Conventions adopted for landscaping projects
Coniferous trees Deciduous shrubs Curtains and massifs
continuation of Appendix A
continuation of Appendix A
continuation of Appendix A
Shrub hedges
continuation of Appendix A
end of Appendix A
Fences, slopes, pergolas, garden benches, stairs, etc.
The number of annuals planted in flower beds per unit area depends on their size and type of flower bed. Correctly calculating the number of plants needed for a given area is very important, since if planted too sparsely, the flower garden will look empty and ugly, and if planted too densely, the plants will be uncomfortable: in dense plantings they stretch out, bloom weaker and are more susceptible to disease. Everything is simple when calculating the quantity based on the size of the plant itself in adulthood, thus all annuals are divided into tall, low and medium-sized.
Annuals such as snapdragon, zinnia, lavatera, aster are classified as medium-sized flowers and are planted in flower beds, ridges, mixed borders (mixborders) at the rate of 9 - 16 pieces per 1 m2 or 25 - 35 cm between plants, depending on the shape of the bush.
Low-growing annuals, such as ever-flowering begonia, lobelia, petunia, purslane (rug), carnation, low-growing varieties of ageratum, marigolds at the rate of 20-40 pieces per 1 m2 or 15-25 cm from each other.
Tall summer plants, such as kochia, castor beans, decorative sunflowers, and tobacco are planted in masses on the lawn or near buildings at the rate of 4-6 pieces per 1 m2 or 40-50 cm between plants.
Perennial plants have slightly different specifics. When planting, it is necessary to take into account not only their size, but also their growth pattern. Based on this characteristic, perennials are divided into dense-bush, loose-bush and rhizomatous (the most aggressive). Dense bushes, such as echinacea and Chinese miscanthus, form a dense, slowly growing bush. From 4-10 plants can be planted per 1m2. Loose bushes, for example phlox and daylilies, form a loose, wide, but not very “spreading” bush. These perennials can be planted from 1 to 4 per 1 m2. Another variety of perennials are cushion or ground cover plants, such as phlox subulate, sedum, tenacious, and saxifrage. In order to quickly create a “rug” effect, plants are planted in heaps or, in professional terms, clumps of 16 to 25 pcs per 1 m2. In rock gardens, they can be planted 1-2 pieces near beautiful boulders or in a row at the base of a retaining wall or at the top.
Planting material for flower beds should be purchased or grown with a small reserve - usually 10-15% more than the required number of seedlings, taking into account possible waste during transportation or during the establishment process.
Classification of plants for landscape design
Despite the main criteria according to which vegetation is selected to decorate a garden area (personal preferences, style direction of the chosen design, climate, etc.), some designers improvise and are quite successful in this direction.
Because of this, most plants are classified into certain types.
Trees
A very successful and popular option for improving the area around the house would be to plant fruit trees. Apple trees, pear trees, plum trees, walnut trees and others can be a good alternative. You can also use their deciduous relatives - linden, birch, maple, oak and some others. Quite often, when designing landscape design, they resort to variations of coniferous trees. Such unpretentious dwarf fir trees and pines, cypresses, thujas and junipers are very popular, as they do not require special care and look decent throughout the year. They look great in combination with other plants, and also look great as individual decorations.
Popular articles Hydrangea Phantom: description, planting and careEvergreens can be very useful - they are an excellent air filter, filling it with useful resinous substances, and emit a pleasant light aroma.
Choosing trees for the garden
Shrubs
Shrubs are able to structure a landscape design and define its boundaries. Most often they find their use in creating hedges and borders, successfully harmonizing in flower arrangements with other representatives of the flora. Shrubs are self-sufficient, and therefore can act as individual specimens. The most common are rose bushes, vines, lilac bushes, jasmine, Louisania, spirea and others.
Shrubs for alpine slides
Ampelous plants
An excellent variation for decorating walls or other vertical structures, indispensable for decorating gazebos, pergolas, trellises, trellises, etc. Climbing plants - vines, wild grapes - are considered the best option. And in the case of hanging pots or baskets, for example, petunias, geraniums, begonias, and surfinias are perfect. These rich flowers create an atmosphere of brightness and airiness.
Hanging plants at the entrance to the house
aquatic plants
This group of plants grows in aquatic conditions in almost any climate, depending on the variety or species. The structure of these plants allows you to decorate an artificial pond with their leaves and flowers floating on the surface
Landscape designers most often suggest paying attention to water lilies, water lilies, and Indian eland
Plants for ponds
Perennials
More often, this type includes ground cover plants that fit well into any landscape style, form a bright cover in the garden area, partially prevent the growth of weeds, and perform a decorative function. Vivid examples of perennials for landscape design include hybrid aquilegia, aconite, alyssum, pearl anafalis, alpine arabis, armeria and others.
Simple perennial plants
Sketch plan drawing rules
The sketch plan provides a graphic design of the functional areas of the site (paths, flower beds, ponds, etc.).
When compiling it, you should adhere to the following rules:
- First of all, take into account the ability to move freely between zones and care for plants.
- Coordinate with the location of structures and utilities.
- Consider the illumination of individual zones throughout the day.
- Take into account the attractiveness depending on the viewing angle and the compositional unity of the elements.
- The landscape is divided into zones taking into account the anatomical features of the human body and its size.
- Take into account the combination of colors and the change in shades on different backgrounds.
- Make 1 accent.
- Stick to style.
When is a plan needed?
When planning the installation of water supply or other utilities, it is not enough to have a landscape drawing of the site. Builders need to navigate according to the finished dendroplane . Often the laying of pipes is impossible without approval from local governments. To do all the work according to the law, you will need to pre-order the drawing up of a dendroplane. Without a site plan, you cannot begin cutting down existing trees. Only after drawing up a dendro project do regulatory authorities issue a felling permit.
Before inviting a developer to your plot of land, he needs to be shown a dendroplane. Professional builders are required to fit the house into the existing landscape with minimal damage to nature. The law states that in the event of damage to trees, the company is obliged to compensate for the damage. To make a claim, you will need a dendroplan of the site.
When calling a landscape design specialist, you can order a dendroplane as the main reference point. The second name of this document is the landing plan. Based on it, you can accept the final landscaping work. A professional designer must know the permissible distances between different types of green spaces and correctly position trees in relation to residential buildings.
A landscape designer can suggest a variety of styles, with a predominance of climbing or deciduous plants. The style determines the presence of a dominant type of planting. These can be coniferous shrubs or flowering plants. Most often, customers choose the orchard style.
When work is carried out in accordance with a clear plan, the result is cheaper and faster. A correctly drawn up dendro project helps a creative person to better imagine the future arrangement of all plants to give his garden an artistic appearance.
Legend
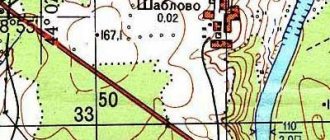
A well-drawn dendrological site plan begins with an indication of the exact scale. Popular options are 1:100 and 1:200 scale plans. The first number means the centimeter of the plan. The second number corresponds to the footage of the site itself. Sometimes there are miniature dendroplanes on a scale of 1:500.
A large scale of 1:100 is used in cases where it is necessary to indicate tree species, trunk height and thickness parameters. At this scale, each tree is drawn separately by the designer. The 1:500 dendroplane is distinguished by the fact that all green spaces are marked only by circles of various diameters. Circles have different meanings:
- A tree that is ready to be cut down is completely painted over.
- The transfer is indicated by half a circle.
- If a plant needs to be saved, it is marked with an empty circle.
Basic plan
Based on the collected data, a basic plan is drawn up. It is drawn on graph paper using a ruler and a triangle. Accuracy is important here, and if the cuttings were done by hand, by eye, then you will need to maintain the scale. For large areas, a scale of 1:100 is suitable (1 cm on the plan corresponds to 100 cm or 1 m on the ground). For a small plot, it is more convenient to take a larger scale of 1:50 (1 cm on the plan corresponds to 50 cm or 0.5 m on the ground).
The plan marks the boundaries of the site, the position of the house and other buildings that will remain after all the transformations; The position of the trees is plotted. Useful information is indicated in the margins of the plan: north-south direction, wind rose, direction of paths (if they are clearly defined).
About fashionable figures and grass sculpture in the following video:
Properties of green spaces
The landscape design master faces the difficult task of combining plants with each other. The desired beauty does not always correspond to harmony, since plants planted too close can inhibit the growth of neighbors.
When drawing up a dendroplan, you need to take into account many rules . Form plantings, keeping in mind the future image of the site. Each young plant will grow, which means it will take up more space than at the time of planting. There are computer programs that show what any tree will look like in a year or five years. This provides a good opportunity to see the future of your garden and make adjustments to the planting plan.
When planting trees, you need to know in advance the size of the crown and root system. The selection of green spaces is made depending on the seasons of the year and the calculation of climatic conditions. Many plants have different needs for water, sun and shade. It is advisable not to place two types of plants together, which have different temperature conditions and watering needs. It is advisable to plant heat-loving species with their own kind, sending them to the sun, while delicate species are best hidden in the shade of the house.
If you add calculations of the sun's movement to the plan, you can determine the places where the shadow is cast the longest. It must be remembered that a young tree does not create as much shade as it will provide in the future. If it covers a significant space, many plants will grow worse in its shade.
Green spaces need to be able to be combined with each other, because each tree or bush has a different effect on the living creatures around it. Properly combined plants help each other develop. Plant compatibility has its own rules. To identify a professional among landscape designers, you can ask him questions about compatibility. A master who has studied this issue deeply is able to warn about poor compatibility of planned plantings.
Knowledge of the biological symbiosis of plants allows you to create a favorable microclimate for plants due to the location of friendly neighbors. Some species are frost-hardy, while others love warmth. It must be remembered that exotic plants may not take root in a temperate climate, so you will have to abandon many species from the plant catalog for your dendroplane.
The design rules provide for the placement of paths in order to have convenient access to each type of planting. Paths are designated by one color, most often gray or pink. Asphalt areas are distinguished by their color. When planning plantings, it is advisable to avoid littering with self-seeding over a large area. Over time, the crowded sector will require more and more effort and attention. Shrubs planted too close not only interfere with each other, but also spoil the appearance. A well-designed graphic design allows you to avoid unnecessary work in the future, when you have to take care of the greenery all year round.
Statement of green spaces
When carrying out new construction, it is necessary to additionally attach a transfer sheet to the planting plan. It is a table that describes the trees and shrubs located on the territory.
As a rule, the following information can be found in the tree counting sheet:
- Planting number;
- Name of the plant;
- Quantity;
- Dimensions of green space;
- Current state of the plant;
- Further actions regarding the plant;
- In case of felling, the compensation cost paid by the developer is indicated.
When creating a dendroplane, a landscape designer shows what the site will look like in a few years, at the moment when all the plants have fully taken root and exhibited their decorative properties.
A well-executed dendrological plan takes into account the characteristics of each plant. With its help, you can organize a spectacular appearance for your garden plot.
List of planting materials
An important appendix to the drawn up plan is the assortment list. It lists all types of green spaces that will be planted within the site.
Using the assortment list, an accurate calculation of the total cost of purchasing seedlings is made. The application reflects the cost of the landscape designer's work. All green spaces are divided into groups:
- Conifers.
- Deciduous.
- Fruit.
- Decorative shrubs.
- Climbing plants.
This list has internal subsections, where species and varieties of plants are sequentially indicated. All significant plants, except the smallest ones, should be included in the list. Each of them gets its own number. A well-designed dendroplane includes a short description of each plant's appearance and quality. Old and young are not separated into separate groups.
The list contains not only the name of the plant, but also its Latin version. The table shows the current height. An important reference point will be the “Crown projection” column. At the end, the optimal time for fruit ripening and flowering period are added.
The landscape designer can add tips on caring for each plant to the assortment list. This document will serve as an assistant with whom you can consult about the watering regime and spraying of each tree or shrub.
Annual and perennial flowers may not be reflected in the list, but in a dendroplane with a scale of 1:100 even flowers with their own serial number can be indicated. The more precise the scale, the more expensive the plan will be.
Balance Sheet
This annex to the dendroplane is in demand if the construction of several residential and utility premises is planned on the new site. An accounting statement is drawn up if utility lines will be installed through the site, which will be accompanied by earthworks.
This sheet lists every single plant in detail. Often the list exceeds two hundred lines. Opposite each plant are the parameters:
- Species: tree, shrub or flower.
- Diameter.
- General condition and presence of damage.
- Current and predicted altitude.
When compiling the statement, the type of tree is not indicated, but the condition is described: how alive or dried it is. Does it have visible damage and an array of dry branches? How old is the tree or shrub? Depending on this, its approximate cost is calculated. This figure is added to the compensation that the developer will have to pay if the plants are damaged during the work.
The accounting statement must show the developer the fate of all green spaces: whether they are subject to cutting down, replanting, or must be preserved in their current location.
When filling out the form, you must adhere to a certain order. Plants are added differently from the way they were planted on the site. The document divides them into separate categories. The counting sheet allows you to distribute planting material in advance, since an inexperienced gardener can easily get confused if the size of the plot is large enough.
Modern computer programs allow you to transfer examples of dendroplanes into a three-dimensional plane for improved visualization of your site. Each plant can be assigned a number directly on the picture, and then filters can be applied. Then the jumble of numbers can be hidden and only the plants can be seen. And for a professional, you can leave a version of the plan with all the numbers.
Popular articles Growing and caring for periwinkle at home
The dendroplan of the site is a detailed drawing on which each significant plant is marked. It must be drawn up when carrying out construction and engineering work. Drawing up assortment and counting sheets is an integral part of the work of a landscape designer. A professionally designed dendroplan helps you better imagine the future appearance of your garden.
https://infopedia.su/15x5a91.htmlhttps://fermer.blog/bok/blagoustroystvo/landshaftnyy-dizayn/otdelnye-elementy-landshafta/rastitelnye-elementy/17055-oboznachenija-rastenij.htmlhttps://pion.guru/ landscape/dendroplane-uchastka