Adolescence refers to the period of a person’s life from 13 to 19-22 years. This stage is considered the final stage of active socialization of the individual.
This is the period of completion of human puberty and the formation of a physiologically adult organism. Youth began to be identified as a separate stage of life at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries as a result of a significant lengthening of the educational process necessary for the formation of a competent personality capable of existing in the modern technosphere.
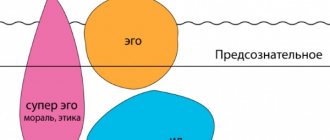
Socialization structure
Socialization is a two-way process, including, on the one hand, the assimilation by an individual of social experience by entering into a social environment, a system of social connections, on the other hand, the process of active reproduction of a system of social connections by an individual due to his active activity, active activity, active inclusion into the social environment. Thus, in the structure of socialization two interrelated processes can be distinguished:
- The process of internalization of social experience (social typification) – the subject’s assimilation of social norms, values and standards of behavior.
- The process of exteriorization (individualization, autonomization) of social experience is the active recreation by a person of acquired experience in the process of independent activity, behavior and communication, the reproduction by the subject of social relations through his own activity.
Types of education
There are mental, physical, and labor education. According to another classification - moral, physical, labor, aesthetic. Legal, gender, economic, and environmental are often added.
What qualities to cultivate? The basis can be considered the content proposed by the Russian teacher Karakovsky, who identified universal human values: Man, Family, Knowledge, Work, Culture, Earth, Fatherland, Peace. Acceptance of values gives rise to positive traits, moral qualities, correct needs, and actions.
Personal education is divided into models that depend on the development of society at various historical stages, the ratio of social groups, and socio-political orientation. It is enough to recall the foundations of a totalitarian and democratic society, which differ in value systems and require the formation of different personality traits.
Education takes place in two ways:
- By communicating, explaining socially significant goals, principles, values, and norms of behavior. The method eliminates the possibility of searching and making mistakes. It is based on the processing of a person’s existing motivations for understanding his relationship to reality.
- With the help of special conditions created to form cognitive interest and stimulate active socially useful activities.
The first method is traditional, the second is modern. Both of them are effective when used together and complement each other.
Socialization results
In the process of socialization, social norms, values and requirements move into the internal plane and become the basis of human behavior. In the process of socialization, there is interaction between the individual and society, coordination of mutual requirements and expectations. At the same time, the individual does not simply assimilate and reproduce social patterns; on the contrary, in the course of socialization, the actualization of its capabilities, potentials, expansion and deepening of self-awareness is carried out, i.e. personality development occurs.
Indicators of successful socialization of an individual are:
- Inclusion of the individual in the system of social relations.
- Expanding and deepening the individual’s connection with people and various spheres of society.
- Mastery of social experience, its appropriation and transformation into one’s own values, attitudes and orientations.
- Active activity of the individual with his active involvement in the social sphere.
- Active reproduction of the system of social connections.
It should be emphasized that the main vector of socialization is a positive focus on morality and law. Deviation has the opposite direction - the deviation of the subject’s behavior from social norms.
Basic forms
Socialization is also divided into forms: directed and undirected. The first type is a system of influence methods developed by society to mold individuals in accordance with established values and morals. One of the ways is education at home, in the first educational institutions. This is an organized and purposeful process aimed at developing a person’s value orientations and social concepts for further cultural activities.
The two forms can interact or oppose each other under certain circumstances. Emerging conflict situations cause problems in the process of personality formation. Undirected socialization should begin in the microenvironment - the family; it is based on already outdated rules and norms of behavior, traditions and customs. Usually it has a positive effect on a person, but sometimes it becomes negative - in the case of social pathology. Therefore, it must be supplemented with factors of the directed group.
Religious organizations may use forms of socialization to bend the will of weak-willed people. The propaganda of neo-Nazism, fascism, and the work of sects is based precisely on a targeted group. Therefore, it is used only for humanitarian purposes and in accordance with moral principles, freedom of conscience, human rights and the moral principles of a democratic nation.
Socialization functions
Socialization plays an important role for both the individual and society. The main functions of socialization are the following:
- For the individual : a comprehensive, time-extended entry into the objective world - a separate part of society, a family or other community. Socialization makes it possible to understand oneself and interpret the behavior of other people, and interact with others.
- For society : socialization is one of the factors of normal reproduction of society. Despite the fact that people are constantly born and die, socialization makes it possible for society to reproduce itself and is a condition for the preservation and development of social culture.
Socialization factors
Socialization is carried out as a result of the influence of certain factors on the individual: on the one hand, the targeted influences of society on its members (raising and teaching children, etc.), on the other hand, random, spontaneous influences of society on the individual. In addition, the result of socialization is also influenced by the individual’s own activity (the process of self-determination), and as one grows older, the importance of self-determination increases and, sooner or later, becomes decisive.
Types and agents of socialization.
Socialization
is the process of an individual’s assimilation of patterns of behavior, psychological attitudes, social norms and values, knowledge, and skills that allow him to function successfully in society, beginning in infancy and ending in old age.
Types of socialization: 1. Primary socialization
. This stage covers the process of formation and development of personality, that is, the process of caring for, raising and educating children primarily in the family, carried out by those agents of socialization who are in direct and regular contact with the child in early and late childhood. During primary socialization, passive assimilation of information, skills, and ideas predominates.
2. Secondary socialization.
This stage covers the rest of the person’s “adult” life. At this stage, the development of the social environment occurs consciously, most of the information coming from outside is subjected to critical consideration. The individual makes a meaningful choice from several options.
3 Early socialization
represents a “rehearsal” for future social relations. For example, a young couple may live together before marriage in order to have an idea of what family life will be like.
4. Resocialization
is re-socialization that occurs throughout an individual's life. Resocialization is carried out by changes in the individual’s attitudes, goals, norms and values of life
5. Organizational socialization
is the process by which an individual acquires the values, abilities, norms of behavior and social outlook that are important for gaining weight in the organization and full participation in it as an employee
6. Group socialization
is socialization within a specific social group. Group socialization is the process of inculcating ideas and principles into an individual as he internalizes the basic values and symbols of the group in which he is involved.
7. Gender socialization
- this is the assimilation, internalization of social roles, differentiation of activities, statuses, rights and responsibilities of individuals depending on gender.
9 pages, 4458 words
GOALS, SUBJECT, OBJECTIVES OF THE EDUCATIONAL PROCESS, TYPES AND TYPES OF EDUCATIONAL PROGRAMS IMPLEMENTED
STATUTES OF THE Gorlovka comprehensive school of I-III levels No. 8 of the Donetsk People's Republic GENERAL PROVISIONS 1.1. Gorlovka comprehensive school of I – III levels No. 8, hereinafter referred to as the School, carries out its activities in accordance with the Constitution, Laws, other legal acts and this Charter. 1.2. The school was created for an unlimited period to carry out work, provide...
Agents of Socialization
- these are structural groups or environments in which the most important processes of socialization take place. In all cultures, the most important agent of primary socialization for a child is the family. However, in later stages of life, many other agents of socialization come into play. Agents of secondary socialization of an individual are school, university, army, church.
Peer groups, the media, mass printed publications, and electronic communications have a great socializing effect on a person.
Mechanisms of socialization
The assimilation of social norms and rules is carried out through socio-psychological mechanisms of socialization, which include suggestion, mental infection, imitation, identification, conformity, stereotyping, social assessment, reference group, authority, popularity, prestige, role prescriptions, social and group expectations - expectations , directed at the subject by society and the group to which he belongs. At different age stages, different mechanisms of socialization are dominant.
Principles of harmonious development
The formation of a harmonious personality is aimed at achieving the following goals:
- formation of the consciousness of a citizen, a patriot;
- familiarization with universal human values;
- development of creativity, ability to create;
- formation of an adequate self-concept, the ability of self-realization.
Principles to be followed:
- respectful, trusting relationships between teachers and students;
- conformity with nature (taking into account age, gender, and other natural characteristics);
- cultural conformity (reliance on the cultural traditions of the people);
- humanization, aestheticization of the environment of an educational institution.
Stages (stages) of socialization
Socialization occurs throughout a person’s life, but most intensively in childhood, adolescence and adolescence. In relation to work activity, three main stages of the socialization process can be distinguished:
- Pre-labor stage of socialization covers the entire period of a person’s life before starting work. This stage is divided into two more or less independent periods:
- early socialization , covering the time from the birth of a child to his entry into school, i.e. period of early childhood. At this stage, uncritical assimilation of social experience occurs; the main mechanism of socialization is imitation.
- stage of learning , which includes the entire period of adolescence in the broad sense of the term. This stage, of course, includes the entire time of schooling. At this stage, a more conscious, intensive assimilation of social experience occurs.
- The labor stage of socialization covers the period of human maturity, although the demographic boundaries of “mature” age are conditional; fixing such a stage is not difficult - this is the entire period of a person’s working activity. At this stage, social experience is reproduced, a person’s impact on the environment occurs.
- The post-work stage of socialization covers old age. This stage is characterized by the transfer of social experience to new generations.
Family influence on the socialization process
The process of socialization is primarily influenced by the family. Each of its members performs specific social roles, the main ones being parental roles. What they have in common is the desire for the safety of children, care and education.
Mutual contacts between the baby and parents depend on many factors, such as: the relationship of the parents, the age and education of the parents, the characteristics of their personality and the norms of education characteristic of a given culture.
Both excessive concentration on the baby and excessive distance from him have a negative impact on the processes of the child’s psycho-emotional and social development.
The wrong attitude of parents, as well as an overly authoritarian or too liberal parenting style can cause various disorders and difficulties in adaptation.
At this age, children surrounded by excessive attentiveness of their parents, or raised too freely, as a rule, are infantile and do not know how to establish positive contacts with peers, and their self-centered and even selfish attitude inevitably leads to rejection by the group.
In the area of social contacts between a child and his brothers and sisters, there are dependencies associated with the baby’s birth order and gender.
Difficulties in adaptation may arise for a baby who is the first in the family, to whom the mother subsequently devotes less time in favor of a newborn brother or sister.
In such a situation, a feeling of envy awakens, and younger children even exhibit aggressive behavior towards the new family member (they can hit, pinch, take away toys, and even try to throw him out of the stroller). According to psychologists, relationships with brothers and sisters at this age are unstable.
In 3, 5 and 7 year old children, the severity of negative emotions towards brothers and sisters weakens, and in connection with this, contacts are friendly and positive, while children 4 and 6 years old are more excitable during this period and enter into frequent conflicts with brothers and sisters.
Children treat older and younger brothers and sisters differently.
The predominance of negative contacts, as a rule, goes away with age, however, sharp quarrels or destruction of objects that are the property of brothers and sisters, and even fights also occur at the end of the preschool period.
Positive social contacts with the older offspring are expressed in interactions in classes or entertainment.
Over the course of many eras and cultures, the rules and roles that the baby must fulfill have changed.
Parents, and later teachers and educators, try to control the child’s behavior with the help of certain influences in order to instill in him these elements of the role that he must fulfill in a given period of life.