Temperament
The unique abilities of people depend on the type of temperament - a set of psychological qualities. Their interaction affects the subject’s behavior in different situations, his attitude towards others, preferences, habits.
History of discovery
Even in ancient times, scientists noticed that people have both similar and different character traits.
Hippocrates was the first to come up with a classification of temperament.
This scientist explained the differences between people depending on the amount of fluids in the body. Based on his teachings, he identified 4 groups of temperament.
Classification
Types of temperament according to Hippocrates:
- Reflux. Mucus predominates in the body of such people. Because of this, they are slow, patient, and imperturbable. They avoid conflicts and do not like sudden changes.
- Melan holi. The body of such subjects is filled with black bile. Because of this, they are gloomy and taciturn. They like to be alone and do not cope well with problems. Hippocrates described them as dismal losers.
- Sangwa. Blood predominates in the body of such people. It gives them the strength to cope with difficulties and achieve their goals. Often such individuals become leaders, commanders who can lead the crowd.
- Hol. The predominant fluid in the body is bile. They are fussy and cannot sit in one place for a long time. Their mood often changes, which negatively affects their communication with others.
From this classification came the concepts phlegmatic, melancholic, sanguine, choleric. The doctrine invented by Hippocrates in ancient times is still relevant today.
Scientists changed the classification depending on new discoveries and data obtained as a result of ongoing research. For example, the Russian physiologist I.P. Pavlov argued that temperament is a dynamic characteristic of the psyche. Its differences are associated with inhibition and excitation. His classification of temperament is based on the teachings of Hippocrates, but has some differences:
- Sanguine people are people endowed with high speed, actively developing nervous processes. Sanguine people are not fussy, but they show increased activity if they are interested in something. They have a stable mood and show high performance at work.
- Melancholic people have weak processes of excitation and inhibition. Sometimes it seems that such people do not know how to enjoy little things.
- Cholerics demonstrate high speed due to the great strength of nervous processes. Such people do not have a stable mood, which is why speed is quickly lost under the influence of external factors.
- Phlegmatic people are characterized by inertia, due to the low speed of nervous processes and the high strength of excitation. This is a braking type of temperament. Pavlov called such people slow-witted, although in life they are workaholics.
Properties of temperament
To make it more convenient to study individual psychological characteristics of a person, you need to take into account the characteristics that make up temperament:
- Activity - determines the degree of performance, the ability to maintain an excited state.
- Plasticity is the ability to adapt to new circumstances and change the field of activity.
- Sensitivity - determines the reaction of the nervous system to stimuli.
- Introversion, extraversion - determine the subject’s ability to establish contact with society or remain withdrawn.
- Rigidity - stubbornness, habits, resistance to changes.
- The pace of mental processes determines the speed of speech, thinking, and mood changes.
To a greater extent, temperament is determined by a set of factors from birth. Throughout life it changes slightly.
General and individual in the human psyche
There is a saying: “Another person’s soul is darkness.” This is true only for those who do not know psychology at all. And this science is quite accurate, and it claims that there are unshakable general principles that govern the mental processes of any person. Not only the similarity of physiological structure, but also the commonality of the characteristics of the mental sphere allows us to classify all people as one species, Homo sapiens. We even go through similar stages of development and we all experience the same age-related crises and difficulties of growing up.
In psychology there is a concept of norm, although it is quite fragile. Too strong a deviation from the mental norm is considered a pathology, is recognized as a mental illness and requires the intervention of a psychotherapist or psychiatrist.
However, people are still different, and this is noticeable, one might say, with the naked eye, even to a person inexperienced in psychology. We behave differently in similar situations, we show emotions differently. There are differences in the course of cognitive processes, and in the level of intelligence, and in the volitional sphere, and in motor skills.
These features appear within the framework of general patterns, but they play an important role in creating a unique image of the individual. And at the same time, they help to understand her motives, desires, and predict behavior. That is, the individual manifests itself in general, and not only through the characteristics of behavior and external activity, but also at the internal level of consciousness.
Despite the diversity of manifestations of our psyche, when we talk about individual psychological characteristics, we primarily mean three areas: temperament, character and abilities. And if, for example, in cognitive processes the individual is only a superstructure, an addition to general patterns, then temperament, character and abilities can be considered as a manifestation of the unique uniqueness of each person.
Character
Character is a set of qualities that are resistant to external changes. Character traits influence a person’s behavior, his reactions to stimuli, and his ability to achieve his goals. Some people consider character and temperament to be the same thing, but they are two different concepts. If temperament is innate, then character is formed throughout life.
Classification in relation to others and oneself
Depending on what or to whom the character traits are manifested, scientists distinguish the following classification:
In relation to himself, an individual is:
- self-critical;
- arrogant;
- narcissistic;
- proud;
- bashful;
- unsure;
- shy.
In relation to others, the subject may exhibit:
- truthfulness;
- kindness;
- sociability;
- tact;
- openness;
- justice;
- gullibility;
- hot temper;
- loyalty;
- caring.
In relation to work, the individual exhibits:
- diligence;
- responsibility;
- hard work;
- dishonesty;
- reliability;
- restlessness;
- ambition.
If we talk about personal property, the following stand out:
- greed;
- jealousy;
- generosity;
- accuracy;
- thrift;
- sloppiness;
- cleanliness.
Accentuations
The character of an individual is more often considered from the point of view of introversion and extroversion. Classification of accentuations:
- Disthymic. A depressive quality of the psyche, under the influence of which many people commit suicide. This condition can occur after numerous problems, disappointments, or last for a long time. The second option is the most dangerous, as it can lead to the development of psychological diseases.
- Hyperthymic. This category includes cheerful, active and optimistic people. They do not like to sit in one place and are constantly interested in new things. They have many hobbies and interests. They become the life of the party because they know how to lift the spirits of those around them. They strive for power. They try to receive praise from others and respect from authorities in everything. They become active, energetic leaders.
- Excitable. People who cannot control their own desires. Since they cannot deny themselves anything, they often find themselves in unpleasant situations. When making decisions they rarely use logic and are guided by instincts and desires. They hate the shortcomings of others, which are directly mentioned during conversation. They take criticism towards themselves negatively.
- Cycloid. People who constantly rush between two states - inspired and depressed. When the mood is good, the subject tries to be among others, can make others laugh, and looks at things with optimism. When they are in a bad mood, they try to hide from society and withdraw into themselves.
- Pedantic. They do not like to manage others; they prefer to remain in the shadows. They show excellent results in their work because they approach it with great responsibility. The decision is taken for an extremely long time, calculating possible options. At the same time, they constantly grumble about people who do not know how to work like themselves.
- Stuck. Such people do not know how to forgive insults. They are vindictive and vindictive. They constantly divide those around them into friends and enemies. Show too strong a sense of ownership in relationships with their spouse.
- Demonstrative. Posers who can’t imagine their lives without everyone’s attention. They can spread false rumors and betray others in order to glorify themselves. They love to retell other people's stories, putting themselves in the main role. They do not pay attention to the experiences of others and put their own interests above all else. They often become speakers, actors, performers, and world-class stars.
- Anxious. Insecure people who constantly doubt when making decisions. They often ask others for help. They tolerate injustice towards themselves. They rarely respond to rudeness and are afraid of conflict situations.
An experienced psychologist will be able to determine the prevailing character traits and temperament using psychological tests.
How to write a term paper on speech therapy
07.09.2010 198528
These guidelines are compiled to help students gain an understanding of the content and structure of coursework in speech therapy.
Logopedia of pedagogical science that studies anomalies of speech development with normal hearing, explores the manifestations, nature and mechanisms of speech disorders, develops the scientific basis for overcoming and preventing them means of special training and education.
The subject of speech therapy as a science is speech disorders and the process of training and education of persons with speech disorders.
The object of study is a person suffering from a speech disorder.
The main task of speech therapy as a science is the study, prevention and elimination of various types of speech disorders.
Coursework in speech therapy is a student's scientific and experimental research. This type of educational activity, provided for by the educational and professional program and curriculum, contributes to the acquisition of skills in working with literature, analyzing and summarizing literary sources in order to determine the range of insufficiently studied problems, determining the content and methods of experimental research, processing skills and qualitative analysis of the results obtained. The need to complete coursework in speech therapy is due to the updating of knowledge concerning the content, organization, principles, methods and techniques of speech therapy work.
As a rule, during their studies, students must write two term papers - theoretical and practical.
The first course work should be devoted to the analysis and synthesis of general and specialized literature on the chosen topic. Based on this analysis, it is necessary to justify and develop a method of ascertaining (diagnostic) experiment.
In the second course work, it is necessary to provide an analysis of the results obtained during the ascertaining experiment, as well as determine the directions and content of speech therapy work, and select adequate methods and techniques of correction.
So, let’s present the general requirements for the content and design of coursework in speech therapy.
The initial and most important stage of working on a course project is the choice of a topic, which is either proposed by the supervisor or chosen by the student independently from a list of topics that are consistent with the areas of scientific research of the department.
Each topic can be modified, considered in different aspects, but taking into account a theoretical and practical approach. Having chosen a topic, the student needs to think through in detail its specific content, areas of work, practical material, etc., which should be reflected both in the formulation of the topic and in the further construction of the study. It should be recalled that the chosen topic may not only have a purely theoretical orientation, for example: “Dysarthria. Characteristics of the defect”, “Classification of dysgraphia”, but also take into account the practical significance of the problem under consideration, for example: “Speech therapy work on speech correction for dysarthria”. It should also be taken into account that when formulating a topic, excessive detail should be avoided, for example: “Formation of prosodic components of speech in preschoolers of the sixth year of life attending a preschool institution for children with severe speech impairments.”
The course work includes such mandatory parts as: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography and appendix.
The text of the term paper begins with the title page . An example of its design can be seen here.
Then the content of the work is given, in which the names of chapters, paragraphs, and sections are formulated in strict accordance with the content of the thesis. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the text, each subsequent chapter and paragraph begins on a new page. At the end of each chapter, the materials are summarized and conclusions are formulated.
The introduction reveals the relevance of the problem under consideration in general and the topic being studied in particular; the problem, subject, object, and purpose of the study are defined. In accordance with the goal and hypothesis, objectives and a set of research methods aimed at achieving the objectives must be defined.
The relevance of the topic lies in reflecting the current level of pedagogical science and practice, meeting the requirements of novelty and usefulness.
When defining the research problem, it is important to indicate what practical tasks it will help to implement in training and educating people with speech pathology.
The object of research is understood as certain aspects of pedagogical reality, perceived through a system of theoretical and practical knowledge. The ultimate goal of any research is to improve this object.
The subject of research is some part, property, element of an object, i.e. the subject of research always indicates a specific aspect of the object that is to be studied and about which the researcher wants to gain new knowledge. An object is a part of an object.
You can give an example of the formulation of the object, subject and problem of research:
– The object of the study is the speech activity of preschool children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The subject of the study is the features of intonation speech of children with phonetic-phonemic speech disorders.
– The research problem is to determine effective directions for speech therapy work on the formation of intonation expressiveness of speech in the system of correctional intervention.
The purpose of the study contributes to the specification of the object being studied. The goal of any research is to solve a specific problem. The goal is specified in tasks taking into account the subject of research.
The research objectives are formulated in a certain sequence, which determines the logic of the research. The research objectives are set on the basis of a theoretical analysis of the problem and an assessment of the state of its solution in practice.
The first chapter is an analysis of literary sources, which examines the state of this problem in historical and modern aspects, and presents the most important theoretical principles that formed the basis of the study.
When writing the first chapter, you should pay attention to the fact that the text of the course work must be written in a scientific style. When presenting scientific material, it is necessary to comply with the following requirements:
– Specificity – a review of only those sources that are necessary to disclose only a given topic or solve only a given problem;
– Clarity – which is characterized by semantic coherence and integrity of individual parts of the text;
– Logicality – which provides for a certain structure of presentation of the material;
– Reasoning – evidence of thoughts (why this and not otherwise);
– Precision of wording, excluding ambiguous interpretation of the authors’ statements.
A literary review of the state of the problem being studied should not be reduced to a consistent presentation of literary sources. It should present a generalized description of the literature: highlight the main directions (currents, concepts, points of view), analyze in detail and evaluate the most fundamental works of representatives of these directions.
When writing a work, the student must correctly use literary materials, make references to the authors and sources from which the results of scientific research are borrowed. Failure to provide required references will reduce your coursework grade.
As a rule, in coursework on speech therapy, references to literary sources are formatted as follows: the number of the cited source in the general list of references is placed in square brackets. For example: General speech underdevelopment is a speech pathology in which there is a persistent lag in the formation of all components of the language system: phonetics, vocabulary and grammar [17].
When using quotations, in square brackets, in addition to indicating the source number, the page number from which this excerpt is taken is indicated, for example: Speech rhythm is based on a physiological and intellectual basis, since, firstly, it is directly related to the rhythm of breathing. Secondly, being an element that performs a communicative function, “correlates with meaning, i.e. controlled intellectually” [23, P.40].
However, course work should not be of a purely abstract nature, so you should not abuse the unreasonable abundance of citations. Quoting should be logically justified, convincing and used only when really necessary.
In the second chapter , devoted to experimental research, the organization should be described and the program of the ascertaining experiment should be presented. The survey methodology, as a rule, consists of a description of several series of tasks, with detailed instructions, visual and lexical material, the procedure for completing tasks by experiment participants, and scoring criteria. This chapter also provides a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the results obtained.
When analyzing the results of an experiment, it is necessary to use a scoring system. Examples of various criteria for quantitative and qualitative assessment are presented in the following works:
– Glukhov V.P. Formation of coherent speech in preschool children with general speech underdevelopment. - M.: Arkti, 2002. - 144 p.
– Fotekova T.A. Test methodology for diagnosing oral speech of primary schoolchildren. - M.: Arkti, 2000. - 56 p.
– Levchenko I.Yu. Pathopsychology: Theory and practice. - M.: Academy, 2000. - 232 p.
In order to visually present the results obtained during the experimental study, it is recommended to use tables, graphs, diagrams, etc. Histograms can be used in a variety of ways - columnar, cylindrical, planar, volumetric, etc. An example of the design of tables, figures, and histograms can be found here.
The third chapter provides a rationale for the proposed methods and techniques and reveals the content of the main stages of correctional work.
The conclusion contains a summary of the material presented and the main conclusions formulated by the author.
The bibliography must contain at least 25 sources. The list includes bibliographic information about the sources used in preparing the work. An example of its design can be seen here.
In the application you can present bulky tables or illustrations, examination protocols, observation records, products of activity (drawings, written works of children), notes from speech therapy classes, etc.
The volume of one course work must be at least 30 pages of typewritten text.
In general, coursework in speech therapy is the basis for a future thesis, in which the study of the begun problem can be continued, but from the standpoint of a different approach or a comparative analysis of the disorders being studied in different age categories of people with different types of speech disorders.
The content and format of theses in speech therapy can be found here.
Literature:
1. How to write a term paper on speech therapy: Methodological recommendations. Educational and methodological manual / Comp. Artemova E.E., Tishina L.A. / Ed. Orlova O.S. – M.: MGOPU, 2008. – 35 p.
2. Research work of students in the system of higher professional pedagogical education (specialty 031800 - Speech therapy). Methodological recommendations for completing the thesis / Compiled by. L.V. Lopatina, V.I. Lipakova, G.G. Golubeva. - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of the Russian State Pedagogical University named after. A. I. Herzen, 2002. - 140 p.
Capabilities
Individual characteristics include abilities. At birth, an individual is endowed with different inclinations. Only with their constant development can abilities be improved. Inclinations are passed on by heredity.
Abilities classification:
- Specific - abilities that ensure life in society. They help you study science, communicate with others, and achieve your goals.
- Natural - abilities given to a person from birth.
Abilities are divided by field of activity. For example, music, mathematics, engineering, sports.
Development of personality abilities
Abilities in the personality structure are its potential. The structural structure of abilities depends on the development of personality. There are two degrees of ability formation: creative and reproductive. At the reproductive stage of development, the individual shows significant ability to master knowledge, activities and implement them according to an explicit model. At the creative stage, an individual is able to create something new and unique. The combination of outstanding abilities that determine the very successful, original and independent performance of various activities is called talent. Genius is the highest level of talent. Geniuses are those who can create something new in society, literature, science, art, etc. The abilities of subjects are inextricably linked with inclinations.
A person’s abilities for mechanical memorization, sensation, emotional excitability, temperament, and psychomotor skills are formed on the basis of inclinations. The possibilities for the development of anatomical and physiological properties of the psyche, which are determined by heredity, are called inclinations. The development of inclinations depends on close interaction with surrounding circumstances, conditions and the environment as a whole.
There are no people who are completely incapable of anything. The main thing is to help the individual find his calling, discover opportunities and develop abilities. Every healthy person has all the necessary general abilities for learning and those abilities that develop during certain activities - special ones. So, the main factor influencing the development of abilities is activity. But in order for abilities to develop, activity in itself is not enough; certain conditions are also needed.
Abilities need to be developed from childhood. In children, engaging in any particular type of activity should evoke positive, constant and strong emotions. Those. such activities should bring joy. Children should feel satisfied with their activities, which will lead to the formation of a desire to continue to engage in further activities without coercion from adults.
Creative expression of activity is important in the development of children’s abilities. So, for example, if a child is passionate about literature, then in order to develop his abilities, it is necessary that he constantly writes essays, works, albeit small ones, with their subsequent analysis. A huge role in the development of the abilities of younger schoolchildren is played by visiting various clubs and sections. A child should not be forced to do things that were interesting to parents in their childhood.
The child’s activities should be organized so that they pursue goals that are slightly beyond his capabilities. If children have already shown abilities for something, then the tasks given to them should gradually be made more difficult. It is imperative to develop in children, along with abilities, self-demandingness, determination, perseverance in the desire to overcome difficulties and criticality in judging their actions and themselves. At the same time, it is necessary to form in children the right attitude towards their abilities, achievements and successes.
The most important thing in developing abilities at an early age is a sincere interest in your baby. It is necessary to pay as much attention to your child as possible and do some work with him.
The decisive criterion for the development of society is the embodiment of the abilities of individuals.
Each subject is individual, and his abilities reflect the individual’s character, passion and inclination towards something. However, the realization of abilities directly depends on desire, regular training and constant improvement in any specific areas. If an individual lacks passion or desire for something, then it is impossible to develop abilities.
Feelings and emotions
Emotions are experiences that arise when one’s own needs are satisfied or not met. Feeling is a complex experience. May be felt for a long period of time.
Classification:
- Aesthetic - appear as a result of the perception of objects. For example, when some people see a picture they begin to be delighted and surprised.
- Intellectual is a product of mental activity. They manifest themselves as curiosity, surprise, doubt, inspiration.
- Moral ones are reactions to one’s behavior and the actions of others.
Feelings can lead to the development of psychological disorders.
Professional abilities of the individual
The main psychological resource that a person invests in the process of work and activity is professional abilities.
So, a person’s professional abilities are the individual psychological properties of an individual that distinguish him from others and meet the requirements of labor and professional activities, and are also the main condition for the performance of such activities. Such abilities are not limited to specific abilities, knowledge, techniques and skills. They are formed in the subject on the basis of his anatomical and physiological characteristics and inclinations, but in most specialties they are not strictly determined by them. More successful performance of a particular type of activity is often associated not with one specific ability, but with a certain combination of them. That is why professional skills are determined through successful specialized activity and are formed in it, but they also depend on the maturity of the individual and his relationship systems.
Activities and abilities of a person regularly change places throughout an individual’s life, being either a consequence or a cause. In the process of carrying out any type of activity, mental new formations are formed in the personality and abilities, which stimulate the further development of abilities. When the circumstances of an activity become more stringent or when the conditions of the tasks or the tasks themselves change, the inclusion of different systems of abilities in such activities may occur. Probable (potential) abilities are the basis of new types of activities. Since the activity is always adjusted to the level of ability. So, professional abilities are both a result and a condition for successful work activity.
Universal human abilities are those psychological properties that are necessary for the involvement of an individual in any professional and work activity: vitality; ability to work; the ability for self-regulation and activity, which includes prognosis, anticipation of the outcome, goal setting; the ability for empathy, spiritual enrichment, cooperation and communication; the ability to be responsible for the social outcome of work and professional ethics; the ability to overcome obstacles, immunity to interference, and withstand unpleasant circumstances and conditions.
Against the background of the above abilities, special ones are also formed: humanitarian, technical, musical, artistic, etc. These are individual psychological characteristics that ensure the success of an individual in performing certain types of activities.
Professional abilities of an individual are formed based on universal human abilities, but later than them. They also rely on special abilities, if they arose simultaneously with professional ones or earlier.
Professional skills, in turn, are divided into general, which are determined by the subject of activity in the profession (technology, people, nature) and special, which are determined by specific working conditions (lack of time, overload).
Also, abilities can be potential and actual. Potential - appear when new tasks arise for the individual, which require new approaches to solution, as well as under the condition of the individual’s support from the outside, which creates an incentive to actualize potential. Relevant – already today they are carried out in a procession of activities.
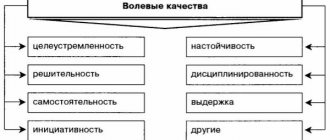
Strong-willed qualities
Will is a skill that allows an individual to control desires and suppress them at the right time. With the help of will, you can achieve your goal by giving up benefits.
Willpower allows a person to move forward past obstacles, to sacrifice interests for the benefit of others.
Man is unique from birth. Throughout his life, he shows individuality in behavior, decision-making, and attitude towards others. Psychologists study features to understand how they affect mental development.
Creative abilities of the individual
Many people mistakenly believe that creative abilities include only drawing, writing and music. However, this is absolutely false. Since the development of an individual’s creative abilities is closely interconnected with the individual’s perception of the world as a whole and his sense of himself in it.
The highest function of the psyche, reflecting reality, is creativity. With the help of such abilities, an image of an object that does not exist at that moment or that never existed at all is developed. At an early age, the foundations of creativity are laid in a child, which can manifest themselves in the formation of the ability to conceive and implement it, in the ability to combine their ideas and knowledge, in the sincerity of conveying feelings. The development of children's creative abilities occurs in the process of various activities, for example, games, drawing, modeling, etc.
The individual characteristics of a subject that determine the individual’s success in performing any creative activity are called creative abilities. They represent a combination of many qualities.
Many famous scientific figures in psychology combine creativity with thinking characteristics. Guilford (an American psychologist) believes that creative individuals are characterized by divergent thinking.
People with divergent thinking, when searching for a solution to a problem, do not focus all their efforts on establishing a single correct answer, but look for various solutions in accordance with all possible directions and consider many options. The basis of creative thinking is divergent thinking. Creative thinking is characterized by speed, flexibility, originality and completeness.
A. Luk identifies several types of creative abilities: finding a problem where others do not notice it; collapsing mental activity, while transforming several concepts into one; using the skills that have been acquired in finding solutions from one problem to another; perception of reality as a whole, and not splitting it into parts; ease of finding associations with distant concepts, as well as the ability to provide the necessary information at a certain moment; choose one of the alternative solutions to the problem before checking it; show flexibility of thinking; introduce new information into an existing knowledge system; see things and objects as they really are; highlight what is noticed from what the interpretation offers; creative imagination; easy to generate ideas; refining specific details to optimize and improve the original idea.
Sinelnikov and Kudryavtsev identified two universal creative abilities that developed in the process of historical development of society: realism of imagination and the ability to see the integrity of a picture before its component parts. Imaginative, objective grasping of some significant, general pattern or tendency for the formation of an integral object, before the individual has a clear idea of it and can introduce it into a system of clear categories of logic, is called realism of the imagination.
The creative abilities of an individual are a set of character traits and properties that characterize the level of their compliance with certain requirements of any type of educational and creative activity, which determine the degree of effectiveness of such activity.
Abilities must necessarily find support in natural personality qualities (skills). They are present in the process of constant personal improvement. Creativity alone cannot guarantee creative achievement. To achieve, you need a kind of “engine” that can put mental mechanisms into action. Creative success requires will, desire and motivation. Therefore, eight components of the creative abilities of subjects are distinguished: personality orientation and creative motivational activity; intellectual and logical abilities; intuitive abilities; ideological properties of the psyche, moral qualities that contribute to successful creative and educational activities; aesthetic qualities; communication skills; the individual’s ability to self-manage his educational and creative activities.
Will
Will is a person’s ability to control and regulate his behavior. Its essence is to help achieve success, realize your plans and intentions, and overcome obstacles.
Characterized by such properties as determination, perseverance, confidence, endurance and patience. If a strong-willed person has something in mind, then no matter what, he will persistently pursue his goal, even if the whole world is opposed to him.
He does not need support when he makes any decision. Yes, the recognition of other people is important to him, but he will not give in to his principles in order to gain their approval.
A strong-willed personality is disciplined, resilient, courageous and energetic. She is not afraid of hard work and is ready to work almost without rest if this allows her to realize her dreams.
Research by specialists shows that will pushes a person to take decisive action; he is even ready to sacrifice his own interests for the sake of the interests of society.
If you want to increase your own level of determination, check out this article.
Personal communication abilities
In the success of an individual, the determining factor is relationships and interaction with surrounding entities. Namely, communication skills. The success of the subject in professional activities and in other areas of life depends on the degree of their development. The development of such abilities in an individual begins almost from birth. The sooner a baby can learn to speak, the easier it will be for him to interact with others. The communicative abilities of subjects are formed individually for each person. The determining factor in the early development of these abilities is parents and relationships with them; later, peers become influencing factors, and even later, colleagues and one’s own role in society.
If in early childhood an individual does not receive the necessary support from parents and other relatives, then he will not be able to acquire the necessary communication skills in the future. Such a child may grow up insecure and withdrawn. Consequently, his communication abilities will be at a low level of development. The way out of this situation can be the development of communication skills in society.
Communication abilities have a certain structure. They include the following abilities: information-communicative, affective-communicative and regulatory-communicative.
The ability to start and maintain a conversation, complete it competently, attract the interest of the interlocutor, and use non-verbal and verbal means for communication are called information and communication abilities.
The ability to perceive the emotional state of a communication partner, respond correctly to such a state, and demonstrate responsiveness and respect for the interlocutor is an affective-communicative ability.
The ability to help the interlocutor in the process of communication and to accept support and help from others, the ability to resolve conflicts using adequate methods is called regulatory-communicative abilities.
Characteristic details for entering a number
Let's create a characteristic attribute for entering a numeric value - speed.
In the item type card, go to the “Additional” tab. details" and in the right panel "Characteristics details" execute the command "Add - New for view".
In the window that opens, enter the name of the attribute (in the example, “Speed (km/h)”). In the “Value type” field, open the editing window and oh, here you can set the length and precision of the number. Then click "OK".
After filling in the details, save the details using the “Save and close” button.
The characteristics attribute has been created.