01/18/2019 Zoryan Freidovich Psychology
The moral and psychological climate (MPC) is a reflection of the real relationships between members of any team. The level of favorable climate in a group determines the quality of the organization and dictates the success or decline of production (the educational process). Normalizing relationships in a team and regulating an optimal working atmosphere belong to the field of social psychology.
The concept of moral and psychological climate
It has been proven that more than 20 cases of decreased performance indicators at work out of 100 are due to unfavorable moral and psychological factors that have a negative impact on the employee during his working life. It is also known that depression, bad mood or depressed team members lead to a 50% decrease in productivity. If we consider a team as a society of people connected by the same tasks and goals, then the alarming nature of such statistics and its impact on the work of the organization as a whole will become understandable.
The formation of a moral and psychological climate occurs at the level of small organizational forms of the team - microgroups belonging to the smallest structural unit of the organization (team, department, committee). It is in these social groups, which include a small number of participants, that a certain psychological atmosphere develops, which subsequently influences the situation within the entire closed structure of the organization.
The enormous importance of the state of the moral and psychological climate of the working apparatus is due to the fact that it characterizes the position of the organization as a whole: the speed of productivity, the quality of products (services) produced, etc. And since almost every person is assigned to one or another field of work activity and is responsible for certain functions of their enterprise, then the importance of IPC seems to be equivalent to the observance of both public and personal interests.
Properties
All mental states have special properties:
- Integrity is the interconnection and interdependence of all components of the psyche. This property influences the efficiency of human activity.
- Sustainability. All types of human mental states are more permanent than momentary emotions.
- Mobility is the property of mental states to change their functions following a change in the situation.
- Polarity – this property expresses the pairing of emotional experiences. For every positive experience, you can select a diametrically opposite (negative) emotional experience.
MIC levels
In the course of studying the moral and psychological climate of a certain organizational structure, 2 levels of this social factor were identified:
- static:
- dynamic.
The static level of relationships within the team is constant and stable. The once established principles and procedures of the work process are supported by all members of the team, and difficulties that arise are sorted out and overcome also together. From time to time, team members adjust the moral and psychological climate within the work mechanism, which is welcomed by the main team as a necessary measure to maintain a favorable environment.
The dynamic level of relationships in a group is considered unstable, fluctuating, and is directly dependent on the mood of all group members, their current mental and physical state, priorities and needs. In contrast to the indicators of the previous level of moral and psychological climate, in organizations built according to a dynamic type, personnel and other changes occur much more often and are perceived by people quite sharply.
In the future, the development of the team’s state according to a negative dynamic scenario can lead to its complete transformation or collapse.
Find out the cost of writing such a paper!
Reply within 5 minutes!
Without intermediaries! Methods of psychological influence are the most important components of psychological management methods. They summarize the necessary and legally permitted methods of psychological influence on personnel to coordinate the actions of employees in the process of joint production activities. Permitted methods of psychological influence include: suggestion, persuasion, imitation, involvement, encouragement, coercion, condemnation, demand, prohibition, censure, command, deception of expectations, hint, compliment, praise, request, advice, etc.
1.3. Professional ethics in the hotel industry
Any manager of a hotel company is concerned about the quality of the services provided. Quality in the hotel business is a reputation, a guarantee of competitiveness and popularity. When staying at a hotel, we encounter receptionists, waiters, luggage porters, and sometimes we notice a maid in the corridor. A favorable impression is made by a hotel where the service is unobtrusive, the staff is “not heard or seen,” but at the same time all wishes are fulfilled. But does the quality of work of hotel staff always depend on the “star rating” of the hotel? As practice shows, not always.
The number of services provided and prices are, of course, indicative facts, and the absence, for example, of a robe in a five-star hotel raises a silent question and irritation of the client. It turns out that they simply forgot to bring a robe. An annoying little thing, an unpleasant conversation with complaints if the request was repeated twice or three times. Isn't this an indicator of the quality of work?
Or such a situation. Encounter with the staff of a two-star hotel: an unsmiling receptionist, a waiter with an obsessive request for a tip in his eyes, a dusty dressing table and the laughter of the maids in the corridor.
Of course, the work is hard - both physically and mentally. The beds can be heavy, during the shift you have to clean rooms that are scary to enter without a gas mask, there are arrivals of 150-200 people, despite the fact that guests, out of habit, try to resolve all issues through the receptionist. Add to this “boiling” telephones and heavy suitcases... It can also be difficult morally, because little depends on these people - the receptionists and maids - politically and organizationally. They are sometimes the last to know about changes, appointments, plans, etc.
The question arises: can the moral climate affect the quality of work performed? Yes, definitely. But these are already questions of professional ethics. It is ethics that should be given attention first. What is professional ethics? Aristotle, Comte, Durkheim asked this question. Professional ethics, having first emerged as a manifestation of everyday moral consciousness, then developed on the basis of the general practice of behavior of representatives of each professional group. These generalizations were contained in both written and unwritten codes of conduct.
Professional ethics is a set of moral standards that determine a person’s attitude towards his professional duty. Society considers the moral qualities of an employee as one of the main elements of his professional suitability. General moral norms must be specified in a person’s work activity, taking into account the specifics of his profession. Thus, professional morality must be considered in the context of a generally accepted system of morality. Violation of work ethics destroys general moral principles, and vice versa. An employee’s irresponsible attitude towards his professional duties is dangerous for others, harms society, and can even lead to personal degradation. In modern society, the listing of an individual’s personal qualities begins with his business characteristics, attitude to work, and level of professional suitability. True professionalism is based on such moral standards as duty, honesty, demands on oneself and colleagues, and responsibility for the results of one’s work.
The scientific approach to professional ethics more often affects the category “Employee”, less often “Leader”; not enough attention is paid to the interconnected system “Leader - Employee”. It is in this connection that the greatest number of misunderstandings and conflicts arise. A well-functioning training system within a hotel is capable of “establishing relationships” within a team, since it consists not only of the features of everyday work, but also the features of business ethics, includes details and little things that are unique only to a given hotel, the laws by which the entire workforce lives - and these are both employees and management.
There is a category of people for whom working in a hotel is simply contraindicated. Even after passing through a competition and occupying a vacant position, such people cannot stand it for long and quit. Therefore, a necessary condition for the candidate selection system is to reduce the risk of such people ending up in hotels. Five and four star hotels have stronger HR departments. And the terms “selection system”, “interviewing”, “certification”, “rotation”, “training” are not only known, but are also actively used in everyday work. Why everyday? Because the nature of working with hotel staff is everyday. Because the hotel works and “lives” around the clock. Because quality control of the services provided must be carried out 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year. Control of work, attention to personnel, prompt correction of errors and shortcomings, awareness - all this is the implementation of business ethics standards.
Elements of business ethics directly affect staff motivation. The feeling of control, attention to work, a clear understanding of directions in work and development creates a feeling of confidence in the future. Cash rewards for excellent work are a natural result of quality services provided. On the other hand, there is absolute certainty that punishment will follow, commensurate with the severity of the “offence.” Turning a blind eye to problems, not communicating the results of inspections to management, or openly violating rules in front of amazed employees are serious violations of professional ethics that entail a decrease in the quality of services provided.
Let us note that most violations come not from employees, but from managers! As a result, the employee suffers. Even considering different hotels, different work teams, the problems in them were and remain very similar. Let's outline these problems. How not to manage staff? What not to do? It is in these details that impressions are formed, details that help change opinions and correct a mistake. Many managers may disagree, saying that such problems exist, but not in their hotels. In this case, you can only be happy for them! But maybe they don’t know everything?
So, let's outline the main aspects:
— The leader should not be “too high.” In a hotel, the manager is its heart. The mood of the team and the actions of subordinates depend on how it “beats”. It is doubly offensive if the effect of vigorous activity takes place only under the director who is nearby. I was asked the question: why does the director meet with the staff? There are line managers for this. The answer lies in the question itself: Because this person is a director, and because this is not just a team, but his work collective.
— A manager has no right to get tired and stop wanting to work. And he also does not have the right to cast doubt on the reputation of the enterprise by his behavior. It is easy to violate the moral climate, but mistakes of this kind are not forgotten for a long time.
— The manager has no right to choose favorites. Friendly and familiar relations are also unacceptable, because all this radically affects a person’s reputation in the team. The collapse of a friendship involving the relationship between a manager and a subordinate is subsequently fraught with a choice: friendship or work. Friendly and other relationships are possible only outside the enterprise and outside working hours.
— The manager has no right to encourage the spread of rumors, the formation of coalitions, public and secret bullying and harassment of members of the workforce on professional and personal issues, regardless of position and age. The leader, however, must be aware of all such situations and be aware of collective sentiments.
— The manager has no right not to fulfill promises, and also to forget about plans and meetings. Deception will not add authority, but, on the contrary, will sharply reduce motivation within the team.
— The manager has no right to exceed his authority, regardless of the nature of the situation. This applies, first of all, to line managers, deputy level and heads of services. An overly commanding tone or inappropriate (rude) behavior will also not increase authority. Particular attention should be paid to young managers whose subordinates are much older than them. I have seen many such bosses - especially close to the director, quite competent, but lacking life experience, and, most importantly, experience in human relations. And this is necessary for making wise decisions and simply wise human behavior.
— What is the concept of “team” in relation to a hotel company? It has been said more than once that hotel workers are a special category. These are, in a certain sense, fanatics of their business. The question is that this “burning” of theirs should be directed only towards the enterprise, work, creative process
— Change is a difficult test for the entire team. It is at this time that it is necessary to clearly understand where everything is going, what needs to be done, how to act. No pressure is acceptable. A smooth, as painless as possible, transition is necessary. The worst thing that can happen in this situation is the incompleteness of the process. Any changes must be brought to their logical conclusion.
- The problem of fathers and children". In the hotel services market there is a clear trend towards reducing the age of service personnel. The advantages are obvious. The disadvantages include the lack of practical experience - this is an omission of training programs. Reluctance to start working in “unpopular” hotels. Reluctance to work in “unpopular” positions. Discrepancy between “knowledge – experience – salary”. Life in our country is quite expensive, but hotels cannot pay much right away if a young specialist has nothing to offer. In many hotels the staff steals. It’s scary to say, but in 70% of cases, young people – young professionals – also start stealing! Otherwise, they will not be able to survive in the team. It's a disease! This is an ethical problem that must be combated through joint efforts - both at the university and at the enterprise.
— You cannot transfer your emotional state to your colleagues or show personal hostility. There is work that needs to be done efficiently, everything else is secondary. Issues of professional ethics concern all categories of workers without exception.
To ensure high-quality work of a hotel enterprise, teamwork and prompt resolution of organizational, financial, and technical issues are necessary. Solving ethical problems will greatly facilitate the further development of the hospitality industry market, the services of which we could be proud of, regardless of the star rating of the hotel.
Chapter 2. Analysis of the psychological climate in the “Gallery” restaurant
2.1. General characteristics of the cafe "Gallery"
Arkady Novikov's restaurants are a cult of success, aesthetics and the right attitude to life. They are known primarily as places that serve healthy food in aesthetically pleasing interiors. To date, 46 Arkady Novikov restaurants have been opened. The restaurant menu contains cuisines from different countries. There is signature cuisine provided by world culinary stars, as well as home cooking by Arkady Novikov.
One of these restaurants is “Gallery”. The restaurant is located at Moscow, Petrovka Street, 27, 1st floor of the Vienna House business center. In the “Gallery” everything is as it should be in a real gallery, here coexist with great success: daily exhibitions of traditional and modern culinary genres, with jazz evenings, exhibitions of contemporary art and photography, incendiary musical performances and film screenings. People come here to enjoy delicious dishes from chef Sergei Markin of European, French, Italian and Russian cuisine. And also Asian and Japanese. A great place that is suitable for any type of holiday. This is one of those establishments that doesn’t really need reviews. Tasty, cozy, beautiful and positive at any time of the day.
Figure 1 – Organizational structure of the “Gallery” restaurant
The restaurant is headed by a director (manager), who is appointed by the owner (founder) to carry out operational coordination of all activities of the establishment.
The second key figure is the chef. Formally, according to his official position, he reports to the manager, but the specificity of the restaurant business is that the chef cannot be a “passing” figure. He must be the person who makes the decision and bears serious responsibility. The success of the establishment largely depends on it. Therefore, manager and chef are two equivalent positions. The first is in charge of the hall, the second is in charge of the kitchen.
In accordance with this functional division into the hall and kitchen, a conventional hierarchical control system is built. Subordinate to the manager are managers, who in turn manage waiters, bartenders, and technical services. The chef supervises the kitchen staff - the cooks. The director (manager) of the restaurant is personally responsible to the owner (founder) for the successful, efficient and profitable operation of the cafe, as well as for maintaining the reputation and positive image of the establishment.
The kitchen team consists of 35 people. To ensure effective work, the chef must have outstanding management skills, be able to not only evaluate a specialist when hiring him, but also act as a mentor and teacher. Moreover, his task is to arrange his employees so that everyone is in his place and does the job efficiently.
Unlike the head of a restaurant, the manager of the hall (maitre d') has to communicate with guests much more often. Thus, for a head waiter, it is very important to have such a quality as personal charm, as well as high communication skills - the ability to communicate with guests. No less important are neatness and impeccable appearance. If we talk about special industry knowledge, then, first of all, it is, of course, an impeccable understanding of service and the ability to organize the smooth functioning of the hall.
All the attention of the staff is focused on the guest as soon as he has crossed the threshold of the establishment. The manager escorts the guest to the table and introduces him to the menu and wine list. At this time, the waiter assigned to this table prepares everything necessary for work (cutlery, napkins, etc.). A professional waiter can easily determine a guest’s readiness to place an order with the naked eye. When accepting an order, the waiter will advise on any questions regarding the method and time of preparation of dishes and drinks, possible changes in the composition to suit the client’s taste preferences, etc. Any self-respecting establishment must be ready to fulfill all possible wishes of the guest.
During observations of the work of the service personnel, it was noticed that many waiters are not familiar with the recipes of dishes and the method of preparation. This can be explained by two reasons. The first is that the chef does not consider it necessary to tell the waiter about the dishes. The second is saving money on preparing dishes for waiters to try. It is precisely this kind of “savings” that, as a rule, results in a significant deterioration in the level of service.
The service standard of the "Gallery" restaurant is defined as a set of mandatory customer service rules that guarantee the established level of quality for all operations performed. The service standard has a number of criteria: time for serving visitors, a system for handling complaints and claims; availability of information and advertising materials; waiting time for a telephone response; payment procedure, etc.
The Gallery restaurant segment in the city market is mainly made up of gilded youth and people with above-average incomes. Their main needs are rest and entertainment.
In the future of the enterprise's development, in addition to organizing new forms of service, it is planned to carry out bright and memorable events to attract the attention of the public, the media and strengthen its position in the market (wine tastings, clothing shows, artist exhibitions, etc.).
The sales volume for a 24-hour cafe is:
with occupancy of 20-40% on weekdays (12.00 - 15.00) about 20% of the average monthly profit;
. with 100% occupancy for seats in the evening (20.00 - 04.00) about 80%:
You can reduce the negative impact of the above factors as follows:
1) establish contacts with new visitors;
2) constantly searching for new connections and maintaining them with regular guests;
3) constant quality control of services;
Analyzing all of the above, we can come to the conclusion that for the effective functioning of the Gallery restaurant it is necessary to expand the range of services provided, improve the quality of services and attract new customers.
Pages: 2
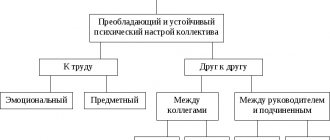
Assessment of the state of the IPC
The state of the moral and psychological climate in a group is always determined by polar values that do not have sublevels of transition from positive to negative. One can never say about the situation in a team that it is “normal”, since such a definition does not correspond to the emotional assessment of the current situation, which is always expressed in one of two extreme states: “good” or “bad”.
A person, whether he wants it or not, at a subconscious level evaluates every phenomenon that takes place in his social life, and these indicators are quite categorical. It is impossible to achieve a high assessment of work and a healthy moral and psychological climate in the enterprise in general if the own assessment of this structure by individual team members is consistently low.
The founder of social psychology, Boris Parygin, argued that the individual psychological perception of individual factors of social life by team members does not yet fully constitute the IPC. Only the concurring opinion of the majority of group members (commonality) is a powerful mechanism that greatly enhances the intrastructural mood. At the same time, the already formed moral and psychological climate in the organization influences each member of the team, increasing or decreasing his work activity, promoting a positive attitude or blocking it.
Definition of mental state
To understand how to formulate a definition of a mental state, you need to turn to the study of the biological and psychophysiological principles of the nervous system.
In psychology, the features of mental life are considered a category of the general methodology of science, which determines the features of the activity of a particular individual. The variety of phenomena in the emotional sphere as an object of scientific research was first discovered in the works of N.D. Levitova.
In theoretical articles, the author defined the state of a person’s mental sphere as a peculiar feature of the psyche, reflecting the work of the nervous system, supporting his judgments with empirical results. At the same time, the researcher draws the reader’s attention to the fact that conclusions about the current emotional status of an individual at the time of his study must be made based on events that happened to him recently. At the same time, the scientist does not deny that tragic events of the past can make themselves felt many years later, when a person, it would seem, no longer remembers them. It follows that signs of a mental state increase or decrease the efficiency of the body.
The psychological state is the basis for mastering the norms and rules of behavior of an individual in society. They occupy an intermediate position between personality traits and processes such as voluntary attention, short-term and long-term memory, logical thinking, imagination, and speech. In labor psychology, this phenomenon is taken into account when preparing a personnel reserve for representatives of different professions.
Examples of mental states are moods, feelings and emotions, as well as sleep and wakefulness. The stages of development of mental states are determined by the predominance of processes of inhibition or excitation in the nervous system.
Favorable moral and psychological climate
With the current level of demand for many goods and services, the tasks assigned to production and intermediary firms are increasing and becoming more complex every year. This increases the psychological load on all participants in the creation and promotion of products, but the actual result of such a load can fluctuate within diametrically opposite values.
Provided there is reasonable stimulation of work activity and an existing reward system, we can talk about the creation of a favorable moral and psychological climate in the organization, which is clearly visible in a number of the following features:
A favorable moral and psychological climate in an organization is achieved only through the cohesion of the enterprise participants - people understand their dependence on each other and try, first of all, to work for quality. In such teams, creativity and innovative qualities are highly valued and welcomed, helping to find a way out of difficult situations and improve working conditions with little funding.
Functions of mental states
Mental states are a structural component of the psyche. The list of functions they perform looks like this:
- formation of personal self-esteem;
- discussion of a person to perform certain actions;
- predicting the success of certain undertakings;
- forcing a person to complete the work he has begun;
- formation of a person’s attitude to activity;
- evaluating the results of your work;
These 6 functions are explained by the essence and classification of mental states.
The concept of corporate culture
Corporate culture today is understood as a healthy moral and psychological climate at the enterprise, formed in conditions of respect by the organization’s leaders for junior management and local employees. The corporate culture policy includes two necessary components:
By default, a healthy moral and psychological climate presupposes that junior employees of an enterprise receive from senior management not orders, but recommendations, control over the implementation of which rests with the performers themselves. As a result of the introduction of such self-organization, the responsibility of local workers reaches a high level, and the need for additional supervisory administration employees becomes minimal.
Problems of psychological states
What are the problems in studying psychological states? First of all, this is the difficulty of separating the subjective and objective factors that give rise to this or that emotional experience.
The predominance of negative psychological experiences leads to a feeling of dissatisfaction with one’s life. Awareness of problems in psychological terms and the ability to analyze one’s own state are not the methods by which a person can cope with psychosomatics. To restore performance, normalize sleep and get rid of causeless headaches, a person needs to consult a psychologist. Only a qualified specialist will be able to correctly determine the cause of the problem and choose effective methods to eliminate it.
Adoption of corporate philosophy and implementation of its ideas
To achieve a favorable moral and psychological climate in the team, it is important that the corporate philosophy is understandable and unconditionally accepted by all participants in the production process. If this condition is met, then the enterprise develops a good reputation, maintained by common efforts and equally valuable to all employees of the company.
It is interesting that during the formation of a healthy moral and psychological climate at the enterprise, the main share of concern for the well-being of the common cause is taken on by employees or junior workers. It is they who, first of all, show conscientiousness when raising a new labor subject in the team, control his appearance at work, and the quality of the products he produces. Often, if a new employee does not strive to meet the already established high standards of the enterprise, the colleagues themselves raise the question of his removal from the team.
Another necessary condition for observing the principles of corporate culture is not to elevate the achievement of a healthy moral and psychological climate to the rank of the enterprise’s mission. A positive atmosphere within an organization cannot be an end in itself, but is only a consequence of constantly improving the quality of working conditions for employees and competently setting tasks.
“Improvement” of the situation
To improve the moral and psychological climate in the team, management must adhere to several golden rules of management:
- carry out personnel selection from the point of view of the candidate’s psychological suitability for the position he expects;
- carry out advanced training for all employees at the required frequency;
- regularly organize semi-official events that help improve mutual understanding between team members;
- clearly set goals and avoid serious deviations from production plans;
- allow and welcome the manifestation of creative potential in employees, encourage individuality and an innovative approach to work activities in every possible way.
The manager must understand that “improving” the atmosphere within the organization is complex, step-by-step work that does not bring immediate results. All members of the directorate and middle managers (foremen, managers, administrators) will also have to make efforts to improve IPC in small corporate structures by introducing direct communication with people on the ground into their practice.
A healthy psychological environment arises only in a team where the value and uniqueness of each employee is realized. Correction of existing shortcomings in communications between members of management and junior staff is carried out in such a way that the former do not suppress the latter with their authority.
Formation of a favorable climate in the team
Both positive and negative moral and psychological climate are developed under the influence of the following factors:
Corporate culture managers concluded that the more extensive the knowledge base of the people who make up the group, that is, the higher the level of development of its participants, the greater the likelihood of the formation of a moral and psychological climate in the team with a “+” sign. However, with a more careful approach to the selection of new employees, when selecting them based on common interests, aspirations, and ways of solving problems, you can achieve almost the same result with an average or even low level of development of the majority of team members. True, in this case there is a danger that in this group it will not be the workers who will prevail, but the personal interests of the workers, which already serves as a low probability of achieving a high level of development of the enterprise as a whole.
Before the moral and psychological climate is finally formed, a young enterprise must go through two stages:
- Stage I is characterized by increased formality of relationships in the group - team members are just getting to know each other, communicating with each other purely on work topics, and trying not to “stand out.”
- Stage II is already indicated by the formation at the enterprise of groups based on interests or other unifying factors, “leaders” and “followers” are clearly distinguished in the team, and a leader is clearly identified. The current situation of some members of the organization may already cause controversy and disagreement. The future structure of relations between management and employees is clearly emerging.
Depending on the direction (positive or negative) that the second stage of development of intra-collective relations takes, the characteristics of the moral and psychological climate in the group are formed. With positive development, people in an organization feel proud to belong to the group and try to do their jobs to the best of their ability. The development of a team according to a negative scenario leads to the growth of conflicts, a constant search for someone else’s wrongs and, as a result, paralysis of the work process.
Forming factors
What factors influence a person’s psychological state? It is generally accepted that the factors of a person’s mental states include: general personality tone, motivation, mood, expectation of success, subjective attitude to activity. Based on these components, the factors received names such as:
- Motivational and incentive is the most powerful factor that stimulates the activity of an individual. The leading components here are a person’s satisfaction with his relationship with his loved one and financial security.
- Emotional-evaluative is a factor indicating a person’s attitude towards a particular type of activity and the result of his work.
- Activation-energy is a factor that characterizes a person’s physiological activity and manifests itself in the natural change of sleep and wakefulness. Human health is also considered an active energy factor. Strong experiences are usually associated with excitement, and weak ones with inhibition in the nervous system.
Leadership as a method of hidden management
In fact, at the head of the management of the moral and psychological climate of any organization is the group leader, nominated from the ranks of the non-managerial staff by members of the work team. Unlike a direct leader appointed by a formal procedure, a leader in a group can become any person who has the necessary character traits, abilities and experience to solve specific problems facing the team.
The current leader has unconditional authority in a given society, thanks to which people voluntarily obey him and consciously take on the role of followers. The leadership qualities of one and the same person, relevant in one society, may not be in demand in another (different values, differences in gender, demographics, age, etc.).
In corporate culture, there are 5 examples of leadership types:
- Organizer. A confident optimist who perceives the group’s problems as his own and successfully and quickly resolves them. In communication, he is distinguished by the gift of persuasion, knows how to encourage and gently, tactfully reprimand for mistakes. Located in the center of all events.
- Creator. Captivates people with innovative ideas, unexpected (but successful) proposals. Ready to take risks, skillfully assigns tasks in the group. A leader of this type never shows himself as a commander and behaves more like an adviser.
- Fighter. Decisive, may show signs of aggression and impatience. Often too straightforward. Often the need for this leader disappears immediately after he solves some critical or particularly protracted problems.
- Diplomat. He is aware of all matters and has a large number of hidden levers of influence on the “right” people. He does not strive to open all his possibilities, but lives up to the expectations placed on him.
- Comforter. The distinctive quality of this leader is goodwill. He consoles the suffering and finds the right words to resolve conflicts. A representative of this type may not solve serious problems, but in his presence it becomes easier for people to endure difficulties.
The existence of a full-fledged team without a leader is impossible, so many managers try to make the task of personnel management easier for themselves by assigning a special manager for this purpose. In practice, such actions are ineffective, since for a formally appointed person the main importance is control and distribution functions, and for the leader - a comfortable psychological environment in the team.
My recommendations
Clients often come to me with complaints of chronic fatigue, loss of appetite, and lack of desire to do anything. They do not understand what is happening to them, they report that they have been to many doctors, have undergone a bunch of tests, but the cause of the decrease in performance and apathy has not been established. "What happened with me?" - they ask me. My answer that these symptoms relate to anomalies in the mental state of the individual usually surprises them. However, my initial assumptions are confirmed by the results of psychological tests. At the next stage of working with the client, I tell him about what types of mental states are distinguished in modern psychology, since often, having familiarized themselves with the diagnostic results, they say: “Indicate what refers to the mental states of the individual.”
In most cases, 5-10 sessions with a psychologist are enough to correct the psychological state that occurs when you are in a low mood. I give recommendations on developing reflection skills and teach relaxation techniques. The main method in my work is art therapy. In my opinion, this method is the key to the inner world of the individual. Through art therapeutic exercises, a person finds harmony with himself and learns to manage his emotional field.
Leadership practices influencing IPC
The moral and psychological climate at the enterprise largely depends on the management style exercised by management. Only 3 types of management style have been identified that have a strong influence on the IPC:
- Authoritarian (dictatorial). Establishment by the manager of strict control over the performance by employees of their official duties, introduction of a system of fines and reprimands. No one is interested in the opinions of employees and the difficulties they encounter during their work activities.
- Collective. The leader is open to two-way communication and does not make important decisions without raising the controversial issue for general discussion. Control over the performance of work and the results obtained is carried out mainly by the employees themselves with minimal intervention from superiors.
- Liberal-anarchist. Otherwise, this management style can be called “who knows what” - employees do not adhere to any protocols when doing their work, they do only what they consider necessary, without fear of punishment. At the same time, the team constantly feels the inferiority of management and loss of spirit.
Of the listed types of management, the preferred type is the collective type of intra-group relations, which is moderately democratic and adequate to the current situation in the economy.
Diagnostics
Some people have the unique ability to accurately assess their mental state. Physical well-being is the main “barometer” for them. Other people need the help of a psychologist in this matter.
In psychology, determining a person’s mental state is an analysis of his psychophysiological and psychological levels. The study of the psychophysiological level allows us to study the nature of the emerging feeling and determine (if necessary) ways to correct it.
The most popular diagnostic tools are psychological tests. With their help, the mood, well-being and level of activity of an individual are diagnosed. The most indicative results are obtained by such methods as the Luscher color test, SAN, PAT, “Nervous-Mental Tension Questionnaire,” “Relief of Emotions,” and personal anxiety tests.
In medicine, methods for diagnosing mental conditions include ECG and GSR results, heart rate, and brain encephalogram.