions with antagonistically directed external motives, can resolve the conflict and act as a mediating mechanism in mastering behavior. Only in the imagination can a person create something that will help him master his own behavior.
Types of directionality
In psychology, the presence of several types of orientation is noted. It can be determined by a person’s behavior in various situations. Main types of focus:
PERSONAL
People with this orientation consider self-realization to be the main thing in life and are always busy achieving their own goals. They are often called selfish, because they do not care about the problems of others. Such people have character traits such as determination, confidence, responsibility, and independence. They do not ask for help from others, but prefer to deal with all problems on their own.
COLLECTIVE
It is focused on communication and mutual actions; such people are usually sociable
For such individuals, communication is extremely important, and they do everything to maintain good relationships with others. They participate in group work, but do not take a leadership position and avoid responsibility
Such a person depends on the opinions of the people around him, does everything to gain approval and usually does not express his own opinion.
BUSINESS
Such people are extremely demanding of themselves and others and are always looking for benefits for themselves and their team. They prefer to lead, while always providing help and support to their subordinates. Such people love society, communicate a lot with people, but at the same time they love freedom and always express and prove their point of view.
EMOTIONAL
Such people often worry, even without reason, and are not indifferent to the problems of others. They have a well-developed sense of compassion, so they can always listen and support. People often turn to them for advice, because such people are relatable and inspire trust. Also, mostly these are creative individuals who love music, literature and painting. They are able to live the life of a hero, experiencing all his experiences.
SOCIAL
Such individuals cannot live without society and always lead active social activities. They are always aware of all events and love communication. People with a socially oriented personality can be both bosses and subordinates, but their work must be connected with society.