Psychological climate is the mood of the team, the moral and psychological atmosphere that permeates the relationships of its participants. We are not necessarily talking about the work collective, although more often this is the case. The psychological climate exists in an interest group, in the family, in school, and in any collective activity. The success of this activity and the health of each of its participants depend on the atmosphere prevailing in the group. Creating a favorable psychological climate is included in measures to prevent psychosomatic diseases, conflicts, and neuroses.
What affects climate
The climate is influenced by a number of factors:
Type of organization, team. Open or closed, private or public, scientific or industrial organization. Family, class, criminal group, charitable association. The image and standard of living of the team members. Micro (everyday for a particular person) and macro (city, country, culture of society) conditions: normal, complicated, extreme. Rational organization of work, compliance with the regime and rights, taking into account the capabilities and characteristics of each team member. Team structure. Informal leaders or groups in a team. Leadership style and features
A favorable climate requires attention from the manager not only to production issues, but also to the personal problems of team members. That is, the democratic style. Individual psychological and personal characteristics of team members
Personal opinion, mood and behavior of a person contribute to the overall climate. This is based on passing external factors and events through the prism of one’s own character and personality. The combination of the characteristics of all participants forms a new collective quality - the psyche of the collective. Therefore, the psychological compatibility of the participants, primarily in terms of temperament, plays a big role. Psychologically, people must be compatible in terms of psychomotor reactions, emotional and volitional manifestations, the work of thinking and attention, and character. Incompatibility causes antipathy, hostility, and conflicts. Self-assessment of each participant. His self-awareness and the correspondence of claims and achievements.
The leader has a great influence on climate formation
You should pay attention to his personal qualities, attitude towards other participants, authority, leadership style. A positive climate is created by a leader who:
- principled;
- responsible;
- active;
- disciplined;
- kind, responsive and sociable;
- has organizational skills.
Rudeness, selfishness, inconsistency, disrespect, and careerism have a negative impact on the health of the climate.
The conditions that dictate the climate also depend on the leader. Necessary:
- be friendly and respectful in relationships;
- provide employees with the opportunity to choose their own area of activity;
- notice and celebrate the activity and creativity of employees;
- promote employee interest in self-development;
- motivate employees for career advancement with the aim of not only material gain, but also to gain prestige and recognition from the team;
- be a good qualified leader and a kind mentor.
What a leader can do for a favorable climate:
- It is justified from a psychological standpoint to select personnel.
- Organize regular training and certification.
- Study and practice the theory of psychological compatibility, that is, have a good understanding of people.
- Contribute through practical activities (through organizing events) to the development of interaction and relationship skills.
Search for a scapegoat
Either a person or a group of people who have absolutely nothing to do with the incident are chosen as the “whipping boy”. But they differ from other workers in that their behavior is not similar to the generally accepted one, and such people are not able to stand up for themselves (that is, they do not have a strong character). Therefore, it is they (these “white crows”) who become objects of attacks, unfounded accusations and hostility from everyone else. The presence of a scapegoat allows the company's team to provide some relief from tension and dissatisfaction, which, as a rule, accumulate in large quantities where there is an atmosphere of fear and mistrust. Such actions help workers maintain a perceived cohesion.
On a note! Such a “whipping boy” is sometimes vital for the normal functioning of some teams, since it acts as a kind of “valve” that allows one to “let off steam” of the negative that has accumulated.
Creating a favorable moral and psychological climate in the team
There are various methods and trainings that allow you to maintain a positive microclimate in the team. Many enterprises employ full-time psychologists and take care of organizing role-playing games, tests, and individual work with staff. Some companies hire outside specialists to temporarily work with staff. Improved working conditions, moral and material stimulation of employees have a beneficial effect on the industrial complex.
Group work with a team
Among the effective measures to reduce social tension, psychologists identify:
- Staffing a team taking into account the psychological compatibility of workers (psychologists recommend first determining the level of leadership in subordinates, then combining people with different types of behavior: followers with leaders).
- Careful selection, placement, training and testing of managers.
- Limitation of the number of employees subordinate to the manager (5-7 people);
- Elimination of unnecessary employees and vacancies.
- Using the substantive elements of climate (rules, norms, values, general opinion and attitude).
- Preventing and resolving interpersonal misunderstandings.
- Engaging employees with personal experience, using brief examples, conducting business games, and using persuasion methods.
Labor collective
The main task of managers should be to set goals, objectives, and fair labor standards. Recognize the need to maintain a balance between business, family, personal, and group interests of employees.
Individual work with team members
Satisfaction indicators are considered the most important; the state of the SPC can be directly determined by the mood of individual employees, so management needs to know exactly:
- employees are satisfied or dissatisfied with their working conditions, relationships with colleagues, status in the team;
- Do employees discuss personal matters?
- whether the team agrees to maintain cohesion;
- is the employee ready to take responsibility for the actions of colleagues;
- what position would you like to take in the overall cause?
The study of subjective satisfaction is carried out on the basis of tests, psychology questionnaires, and personal interviews. Harmony is the result of employee compatibility. The phenomenon promotes maximum success of teamwork at minimal cost.
Compatibility of a socio-psychological nature
This type of compatibility includes consistency of interests, social attitudes and roles. In the event that two (or more) individuals are working on a project and each claims a dominant role, it is unlikely that their joint activity will end in success. Most likely, the task will be disrupted.
It would be more advisable to pair a hot-tempered (that is, impulsive) person with an employee who has a calm and balanced disposition, and is also able to listen and be tolerant and trusting of his partner. Everyone will “win” from such a tandem: both the company and both employees who complete the task in the minimum amount of time in a normal psychological environment (and, possibly, receive a reward in monetary terms).
What is the socio-psychological climate of the SEC
The microclimate in a team is a set of moral values, official and informal relationships and assessments that influence the emotional mood. SEC contributes to the activation or suppression of the life processes of the collective.
In the structure of the socio-psychological climate, there are two key sections: the attitude of employees to work and to each other. In both situations, there are emotional and objective elements (work environment, time of action).
Interpersonal relationships are differentiated by levels: horizontal – between employees; vertical – between management and subordinates. Manifestations of SPC also depend on the attitude of individuals towards themselves and the world around them; they can be direct or indirect (which are determined by a person’s lifestyle).
Climate levels
Climate has two levels: static and dynamic.
Static
This is a stable attitude of employees towards work, constant interpersonal relationships. The climate is stable and tolerates external influences well. It is not easy to create a climate at this level, but then it is easy to maintain. Team members feel this stability, which makes them more confident in their own position. Climate correction is practically not required, control is occasional. This level is also called the socio-psychological climate.
Dynamic
This is the changing nature of the team. The climate changes daily due to the changing moods of its participants. This level is also called the psychological atmosphere. It changes faster and is less felt by the participants. As changes accumulate, it can create an unhealthy climate in the team.
Satisfaction as a criterion
The basis for climate assessment is people’s satisfaction/dissatisfaction with relationships in the team and the activity itself. However, you need to understand that satisfaction can be subjective and objective.
It often happens that one person is completely satisfied with the team, while another is not at all satisfied with the working conditions. This is subjectivity in assessment. Differences in experience, conditions and quality of life, interests, character of people and other individual characteristics contribute. The principle of subjective satisfaction is the relationship between the parameters “I give” and “I receive”.
Dissatisfaction with delayed wages, regular punishments, non-compliance with labor standards, violation of rights is an objective indicator.
Additional tools for influencing the microclimate
In addition to the proposed methods, it is worth implementing the following principles in the company:
- Information openness. Eliminate secrets, secrecy and vague formulations that create a tense, oppressive environment in the team. Do not leave room for gossip: discuss the current situation, plans and innovations honestly and openly. Engage staff in dialogue.
- Finger on the pulse of the team. Maintain feedback with staff, ask about working conditions and desired changes, and be interested in emerging difficulties and problems.
- Adaptation to current reality. Take into account current events in the world, look for ways to support the team in a crisis situation. Provide the opportunity to work remotely, pay for online training sessions, and issue wages and bonuses on a timely basis.
Signs characterizing climate
Externally, you can judge the climate of a team by the following signs (useful for those applying for a job):
- staff turnover;
- product quality;
- level of discipline;
- claims and complaints, negative feedback from employees;
- frequent breaks from work;
- negligence and carelessness.
The better these indicators, the more favorable the climate. Signs of a favorable climate also include:
- trust and high demands in relationships;
- kind and constructive criticism;
- freedom of speech and opinion;
- providing initiative to employees, lack of managerial pressure;
- awareness of participants in team issues;
- satisfaction from belonging to this group;
- mutual assistance and highly developed empathy;
- responsibility for yourself and the entire team.
Climate diagnostics
The socio-psychological climate in a team is an indicator of the level of development of the team. Therefore, it is important to regularly carry out diagnostics and monitor dynamics, to identify the properties that hold the team together or destroy it. For this purpose, the method of assessing the level of psychological climate of A. N. Lutoshkin’s team is suitable.
The subject is asked to answer 13 statements regarding the team in which he is located. The score can be from -3 to 3.
Answer form
22 points and more – highly favorable climate.
8-22 points – moderately favorable climate.
0-8 points – low favorable climate.
From 0 to -8 – initial unfavorability.
From -8 to -10 – moderately unfavorable climate.
From -10 and more – pronounced unfavorability, unhealthy climate.
Each team member takes the questionnaire. When summing up, all points are summed up and divided by the number of people surveyed. The final number is the overall score of the team. You can also calculate an overall score for individual criteria.
What is psychological climate
The psychological climate in a team is a complex characteristic of interpersonal relationships, the degree of satisfaction of workers with working conditions and quantitative assessment (i.e., salary) of their activities in the group, as well as conditions that promote (and perhaps hinder) productive teamwork and comprehensive personal development in this particular community of people.
A favorable psychological attitude promotes work motivation and increases the level of social optimism of everyone. The socio-psychological climate in the team (SPCC), maintained at a normal level, allows each participant in the labor process to feel like a part of a huge group of people making a certain contribution to the common cause. Thus, a person maintains an interest in what he is doing, which is an incentive to fairly evaluate the successes (and sometimes failures) not only of his own, but also of his colleagues and the entire enterprise as a whole.
Psychological climate is a well-defined system of customs and norms accepted in this particular group of people. Each participant in the labor process depends on each other (that is, so-called social connections work), at the same time they depend on the functions performed together (that is, task connections function).
SPCC influences labor productivity, the attitude of employees both to the organization in general and to a specific manager in particular, as well as to their immediate responsibilities.
What it is
The term “psychological climate” was first uttered by N. S. Mansurov in the context of studying a production team. A little later, psychologists began to distinguish between socio-psychological and moral-psychological climate. Psychological climate is a broad concept, the rest are included in it.
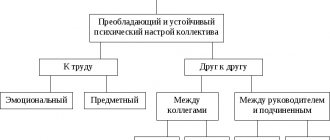
Psychological climate is the nature of emotions that arise in relationships between people, based on their sympathies, coincidence of interests, characters and inclinations. The psychological climate includes 3 areas:
- Social climate – awareness of goals and objectives by all participants, respect for rights and responsibilities.
- Moral climate - values accepted in the group. Their unity, acceptance, consistency.
- The actual psychological climate is informal relationships in the team.
There are 4 approaches to studying the psychological climate in a team:
- Climate is a collective consciousness. Awareness by each member of society of relationships in the team, working conditions, methods of stimulating it.
- Climate is the mood of the team. That is, the leading role is given not to consciousness, but to emotions.
- Climate is the style of interaction between people that influences their condition.
- Climate is an indicator of the compatibility of the group, the moral and psychological unity of its participants. The presence of common opinions, traditions and customs.
The peculiarity of the psychological climate as a phenomenon is that it is created by the person himself, he is able to influence the climate, improve and change.
How to improve a company's SEC
Just like corporate culture, the atmosphere in the team largely depends on the actions of the owner (or his representative) and the company’s top managers. For example:
Behave fairly with employees and customers. You cannot demand honest behavior from employees if the company itself treats its employees and customers dishonestly. Promise only what you can deliver. It is better to promise less and give more than to deceive a person’s hopes. Adhere to the rules adopted by the company. As a rule, in companies with a favorable SPC, the rules are the same for everyone, including the owners. Create a fair system of staff motivation. There should be no favorites or outsiders in the company. Comply with moral standards and legal requirements. Provide quality feedback. Inform subordinates about the results achieved. To do this, hold meetings/rallies/planning meetings. Regularly inform employees about important decisions made by company management. Make your actions clear and reasonable. Show genuine interest in employee suggestions. Create and maintain an atmosphere of mutual respect. Show the company's prospects in the market, its future
It is especially important during a difficult situation in society, both economic and political, when the level of people’s anxiety increases. Provide good sanitary and hygienic working conditions. Dim lighting, continuous noise, heat or, conversely, cold, lack of conditions for lunch can irritate workers, which can negatively affect the atmosphere in the team. Determine at the interview stage whether the future job is attractive for the candidate: whether it will be creative, varied, interesting for the employee, how much it meets his expectations financially, in the implementation of his professional or career development, and the disclosure of potential. Clearly distribute the professional responsibilities of employees and their areas of responsibility. Provide employees with accurate data on an issue that is important to them
This will protect the company from gossip and double understanding of information. Choose a leadership style that is appropriate for the company. For example, a democratic style brings trust and friendliness to relationships, gives the opportunity to all team members to participate in solving work issues, an authoritarian style will be justified in sports, the army, the police, in situations where the cost of a mistake is very high (surgery, pharmaceuticals, etc. ), in creative companies, in which all employees are highly qualified specialists, a liberal leadership style has proven itself well.
If you are interested in having loyal, results-responsible, positive-minded employees working in your company, manage the creation and maintenance of a favorable atmosphere in the team, set a worthy example with your mood and activities.
The concept of corporate culture
Corporate culture today is understood as a healthy moral and psychological climate at the enterprise, formed in conditions of respect by the organization’s leaders for junior management and local employees. The corporate culture policy includes two necessary components:
By default, a healthy moral and psychological climate presupposes that junior employees of an enterprise receive from senior management not orders, but recommendations, control over the implementation of which rests with the performers themselves. As a result of the introduction of such self-organization, the responsibility of local workers reaches a high level, and the need for additional supervisory administration employees becomes minimal.
Compatibility and harmony of team members
Those relationships that were formed in the process of communication between people are an indicator of their psychological compatibility. It is believed that it is much easier for people who are similar to each other to establish interaction. Similarity helps the employee feel safe and increases self-esteem.
However, it is necessary to distinguish between concepts such as harmony and compatibility. If psychological compatibility is based on the characteristics of relationships between people, and it can be judged after a relatively short period of time after the start of joint activities, then harmony takes years to develop. Its basis is the successful results of joint activities. In this case, both harmony and compatibility matter.
Psychological compatibility
Psychological compatibility of employees, which presupposes good communication between all workers in a given company (due to the same characters, motivations and behavioral types) and their ability to act together, is a component of the psychoclimate in the team in general.
It is much easier for people with similar personal qualities to “find a common language,” that is, to establish the interaction that is necessary for the successful completion of a particular project. At the same time, communication between people who experience negative emotions towards each other is not at all conducive to effective work.
Basic strategies for managing social tension in a team
Currently, there are many strategies for creating a favorable socio-psychological climate, that is, reducing social tension. They provide for the following activities:
- When recruiting a work team, it is necessary to take into account the psychological compatibility of employees. Depending on the goals, it is necessary to combine different types of human behavior. In many situations, a group with representatives of the same character will turn out to be of little efficiency, for example, if only employees who are waiting for instructions and do not know how to take initiative, or only those who like to command, gather together;
- Optimal selection, placement, training and periodic certification of management personnel;
- Acceptable limitation on the number of employees subordinate to one manager (5-7 people);
- No extra workers or vacancies. Both a lack and an excess of team members lead to its instability. There is room for tension and conflict to arise due to the desire of several candidates to take a position and receive promotion, or due to the resulting unevenness of workload due to the presence of “extra hands”;
- Reliance in work on the most authoritative, active members of the team (informal leaders) who enjoy the trust of the staff;
- Managing the process of forming meaningful psychological components of climate (norms, expectations, values, attitudes, group opinion and mood);
- Prevention and resolution of interpersonal conflicts;
- The use of socio-psychological methods that contribute to the development of effective mutual understanding and interaction among team members (employees’ passion for personal example, the use of socio-psychological trainings, business games, persuasion methods, etc.).
Psychologists have developed many social and psychological methods for creating a good climate in a team. These include:
1. Body psychotherapy. It is based on the recognition of the close connection between mental and physiological processes, in particular on the fact that personal characteristics are manifested in postures, gestures, and movements. In management, bodily psychotherapy is used in organizing psychological relief rooms at enterprises, booths with mannequins for managers (to release negative emotions, etc.).
2. Art therapy. This technique is based on the fact that a person’s inner “I” is reflected in visual images every time he draws, paints a picture, or sculpts a sculpture, without thinking about his works (that is, spontaneously). The materials obtained during work with the group make it possible to identify the degree of aggressiveness and other negative feelings in people, help resolve conflicts and improve relationships between participants. Art therapy is used in the fields of social rehabilitation and occupational therapy.
3. “Skills training” groups. They belong to the behaviorist direction in psychology. The approach to work is based on a training model, goal setting, measurement and assessment of behavior. An example would be “self-confidence training” groups. In this way, they teach the ability to plan a career and make decisions, develop the ability to cope with anxiety and improve communication skills.
There are also many other methods and trainings aimed at creating a favorable emotional climate. Currently, some enterprises employ full-time psychologists. They organize psychological games, tests, and work with staff. Some companies invite outside specialists for a while. This, of course, has a beneficial effect on the socio-psychological climate.
Leadership practices influencing IPC
The moral and psychological climate at the enterprise largely depends on the management style exercised by management. Only 3 types of management style have been identified that have a strong influence on the IPC:
- Authoritarian (dictatorial). Establishment by the manager of strict control over the performance by employees of their official duties, introduction of a system of fines and reprimands. No one is interested in the opinions of employees and the difficulties they encounter during their work activities.
- Collective. The leader is open to two-way communication and does not make important decisions without raising the controversial issue for general discussion. Control over the performance of work and the results obtained is carried out mainly by the employees themselves with minimal intervention from superiors.
- Liberal-anarchist. Otherwise, this management style can be called “who knows what” - employees do not adhere to any protocols when doing their work, they do only what they consider necessary, without fear of punishment. At the same time, the team constantly feels the inferiority of management and loss of spirit.
Of the listed types of management, the preferred type is the collective type of intra-group relations, which is moderately democratic and adequate to the current situation in the economy.
Features of the working atmosphere among teachers
Special attention should be paid to the issues of psychological climate in the teaching staff. This area is always stressful, and the working atmosphere is often one of the factors that determines the effectiveness of a teacher.
The unity of the teaching staff always occurs within the framework of performing some common task or activity - first of all, social, pedagogical. In such events, each teacher should have the opportunity to realize their creative abilities.
Of course, holding methodological days or creative meetings of teachers often requires additional time, but such events remain in the memory of teachers for a long time as bright and unforgettable events.
Democratic style
This type of management is based on very trusting and friendly relationships between all team members, as well as goodwill and sociability. In this case, all responsibilities, powers and initiatives are distributed between the manager, his deputies and subordinates. All decisions are made collectively.
The director, who has adopted a democratic management style as a basis, cares about the opinion of his subordinate team regarding key production issues. Communication between the manager and employees occurs exclusively in the form of wishes, requests, advice and recommendations.
Rewards for quickly and efficiently completed work are not excluded. Communication takes place in a polite and friendly manner. If necessary, orders are used (extremely rarely).
Authoritarian style
It is based on the dominance of unity of command, which is expressed in the fact that only the leader himself makes all important decisions (without consulting anyone). The opinion of the team in this case is not taken into account.
The main methods of management are orders, instructions, reprimands, comments and punishments. Communication between a manager and his subordinates occurs in a rude and harsh manner. In the team, “ear-mongering” and widespread control are encouraged. Any employee initiatives are not supported, and the interests of the company are placed above the interests of people.
Such a leadership style can generate in the team a feeling of some psychological discomfort, conflict, fear, envy, ingratiation and hostility.
How to improve the psychological climate in a team
In order to understand how to improve the psychological climate in a team, it is important to follow some schemes:
Remember that it is easier for people to focus on work if they have the ability to control their environment. Let them set up their own workspaces. This way a person becomes freer, the number of internal conflicts in the team decreases; employees are pleased to understand that something depends on them too. Even if it’s choosing a calendar for your desk at work. The main thing is that it puts people in a positive mood and gives additional incentives to work. You will notice that the returns will be much greater. Workers should not be placed into too strict a framework, although some dress code is still required to maintain discipline;
It is important for the manager to understand that employees need to communicate with each other. A ban on this will cause a decrease in labor efficiency, suppress people, and cause a split in society
Such an environment will not help to unite and develop mutual understanding at work. Therefore, it is important to create a friendly atmosphere; in addition, you can create something like a canteen where employees can have lunch together and communicate on abstract topics. In addition, arrange tables at work places so that everyone feels in the center. No one should be singled out, otherwise there is a chance of conflicts;
To normalize the climate, it is important to let employees participate in the organization of the work process and feel involved in the main mechanisms of the company. It’s also important to let employees feel that the office is not just a workplace
It is worth organizing informal events here: team building, corporate events, etc. Conducting collective training seminars also promotes team cohesion. And if you allow people to celebrate birthdays in the office, the atmosphere at work will be filled with ease and ease, and performance will certainly rise
It is also important to let employees feel that the office is not only a workplace. It is worth organizing informal events here: team building, corporate events, etc.
Conducting collective training seminars also promotes team cohesion. And if you allow people to celebrate birthdays in the office, the atmosphere at work will be filled with ease and ease, and performance will certainly rise.
Thus, to achieve the norms of a positive psychological climate, special training is required, the use of suitable methods and schemes for organizing the labor process.
Favorable and unfavorable climate
The psychological climate can be favorable or unfavorable. The first is characterized by:
- friendly attitude of participants towards each other;
- camaraderie;
- adequate mutual exactingness, which determines creative and effective activity;
- mutual assistance;
- joy from communication and openness of communications;
- safety and comfort;
- optimism;
- self-confidence and team confidence;
- the opportunity to think freely and creatively, to discover and realize one’s own potential.
But it is worth noting that a combination of mutual demands and mutual assistance is mandatory. Mutual assistance alone will turn into permissiveness, a “brotherly” attitude, which over time will create an unfavorable climate.
An unfavorable or unhealthy climate includes the opposite characteristics:
- pessimism;
- mistrust and disrespect;
- coldness and secrecy in relationships;
- inhibition of personal potential;
- irritability;
- tension and conflict;
- uncertainty;
- misunderstanding;
- fear of error, punishment and rejection;
- suspicion.
It has been noted that a healthy climate increases productivity and labor efficiency. Unfavorable climate causes frequent incidents of safety violations and reduces productivity by 20%.
A healthy climate satisfies the needs of its members and does not conflict with social norms and values. For example, in a criminal group there may be a unity of opinions, views and beliefs, but for society the activities of its members are harmful, in fact, as in the end for the participants themselves (they just don’t know it).
Favorable psychoclimate
Criteria for a favorable psychological climate in a team:
- Optimism and confidence “in the future” that all employees experience.
- The joy of commuting with each other.
- Trusting relationships between employees that do not exclude demandingness towards each other.
- Satisfaction with working in this team.
- Having a feeling of comfort and security.
- Respectful and fair treatment of all participants in the labor process.
- Hard work, selflessness and honesty are welcomed and encouraged.
- The presence of mutual assistance.
- Full awareness of employees about the intended goals and ways to achieve them.
- Employees maintain a loyal attitude towards the company’s management and the enterprise as a whole.
- A favorable psychological climate in the team is expressed in the fact that all participants in the labor process not only work together with pleasure, but also relax.
- Management does not put pressure on subordinates and reserves for them the right to make decisions that are important for the activities of a particular group.
- New employees are greeted positively within the team.
- Freethinking. Employees do not feel any fear when expressing their opinions on a particular issue (including criticism about the business qualities of colleagues).
- There is an opportunity for intellectual and professional growth, as well as the opportunity to express your creative potential.
- Each employee is ready to take full responsibility for the work done.
- Success and failure are shared by all employees.
- Each employee happily makes his personal contribution to the common cause.
- The ability to make mistakes without fear of punishment.
Signs of a positive socio-psychological climate
1. The attitude of the company (represented by the owner, top managers) to the team:
- trust in your employees
- respect for the personality of each employee
- providing employees with a sense of security, safety, and comfort
- ensuring fair competitive wages and benefits package
- providing opportunities for professional and career development
- “instilling” positive habits, traditions, and attitudes into the team
- providing employees with truthful and complete information about tasks and problems
- providing constructive feedback based on work results
- development of social activity
- providing an opportunity to express one's opinion
- attentiveness in resolving personal issues of employees
- top managers take leadership roles in the team
2. Attitude of employees towards the company. Employees:
- worried about the overall result
- do their job efficiently
- treat company property with care
- emotionally involved in work
- take responsibility for the state of affairs in the company
- satisfied with working conditions, system of material and non-material motivation, mode and nature of work
- know their responsibilities well
- believe in the company's product/service
- if necessary, take on team leadership
- support the traditions established in the team
- optimistic
- are proud of their achievements and the company's achievements
3. Attitude of employees towards each other. Employees:
- trust each other
- are demanding of colleagues in work matters
- treat all employees with respect
- help newcomers quickly integrate into the team
- support established rules and regulations
- rejoice at each other's successes
- behave tactfully with each other
Liberal style
In this case, the manager to some extent withdraws from active participation in the management of the company. He either simply “goes with the flow”, obeying the will of chance: either he falls under the complete influence of the team, or he waits for instructions from above. Such a leader tries to “keep his head down” and not take risks. He evades directly posed questions and resolution of conflicts that have arisen, and also does not take responsibility for anything (but tries to find someone to whom he can “throw” his guilt, that is, a “scapegoat”).
This style of leadership does not contribute to increasing labor productivity and improving the climate in the team.
Features of communications
The atmosphere of a team is always based on the personal characteristics of each of its members.
It is important to have communication skills, the characteristics of their assessments, opinions, and social experience. For example, the difficulties that some group members experience in communication can affect the situation in the team as a whole.
For this reason, tension, mistrust may increase, disputes and conflict situations may arise. If each member of the team is able to clearly and accurately express their point of view, properly masters the techniques of constructive criticism, and has active listening skills, then this helps to create a favorable psychological climate in the group.
When analyzing the characteristics of the psychological compatibility of each member of the team, it is necessary to take into account such a factor as the type of communicative behavior. This classification was first developed by V. M. Shepel and includes the following categories:
- Collectivists are sociable people who will always support any initiative. If necessary, they are capable of taking the initiative.
- Individualists. Those employees who prefer to work alone rather than interact as part of a team. They are much more inclined towards personal responsibility.
- Pretenders. As a rule, such employees are often called vain, touchy, and eager to be the center of attention while working. And such a characterization is not without foundation.
- Copycats. People who seek to avoid complications, and for this purpose imitate other people's behavioral manners.
- Opportunists. Weak-willed team members who rarely take initiative and fall under the influence of others.
- Isolated. People who avoid contact. They often have a completely intolerable character.
Leadership as a method of hidden management
In fact, at the head of the management of the moral and psychological climate of any organization is the group leader, nominated from the ranks of the non-managerial staff by members of the work team. Unlike a direct leader appointed by a formal procedure, a leader in a group can become any person who has the necessary character traits, abilities and experience to solve specific problems facing the team.
The current leader has unconditional authority in a given society, thanks to which people voluntarily obey him and consciously take on the role of followers. The leadership qualities of one and the same person, relevant in one society, may not be in demand in another (different values, differences in gender, demographics, age, etc.).
In corporate culture, there are 5 examples of leadership types:
- Organizer. A confident optimist who perceives the group’s problems as his own and successfully and quickly resolves them. In communication, he is distinguished by the gift of persuasion, knows how to encourage and gently, tactfully reprimand for mistakes. Located in the center of all events.
- Creator. Captivates people with innovative ideas, unexpected (but successful) proposals. Ready to take risks, skillfully assigns tasks in the group. A leader of this type never shows himself as a commander and behaves more like an adviser.
- Fighter. Decisive, may show signs of aggression and impatience. Often too straightforward. Often the need for this leader disappears immediately after he solves some critical or particularly protracted problems.
- Diplomat. He is aware of all matters and has a large number of hidden levers of influence on the “right” people. He does not strive to open all his possibilities, but lives up to the expectations placed on him.
- Comforter. The distinctive quality of this leader is goodwill. He consoles the suffering and finds the right words to resolve conflicts. A representative of this type may not solve serious problems, but in his presence it becomes easier for people to endure difficulties.
The existence of a full-fledged team without a leader is impossible, so many managers try to make the task of personnel management easier for themselves by assigning a special manager for this purpose. In practice, such actions are ineffective, since for a formally appointed person the main importance is control and distribution functions, and for the leader - a comfortable psychological environment in the team.